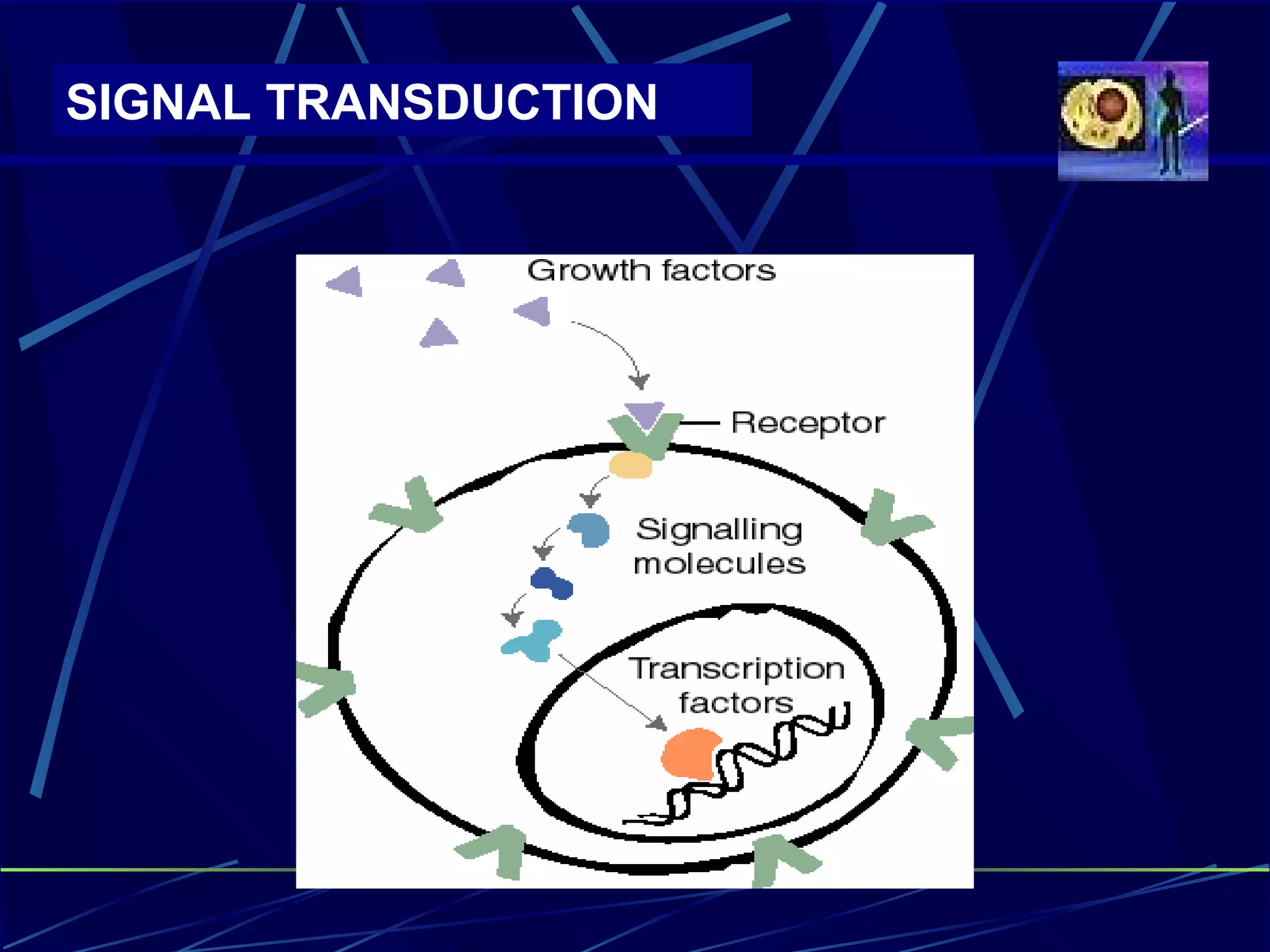
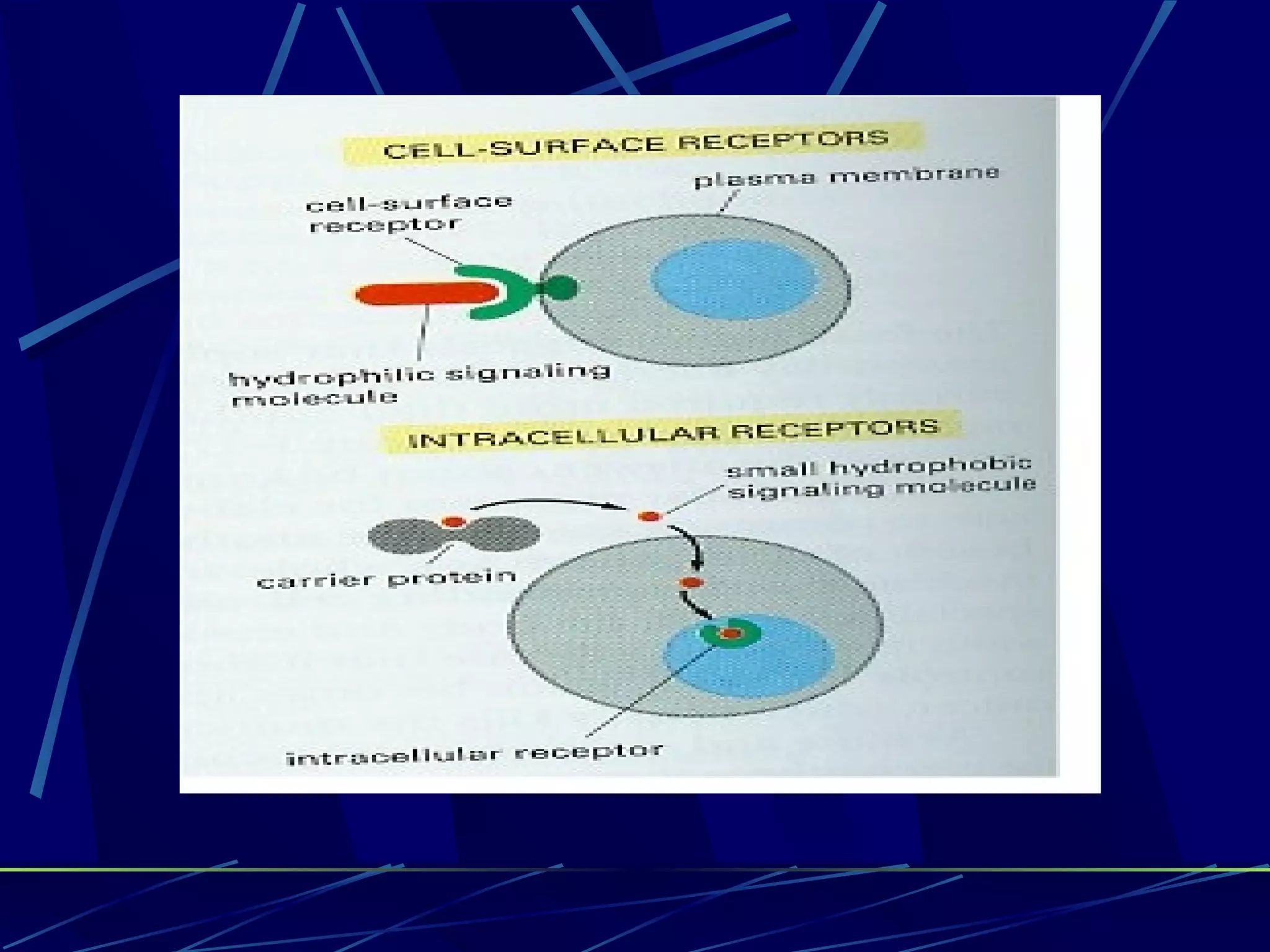
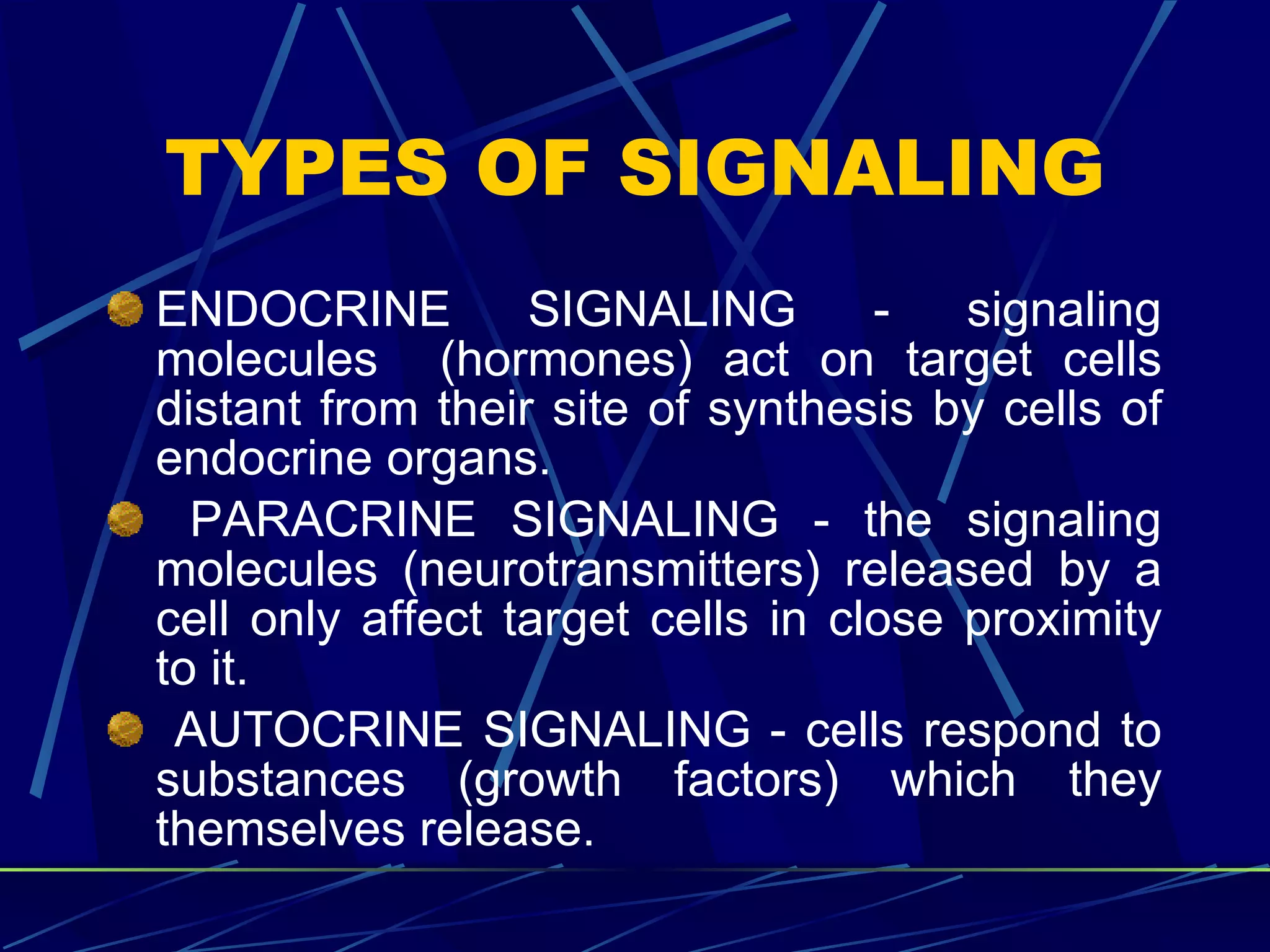
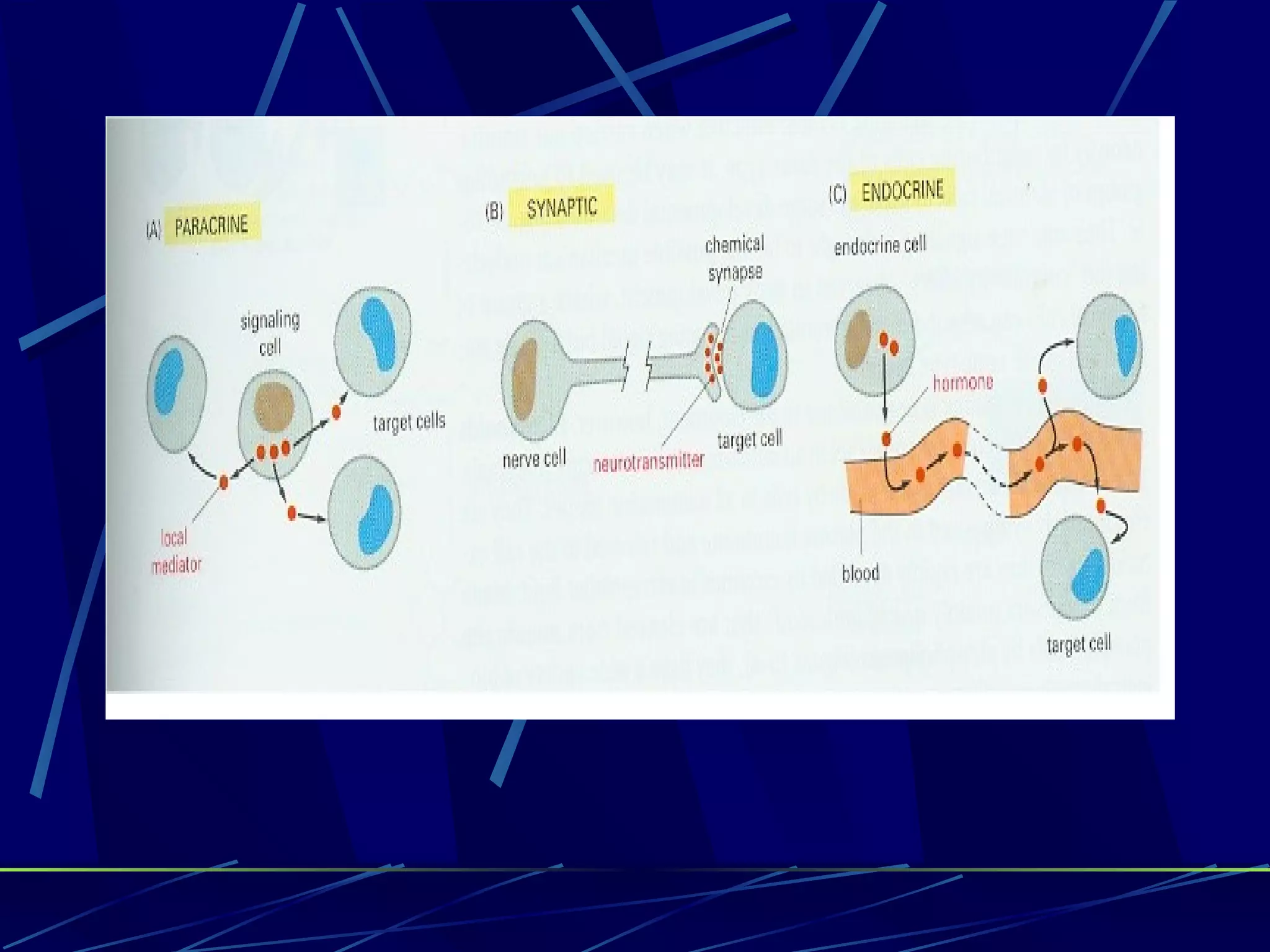
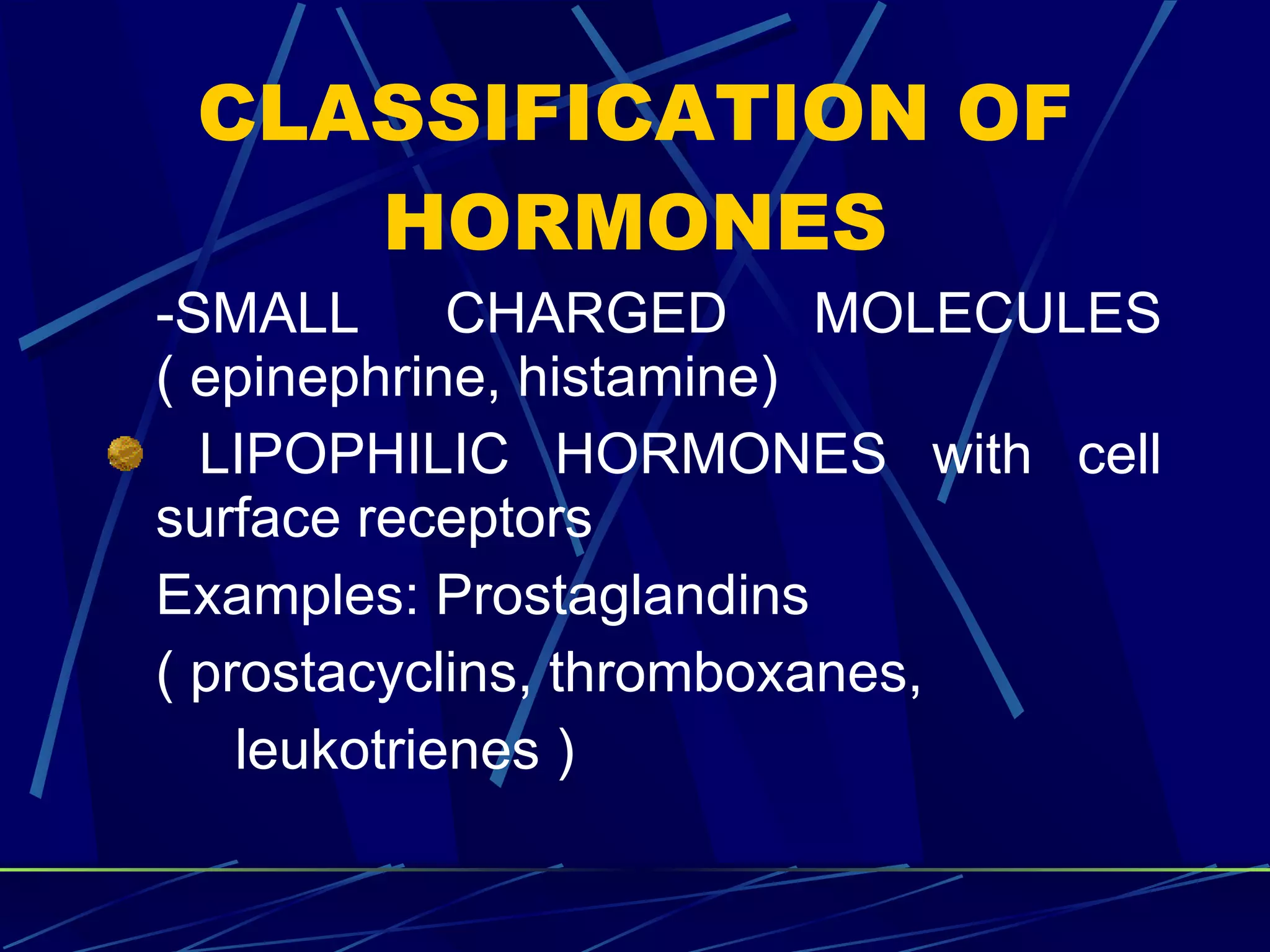
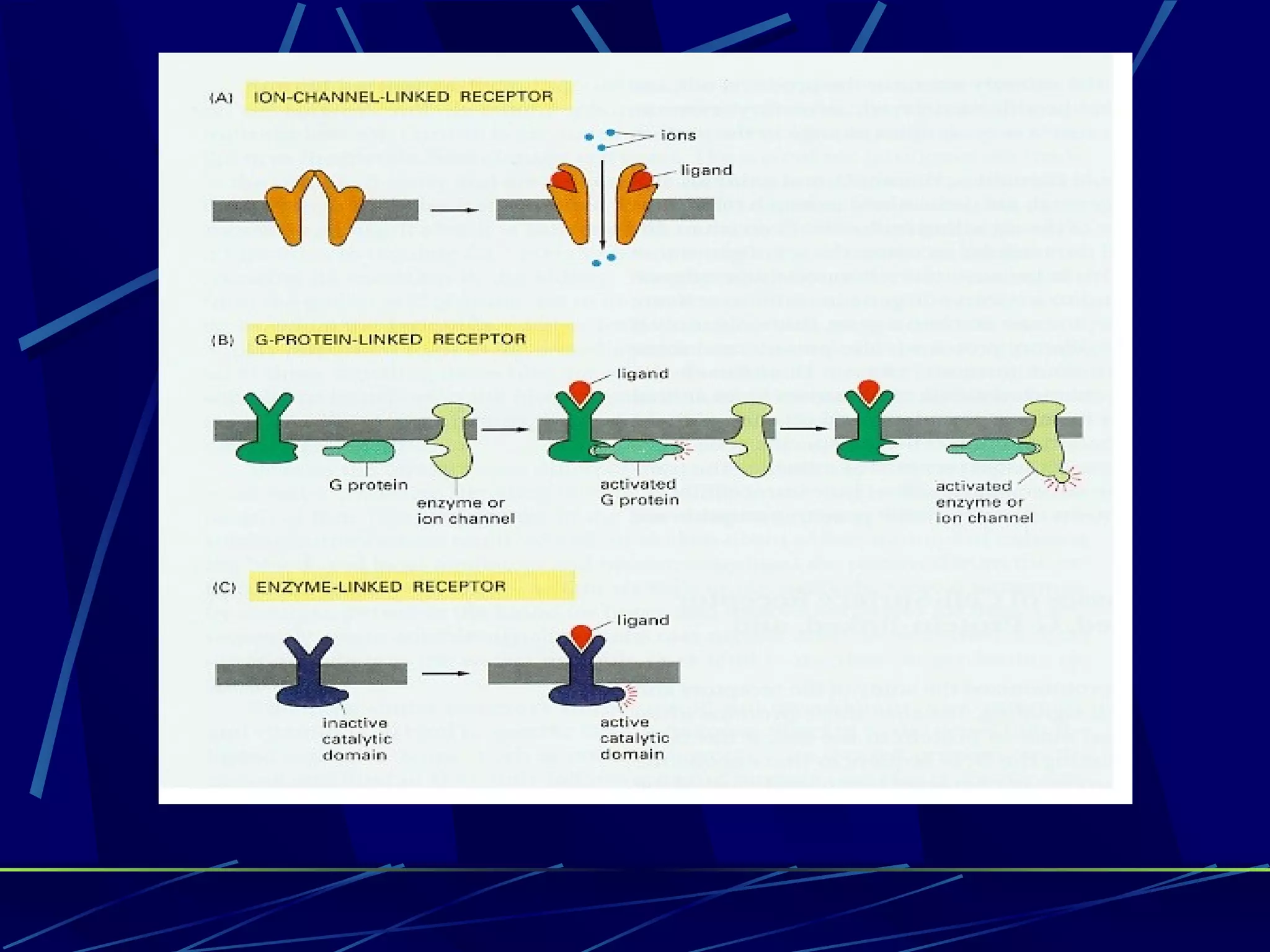
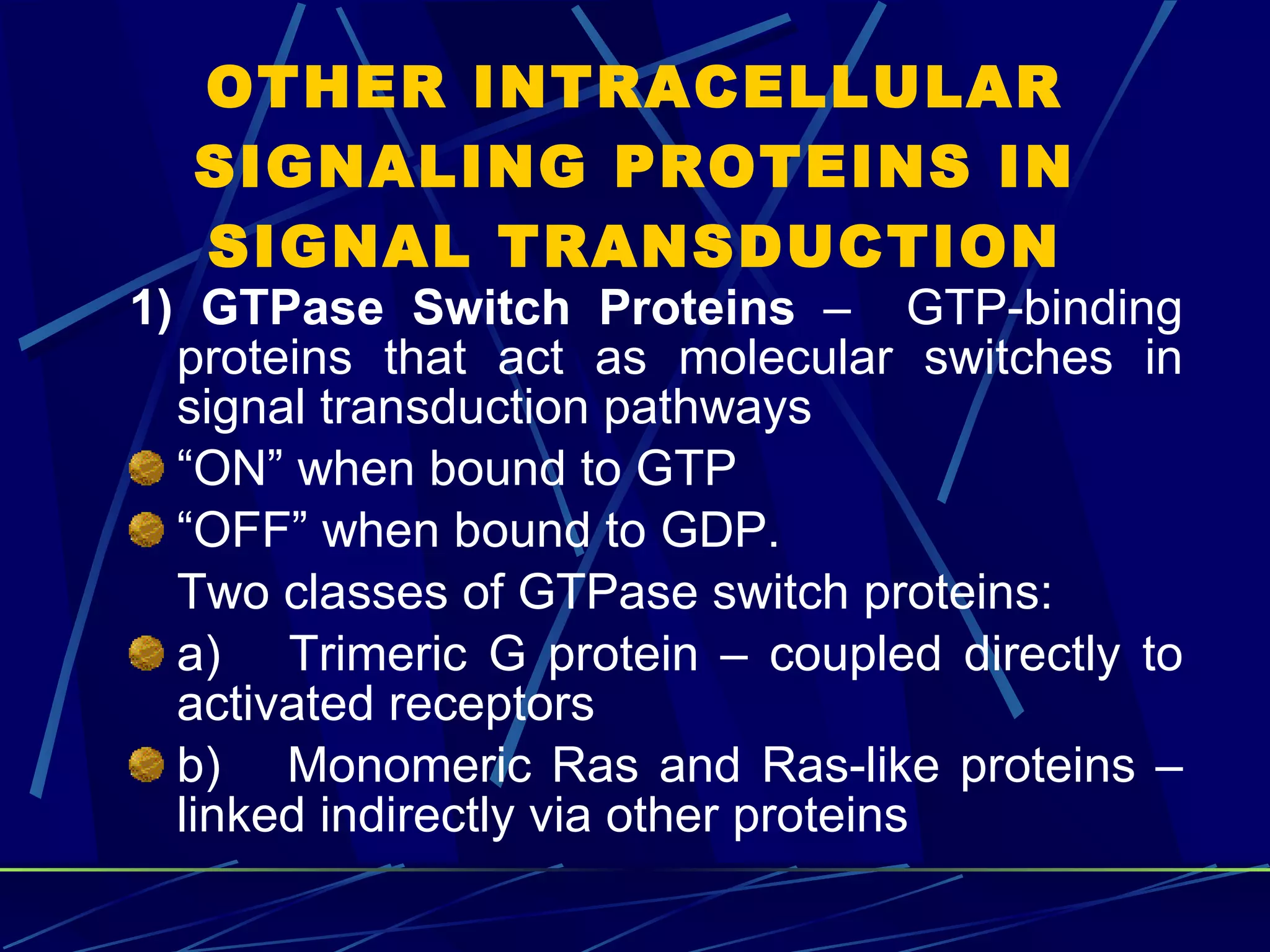
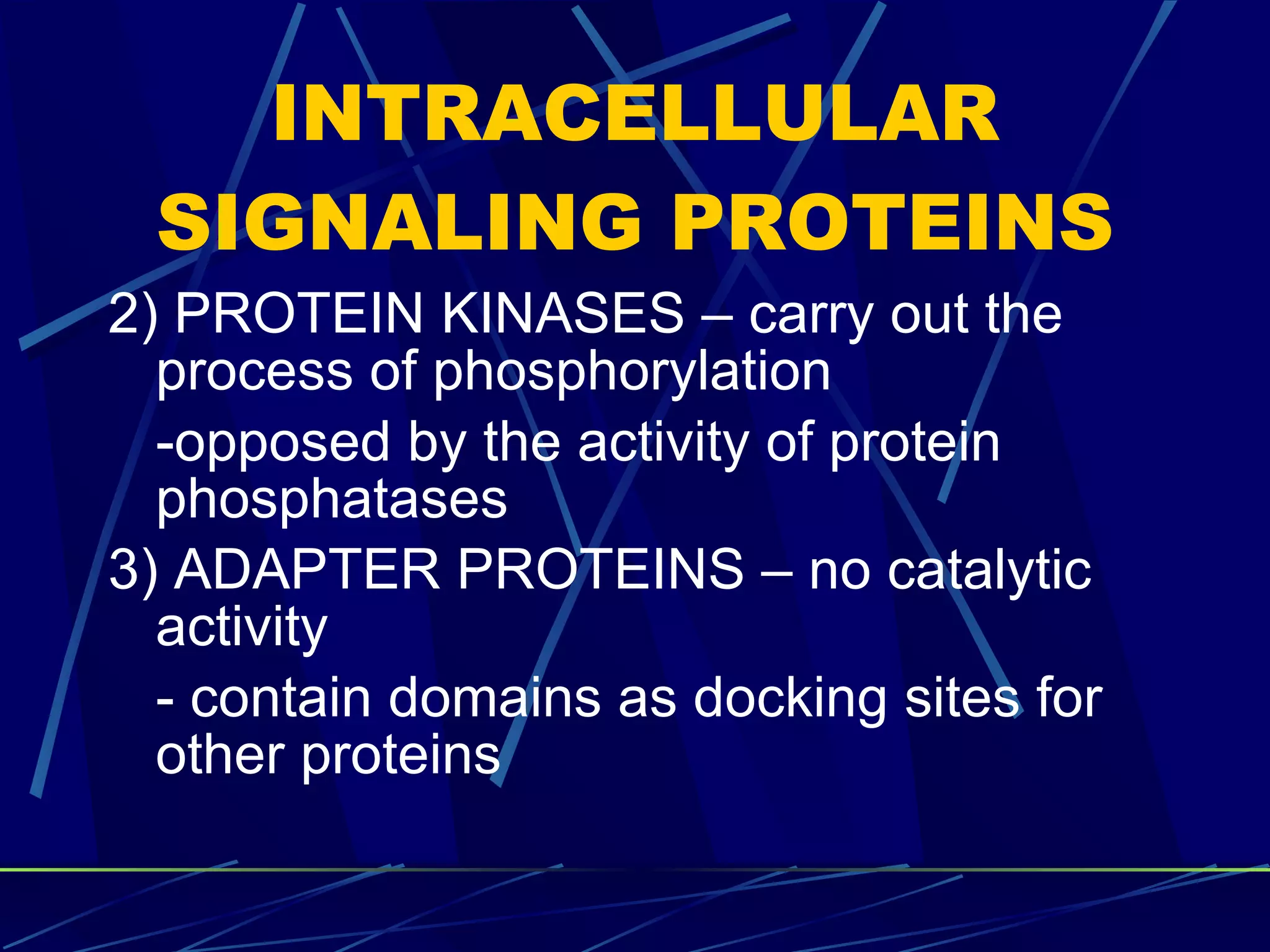
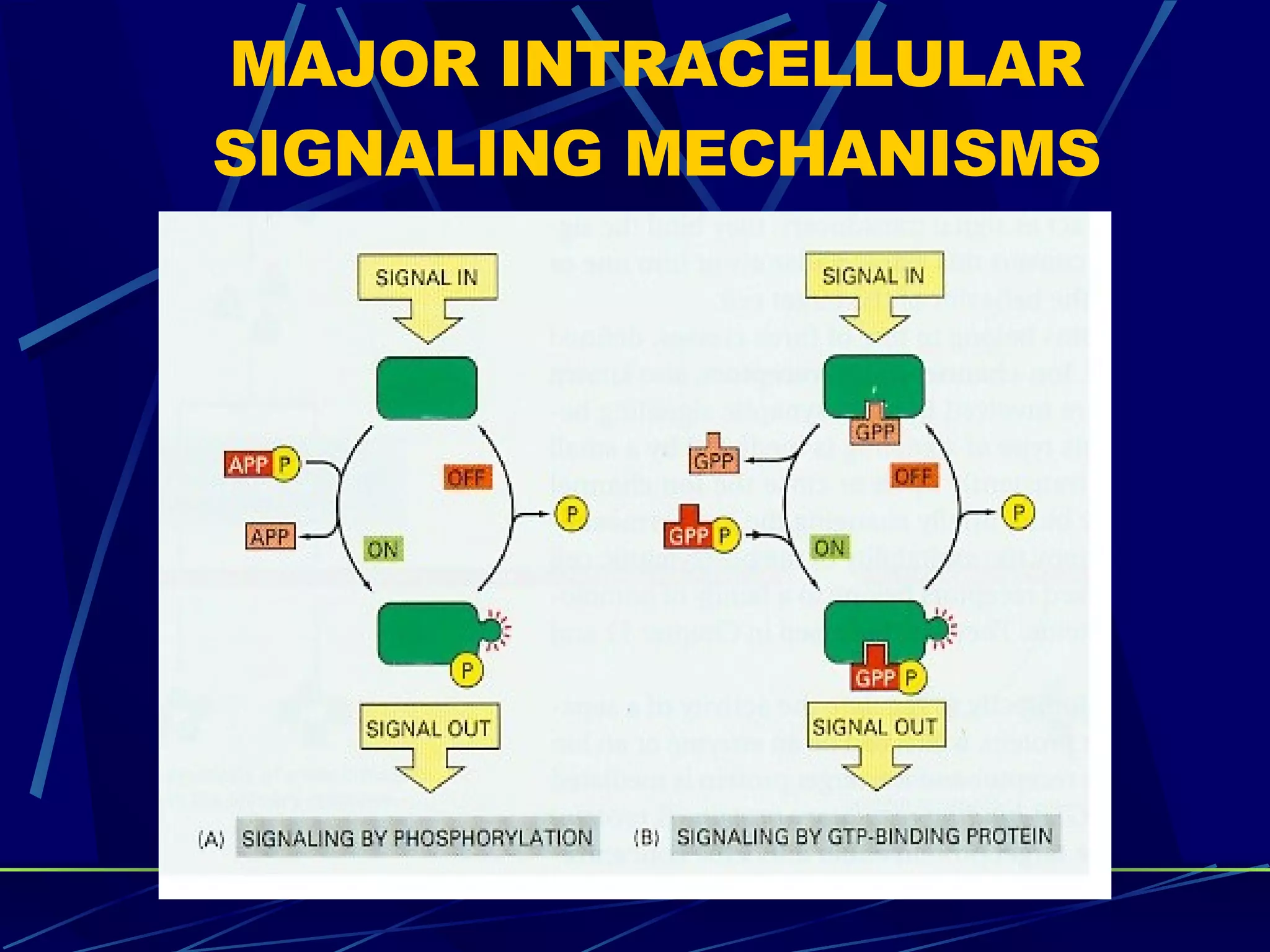
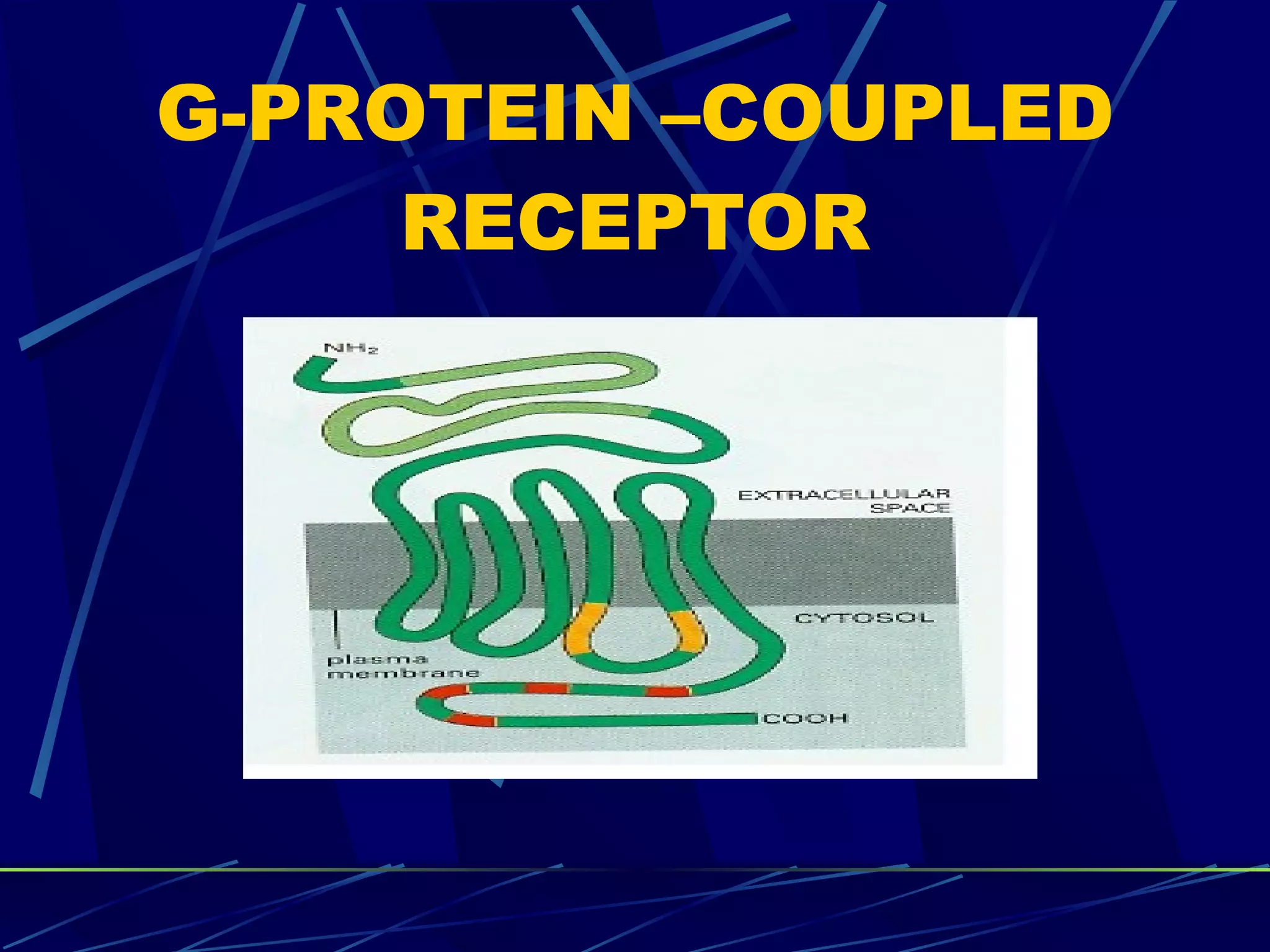
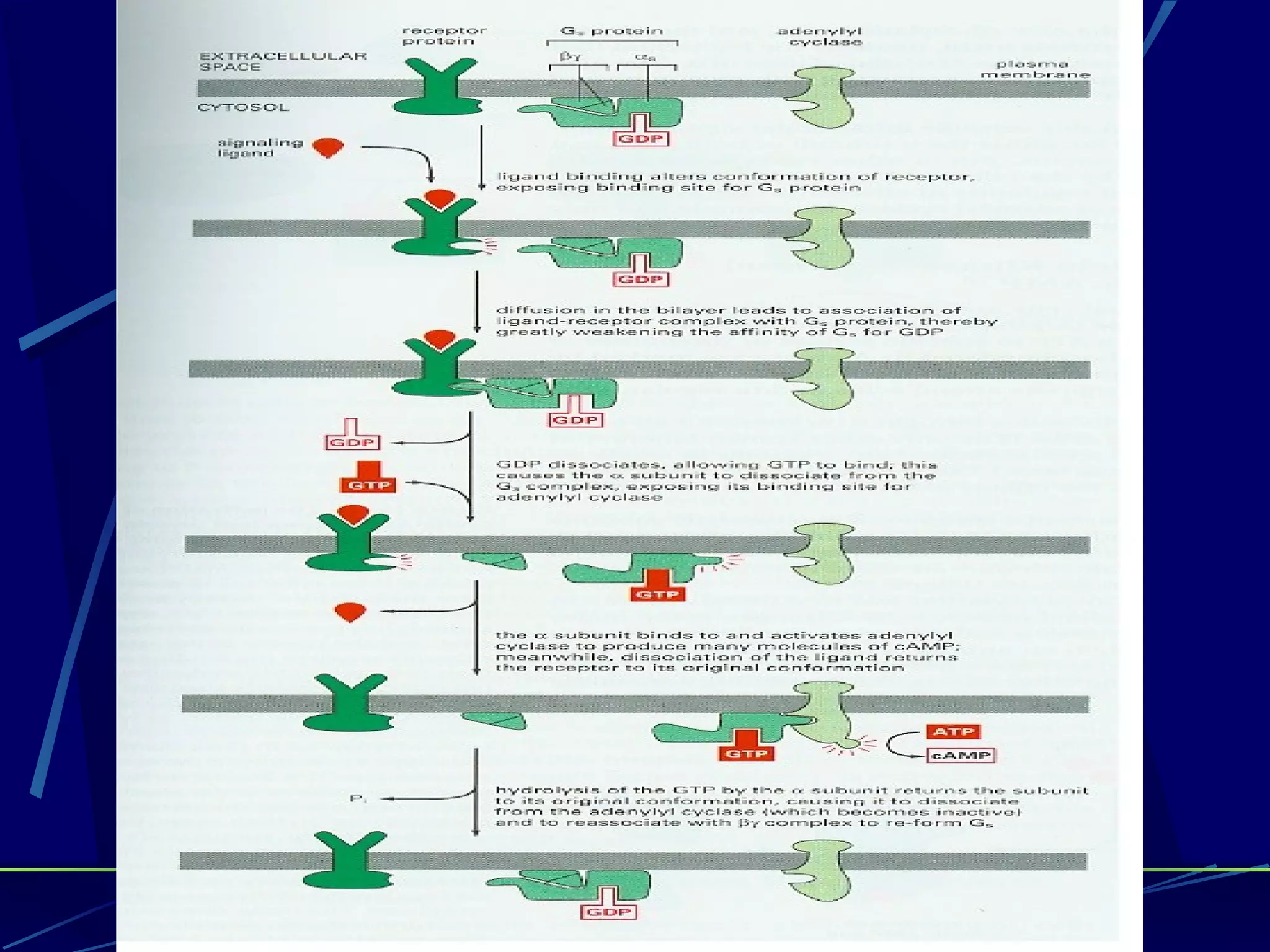
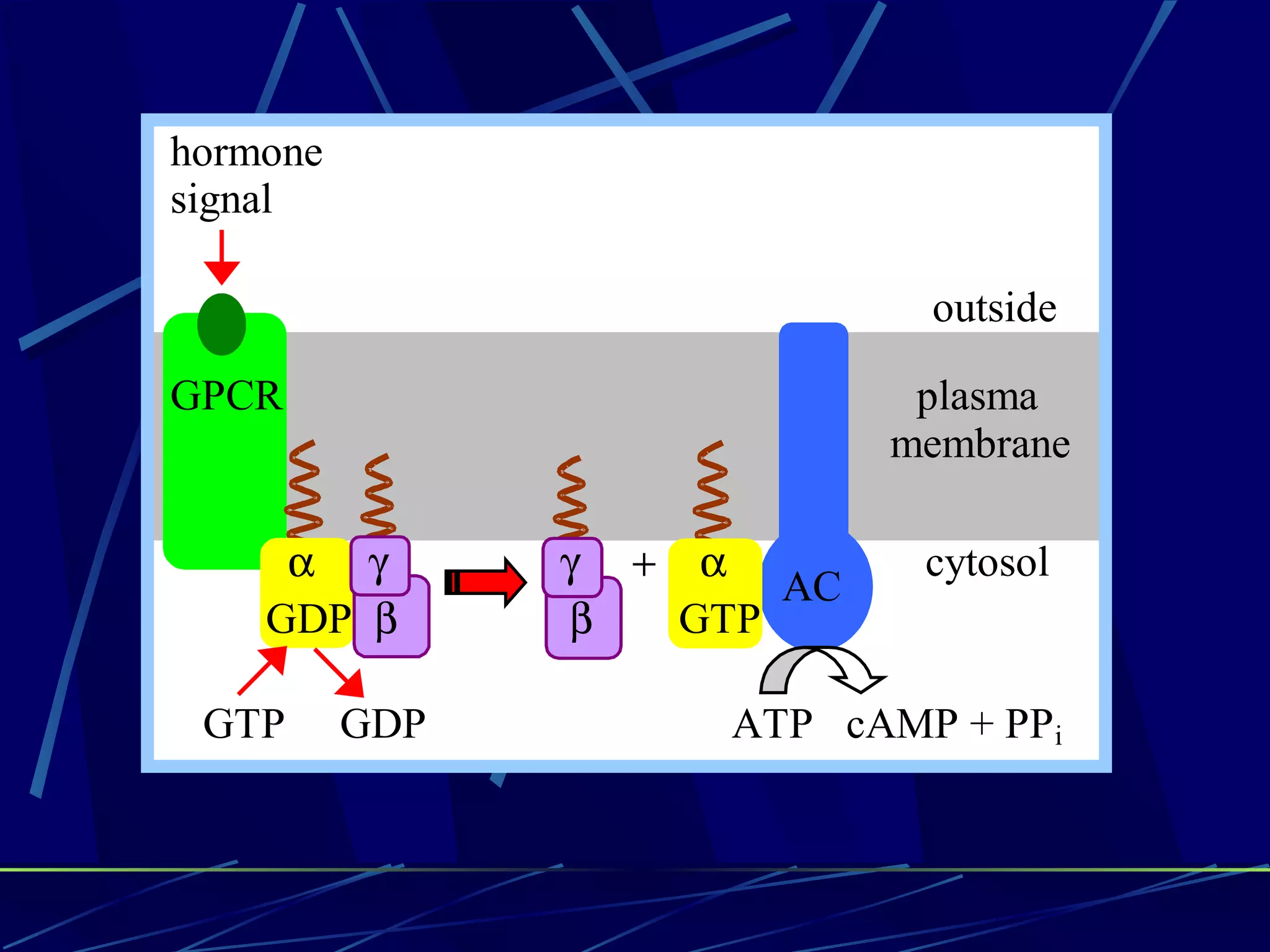
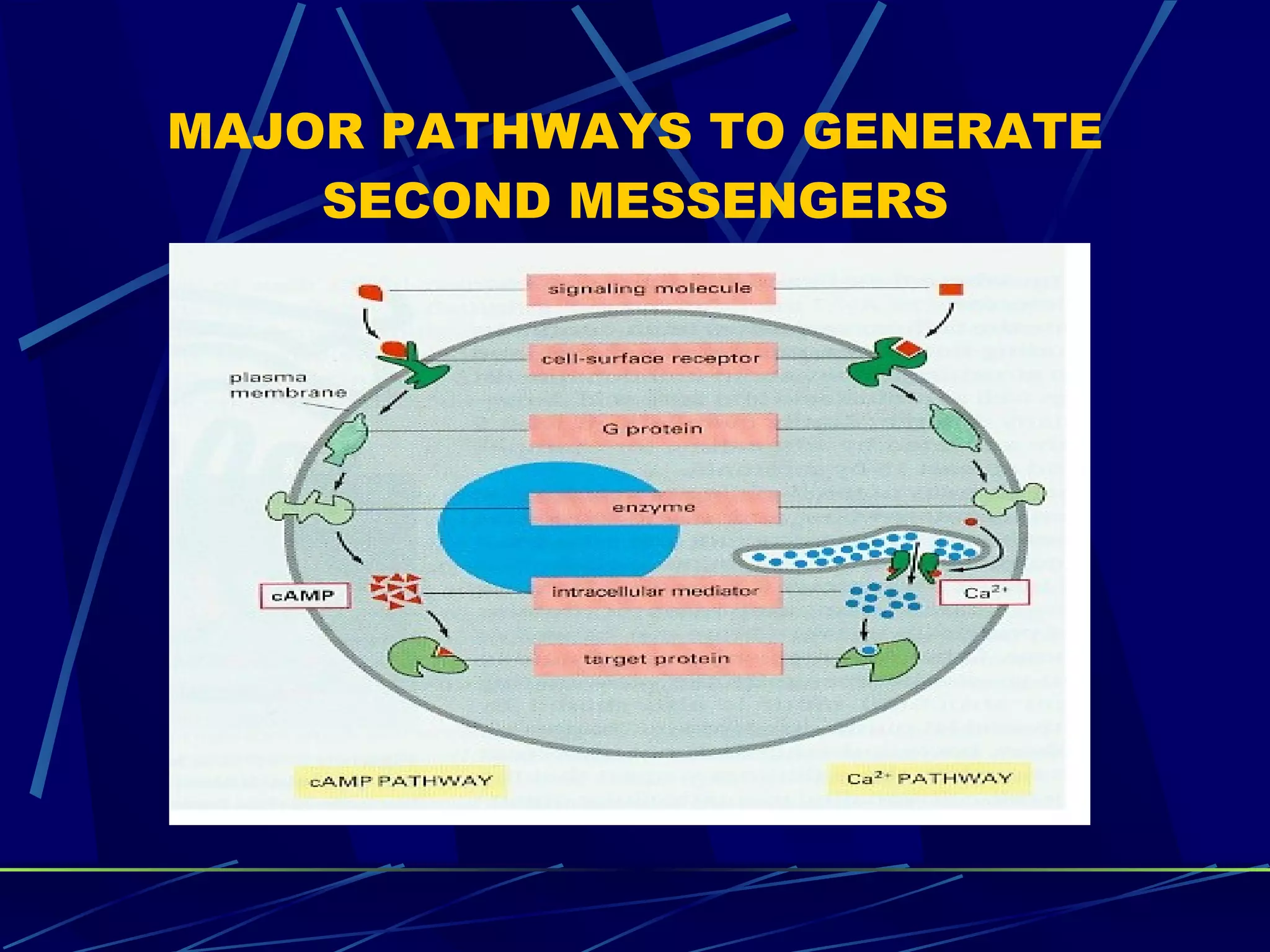
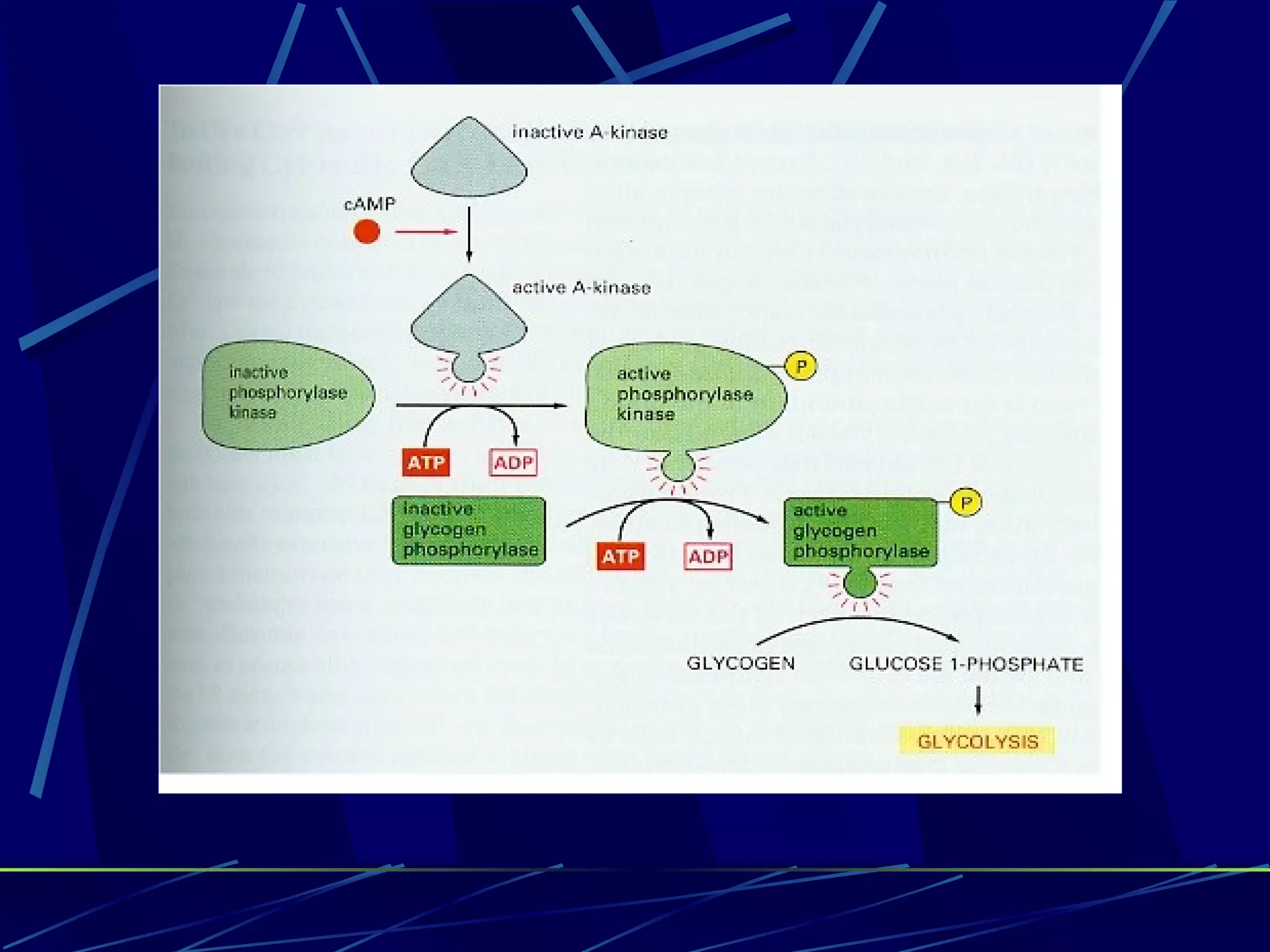
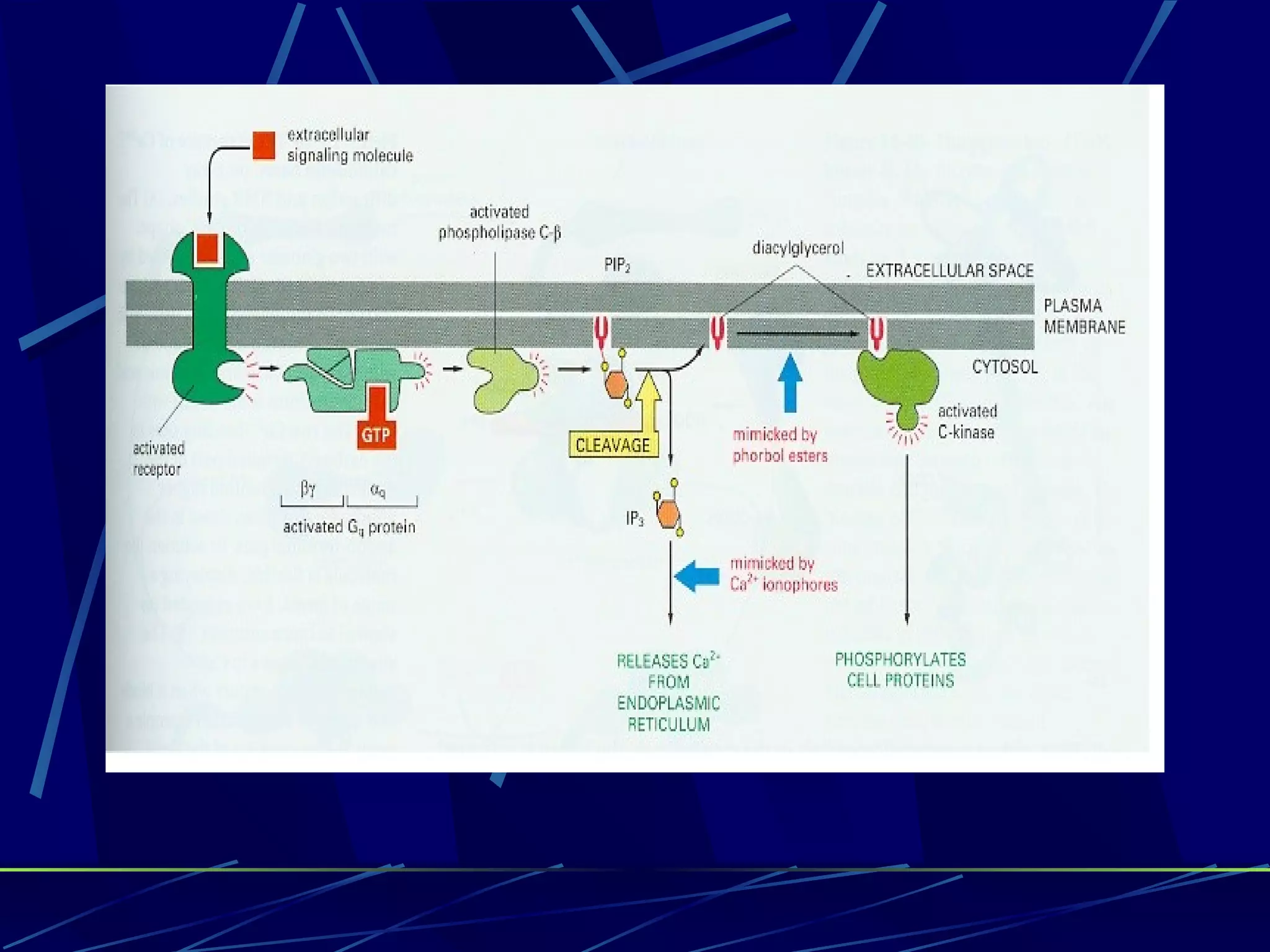
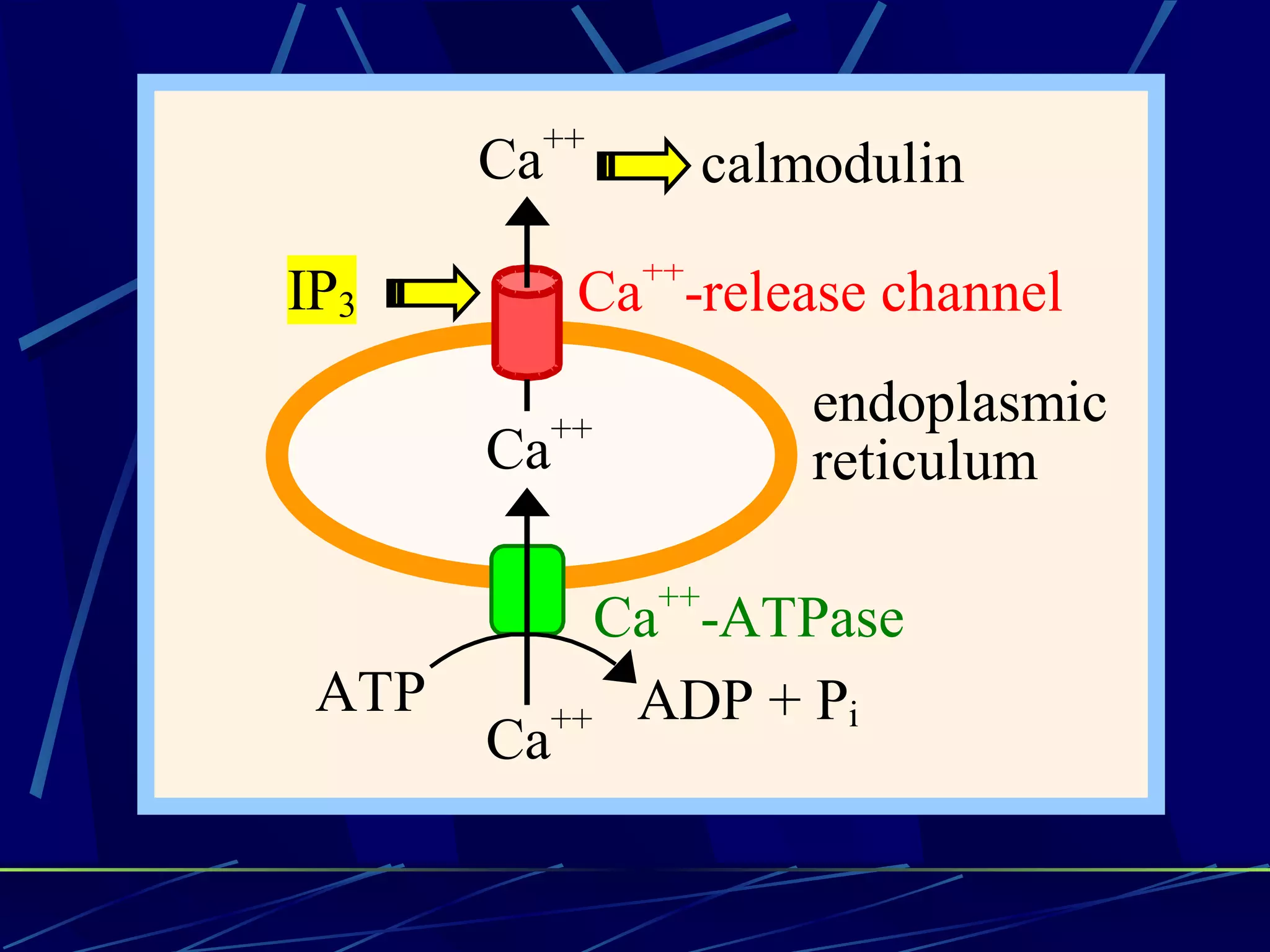
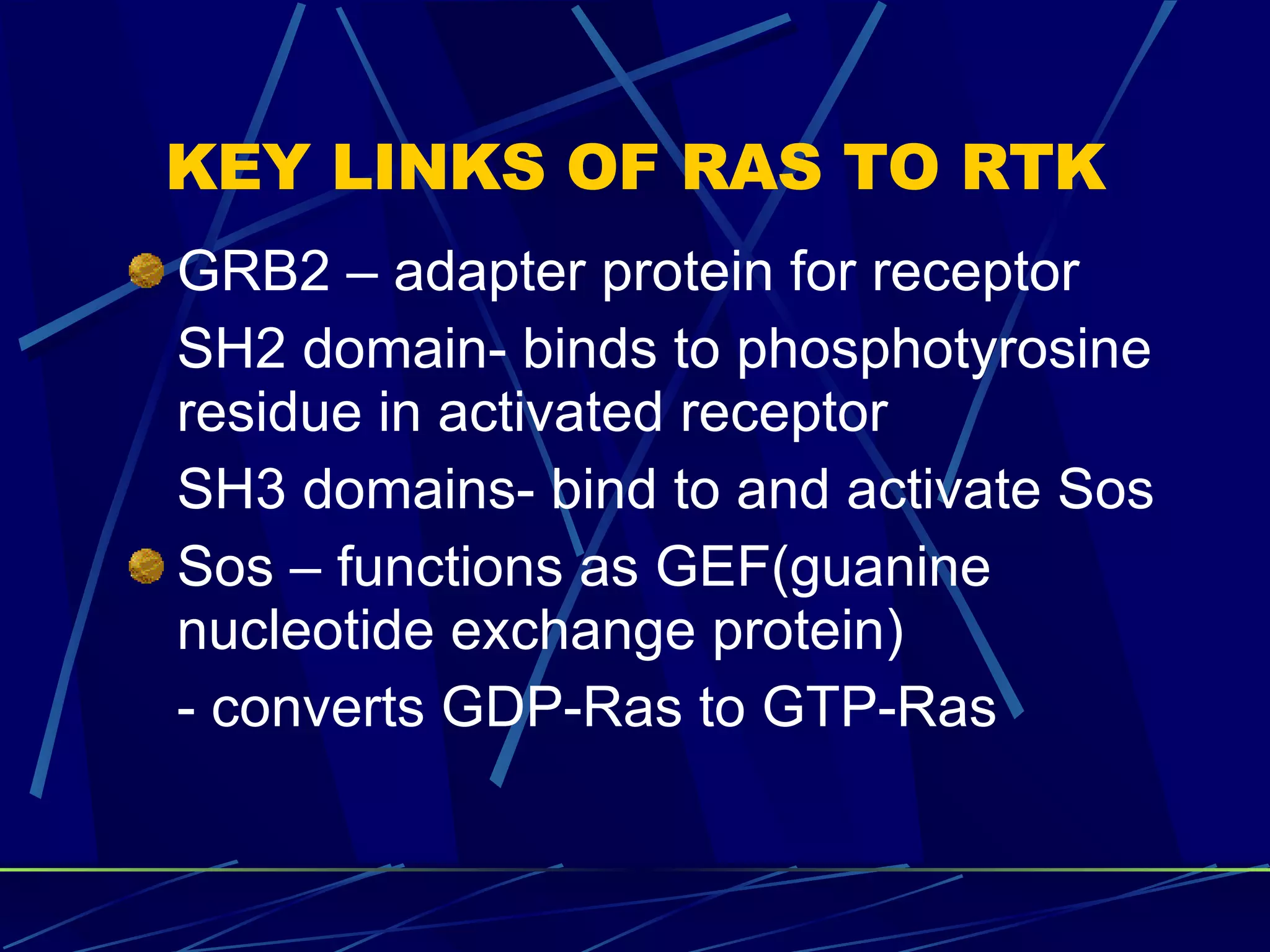
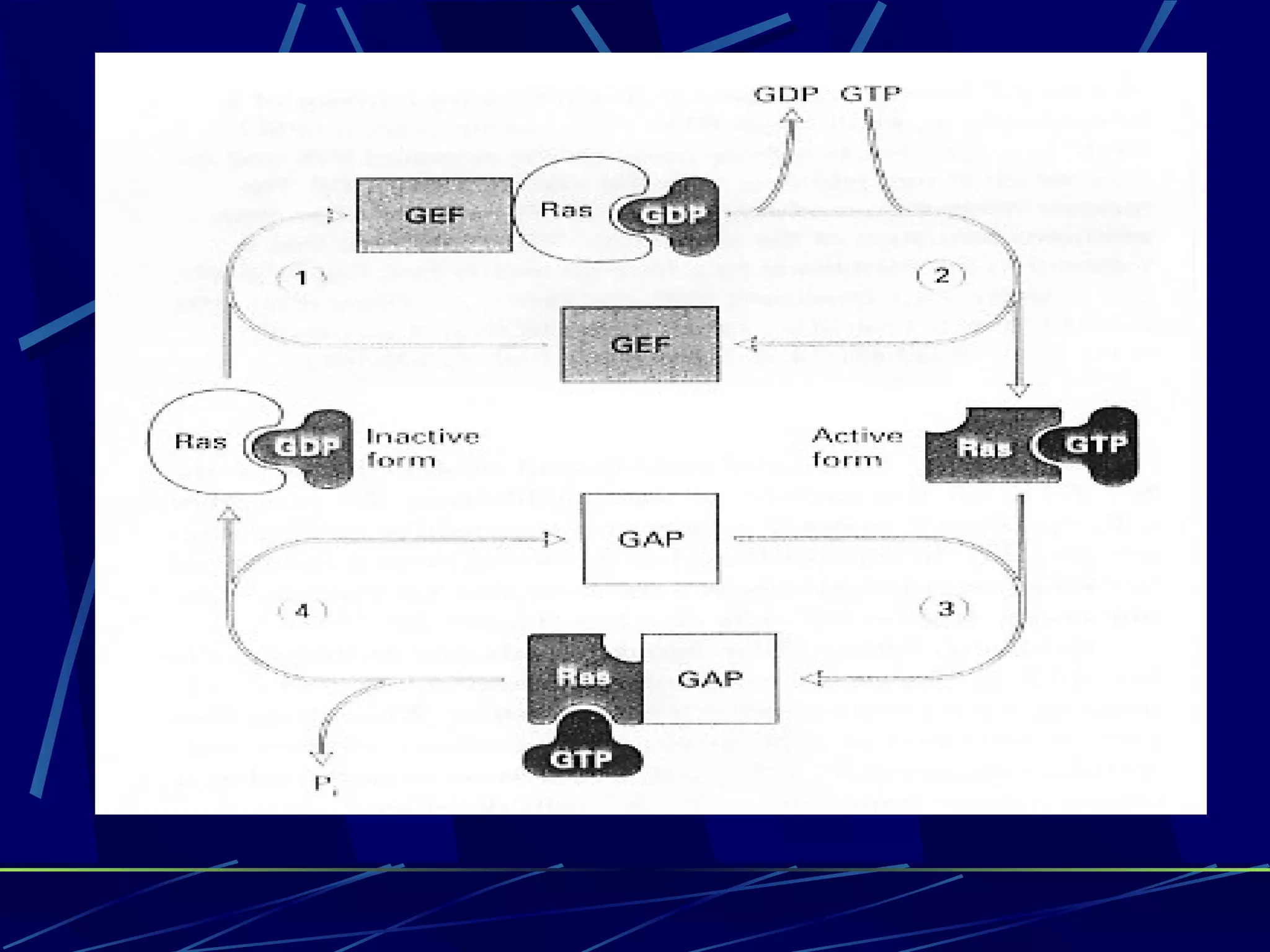
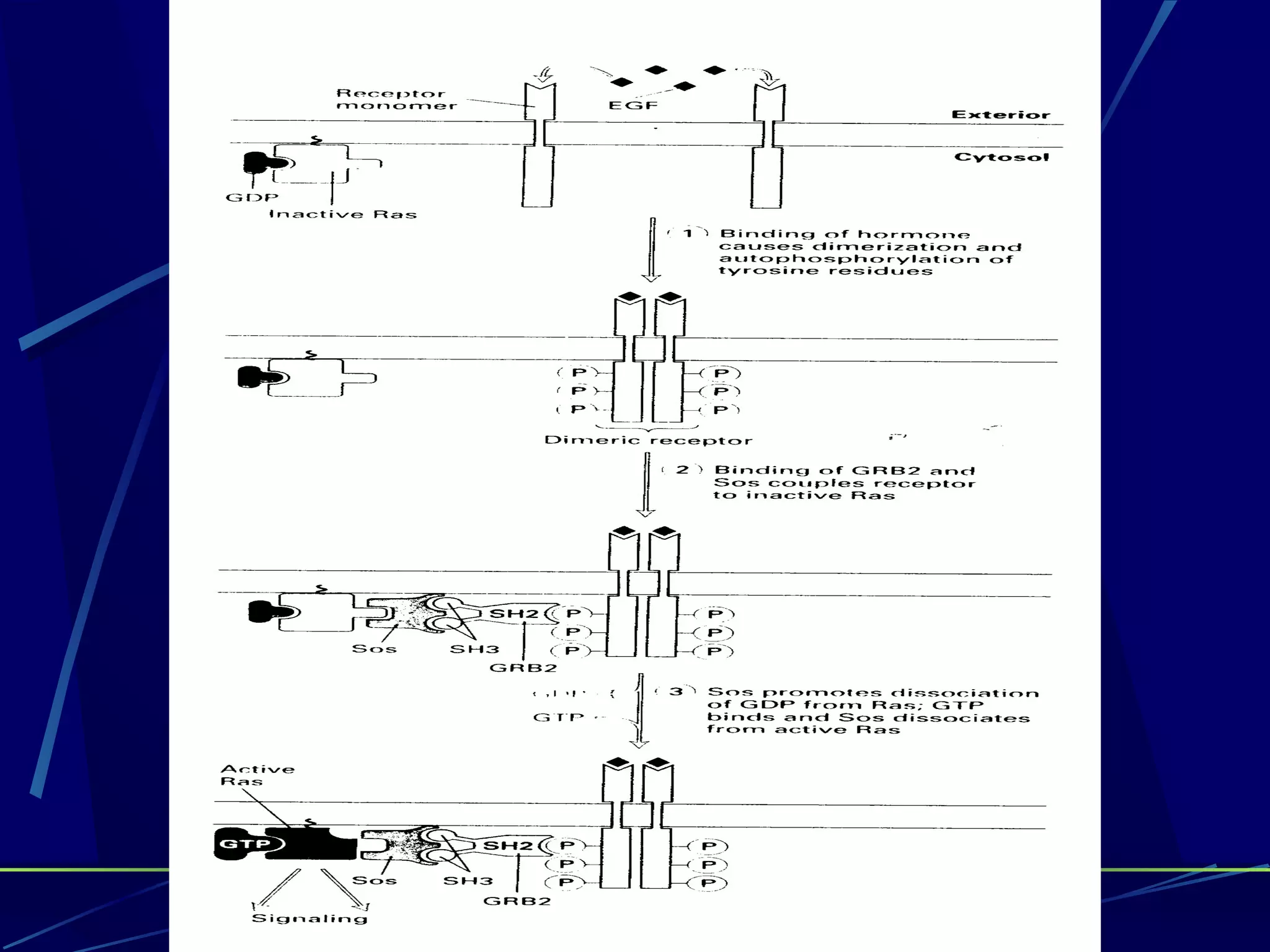
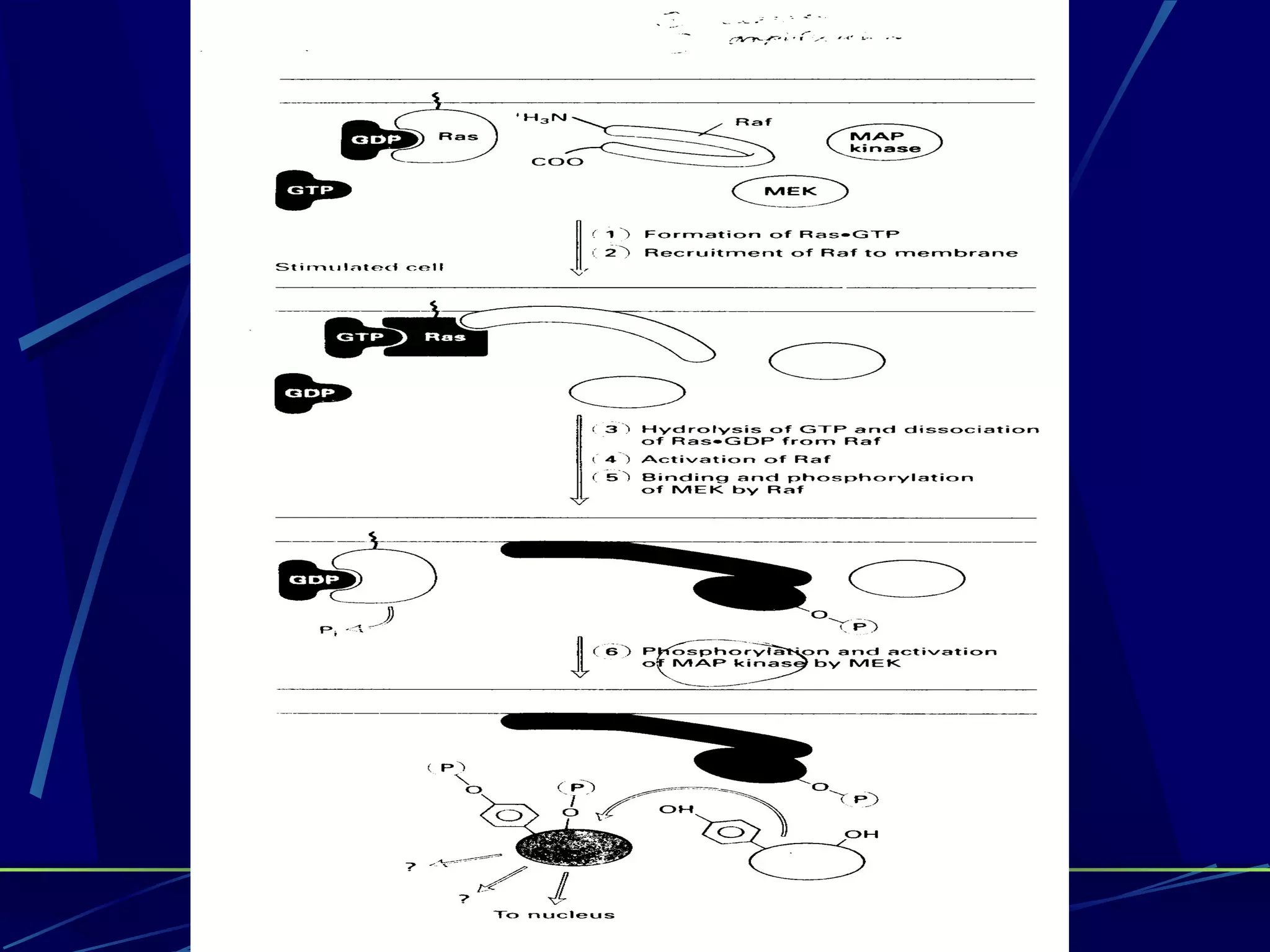
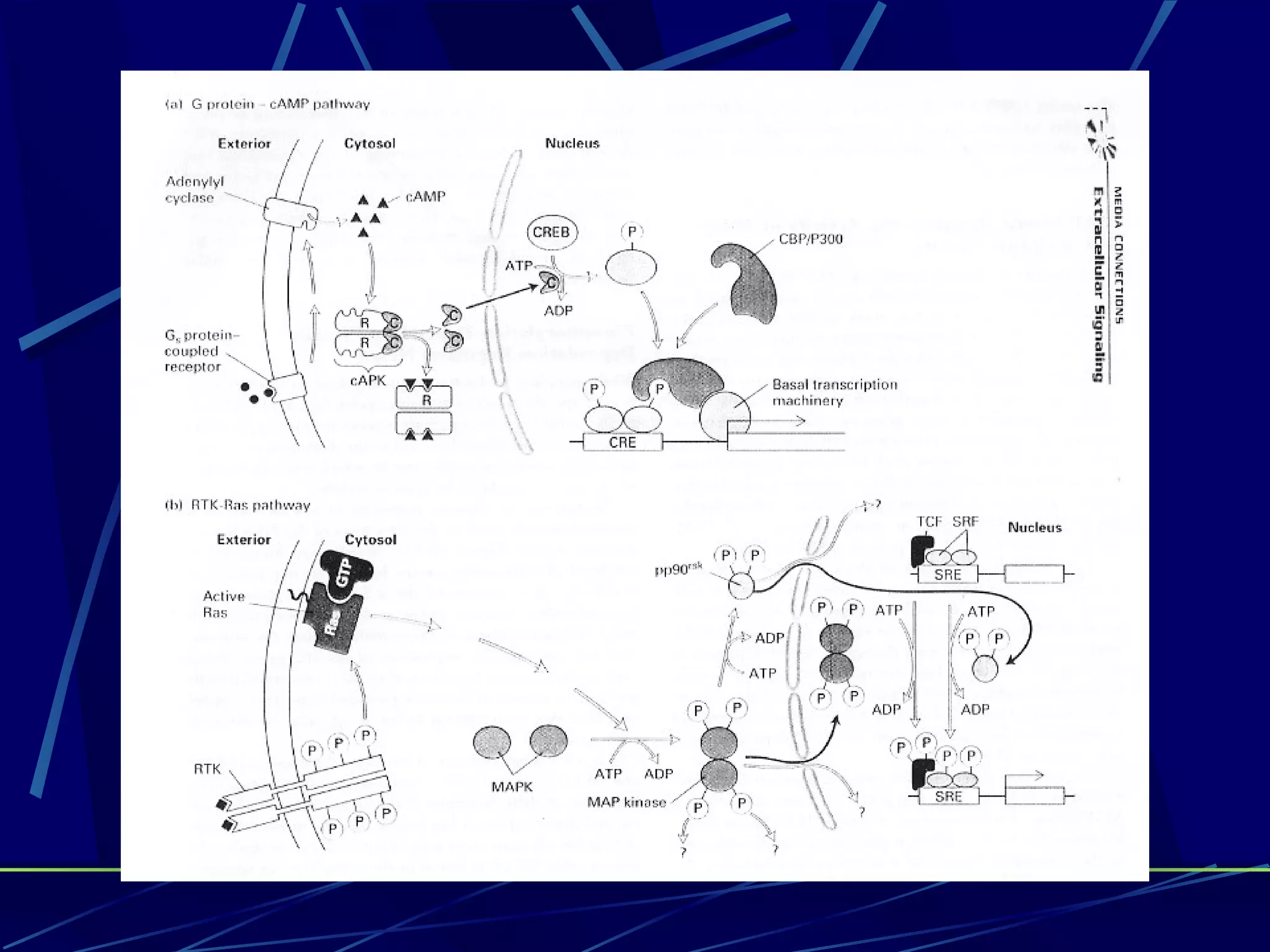
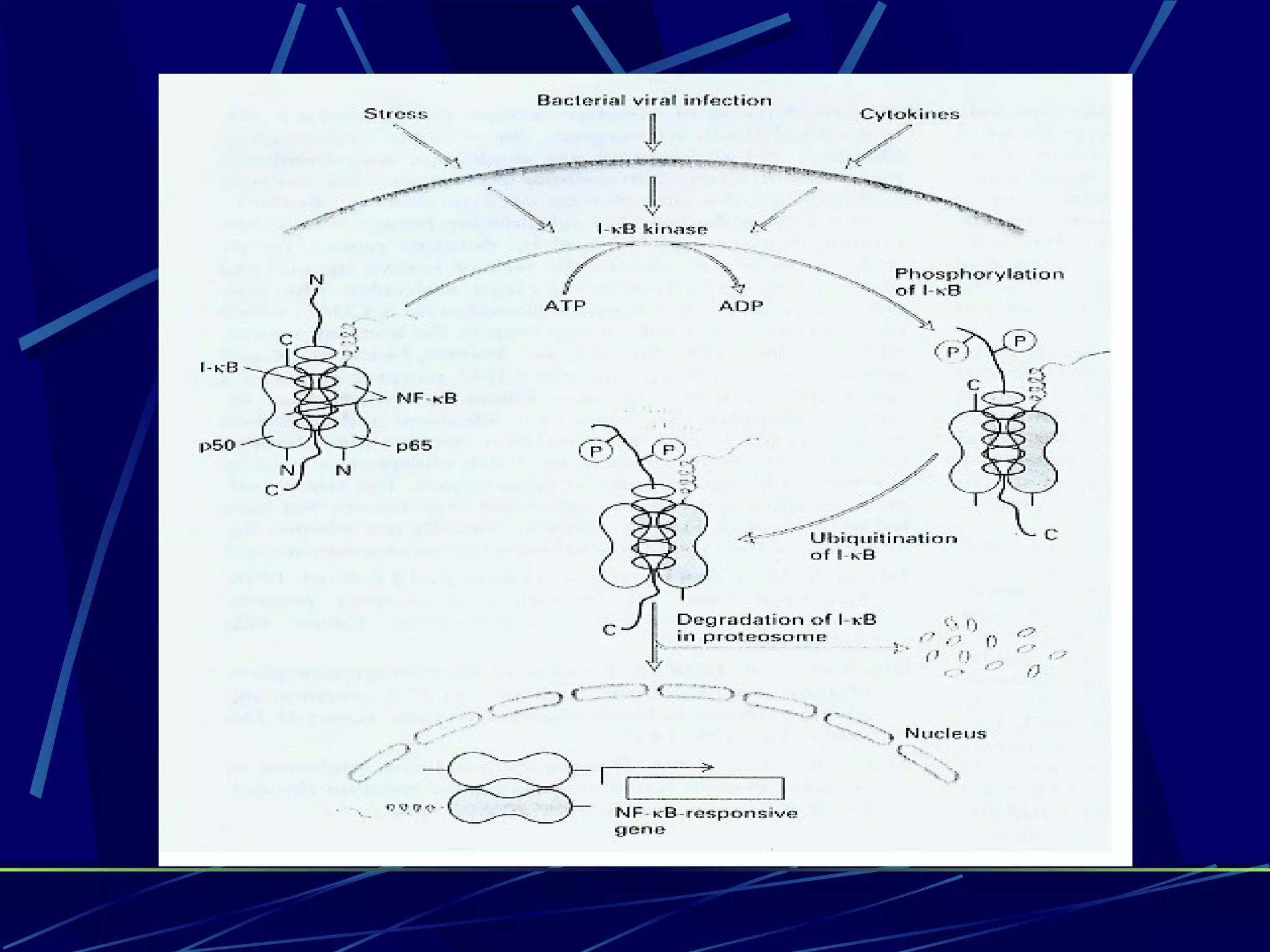
The document discusses signal transduction, which is the process by which extracellular signals are converted into intracellular responses. There are six main steps: 1) synthesis and release of signaling molecules, 2) transport to target cell, 3) detection by receptor, 4) change in cell function triggered by receptor-signal complex, 5) removal of signal, and 6) termination of response. Signal transduction involves cell surface receptors and intracellular receptors that bind ligands and mediate specific cellular responses. Major types of signaling include endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine signaling.