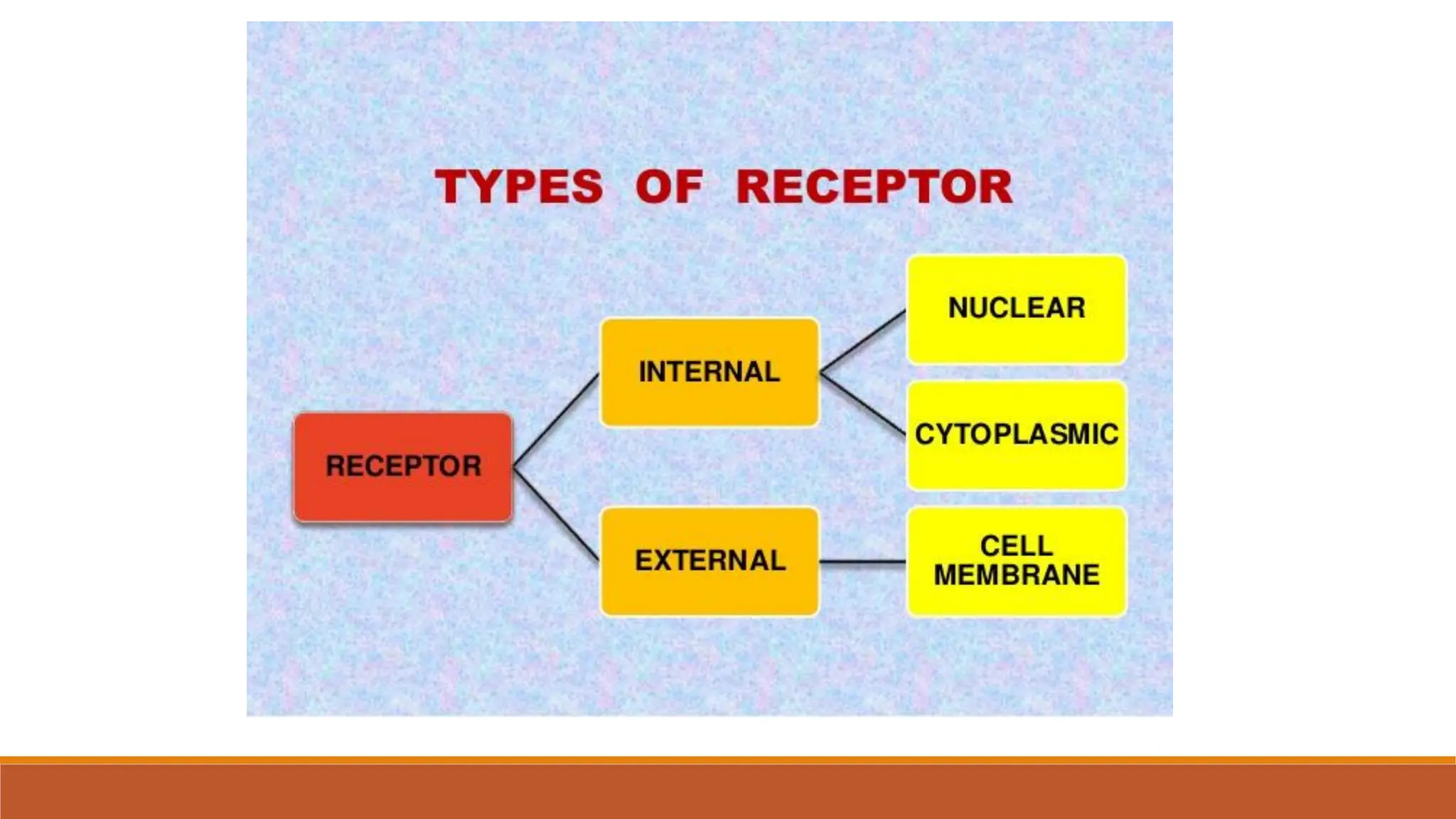
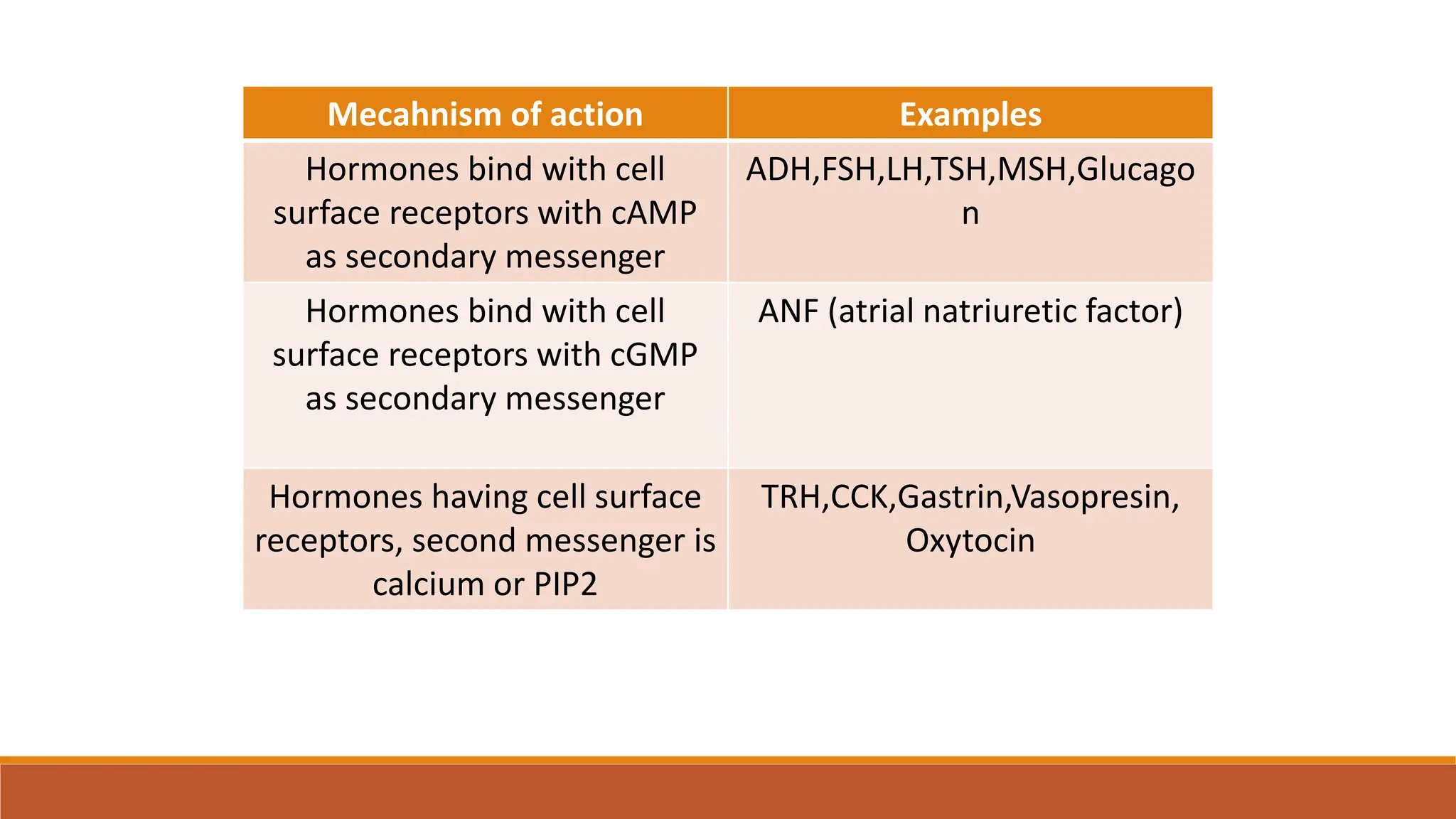
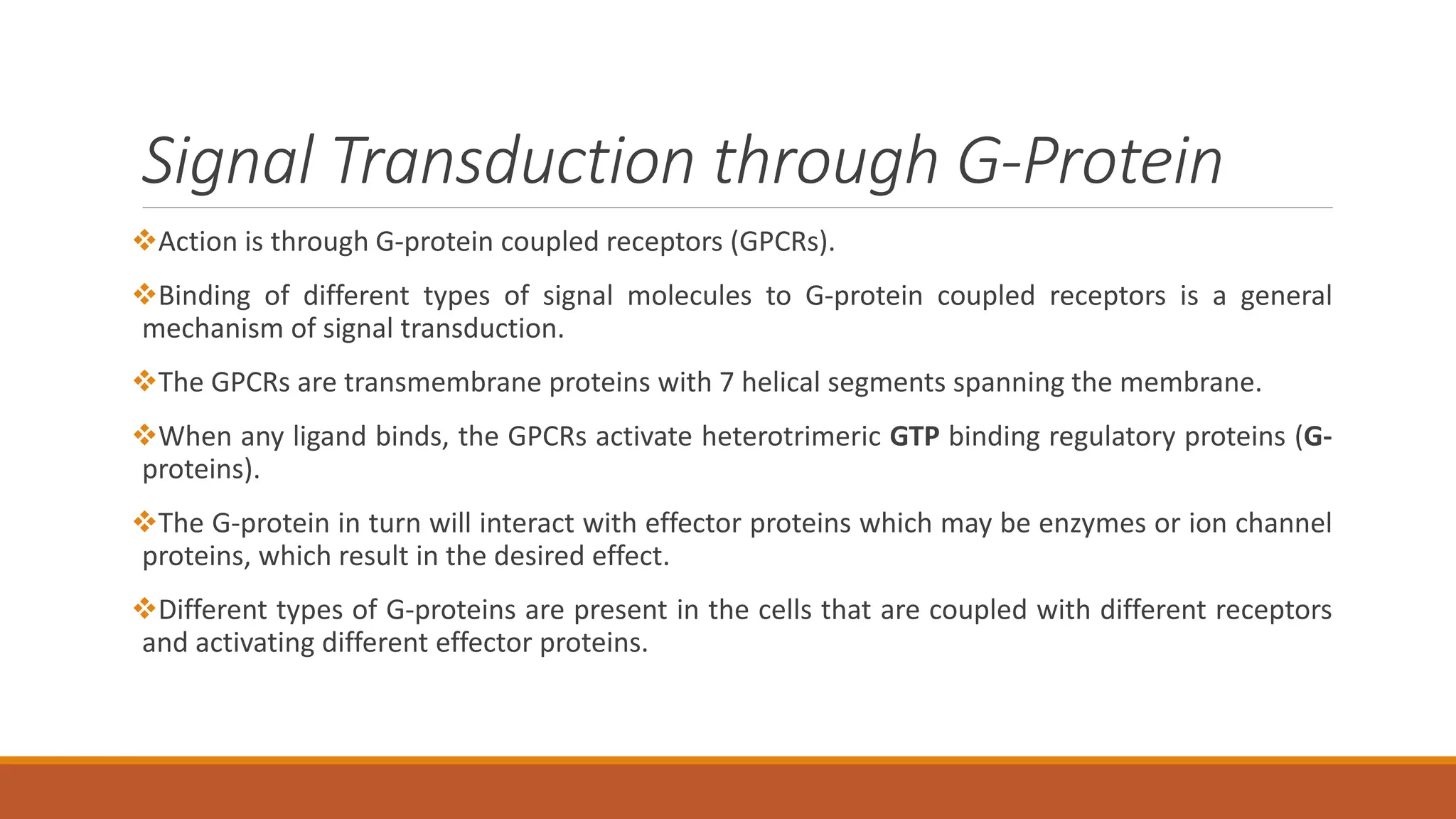
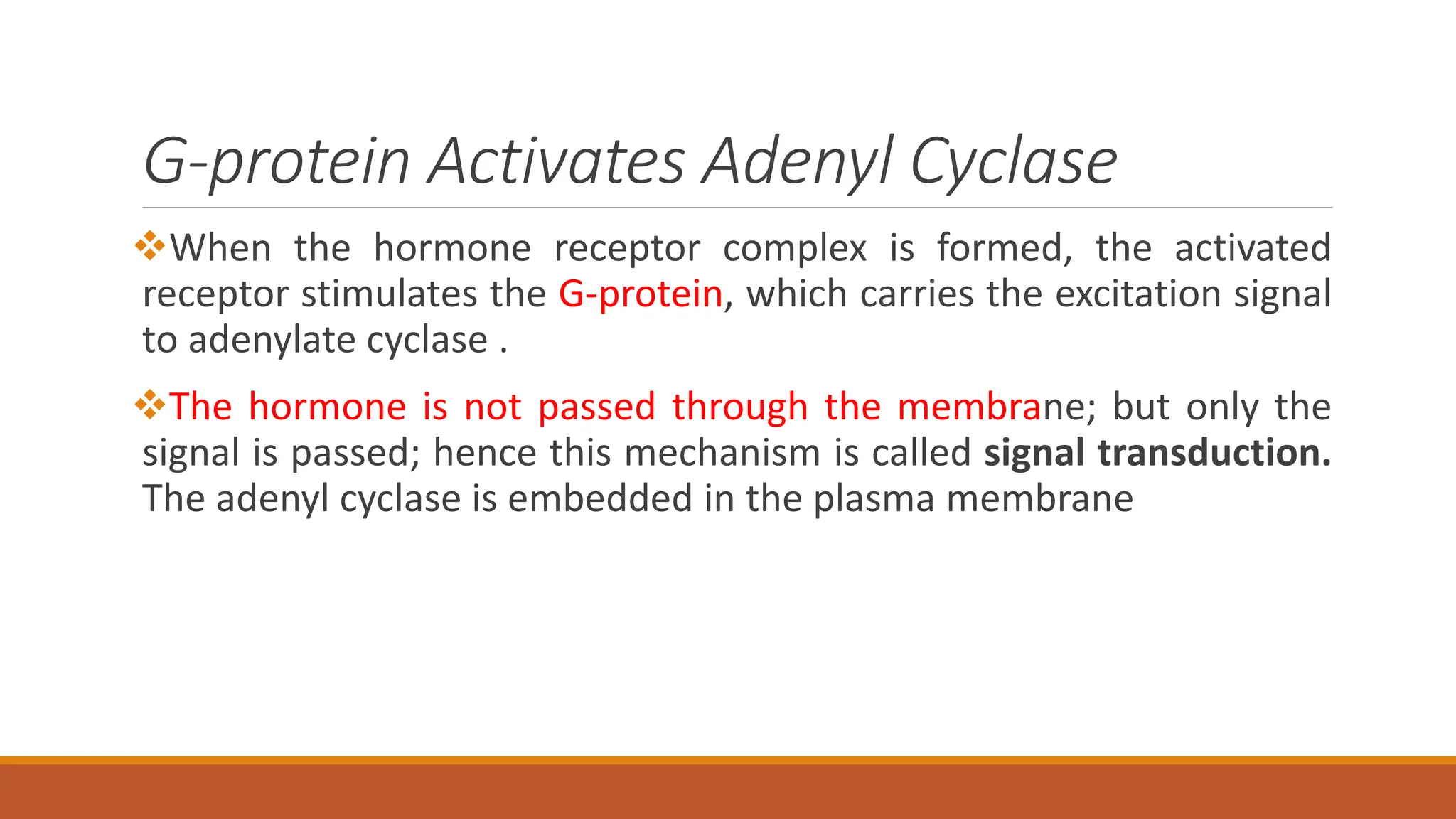
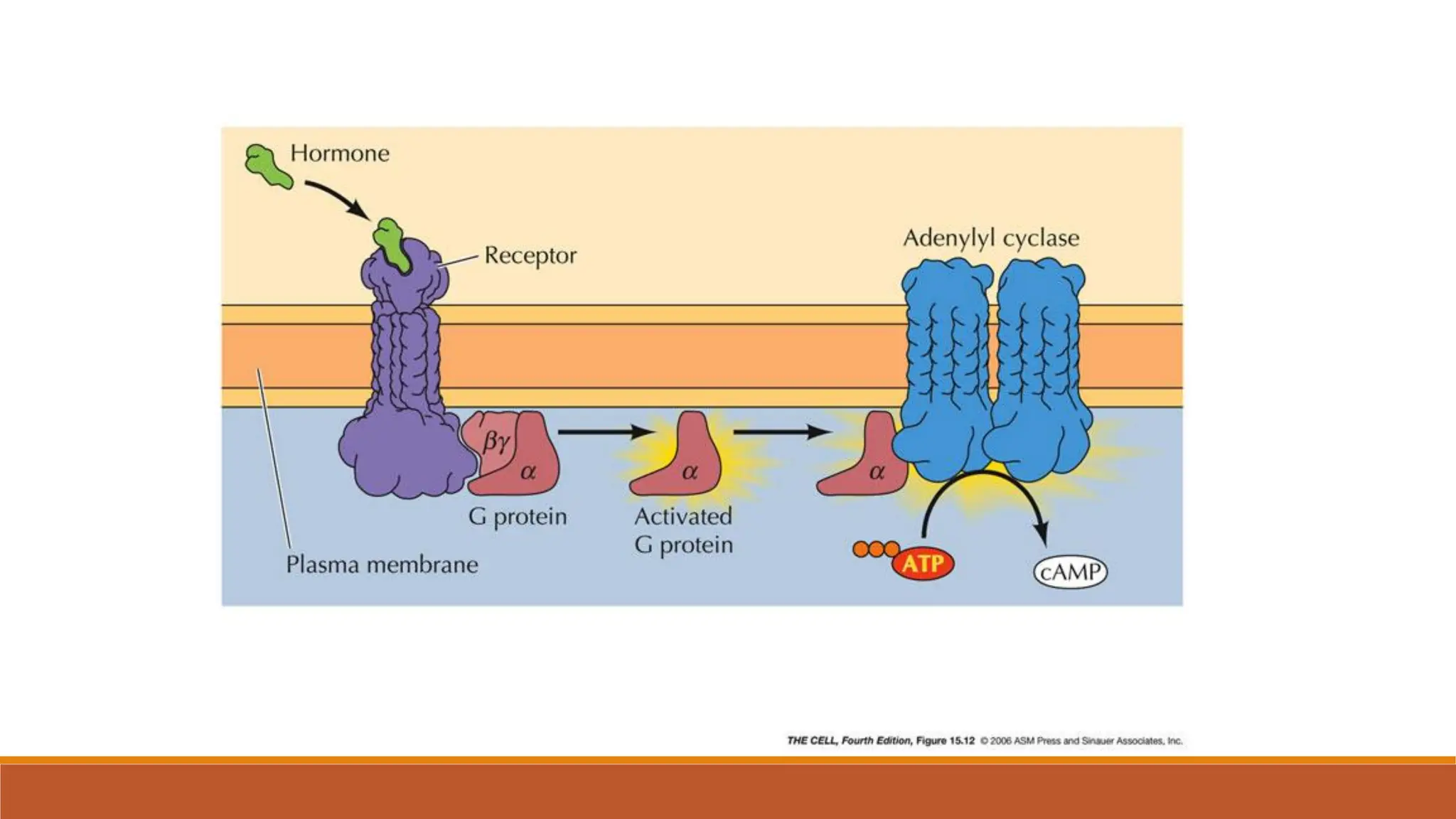
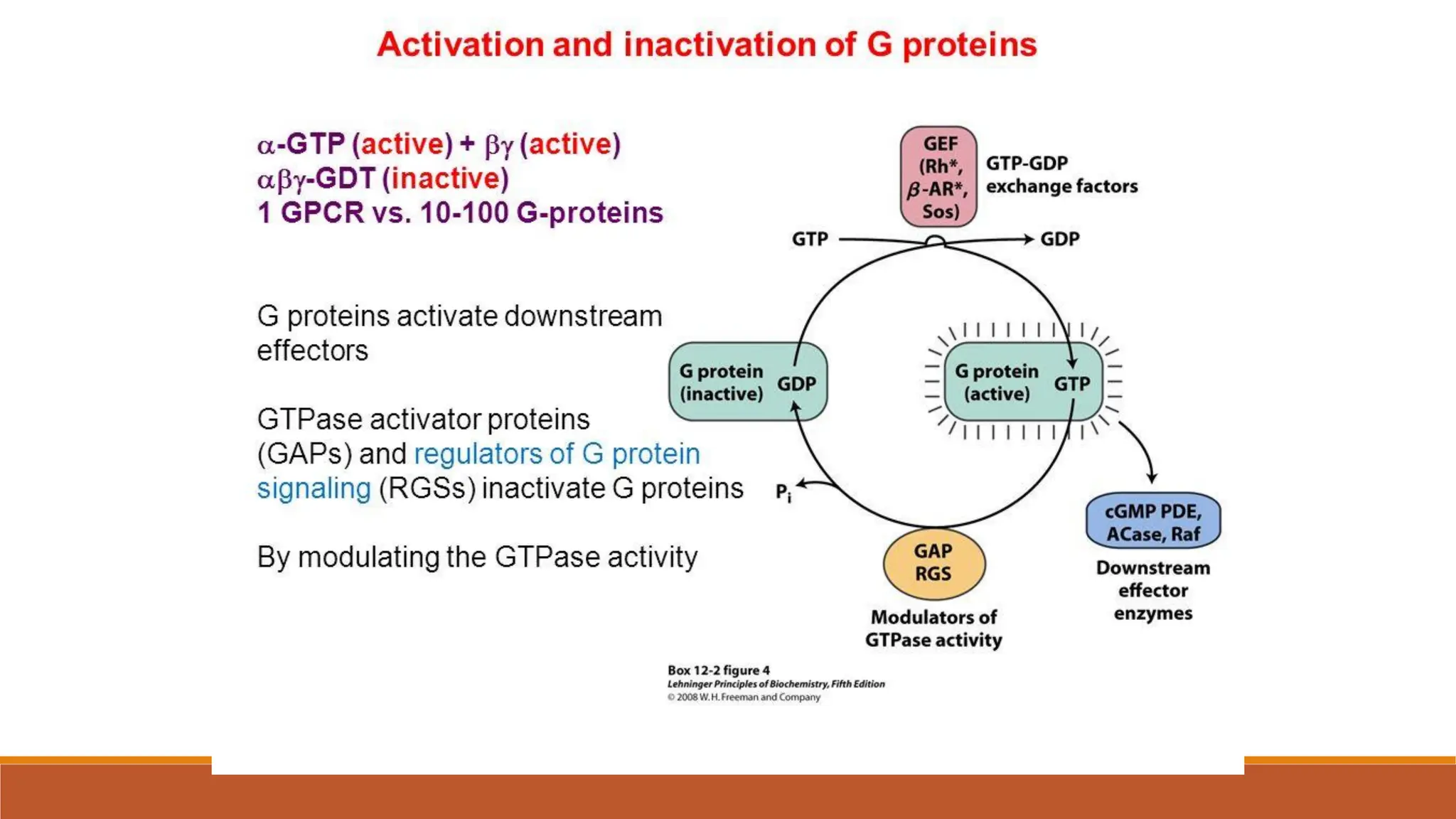
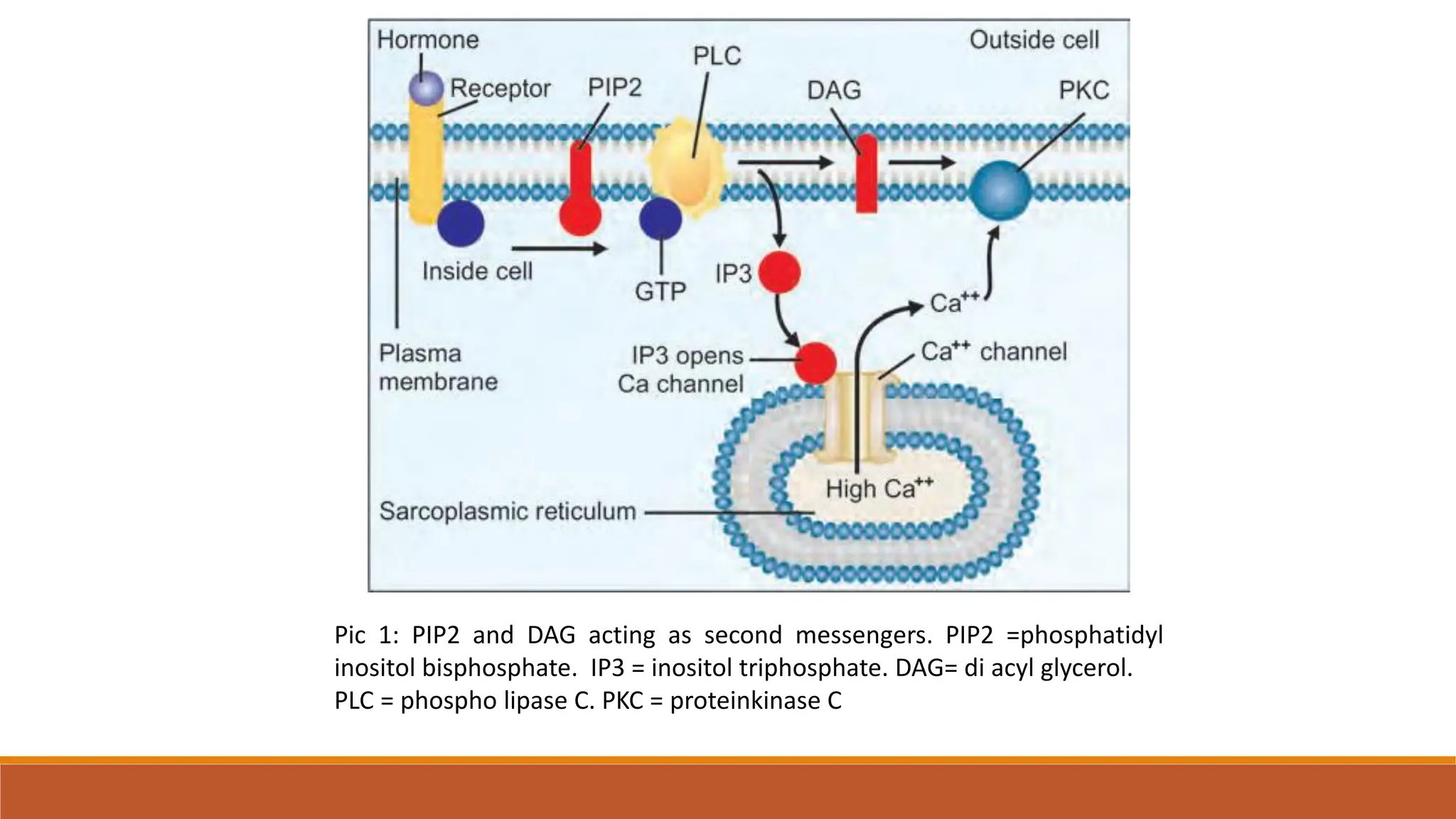
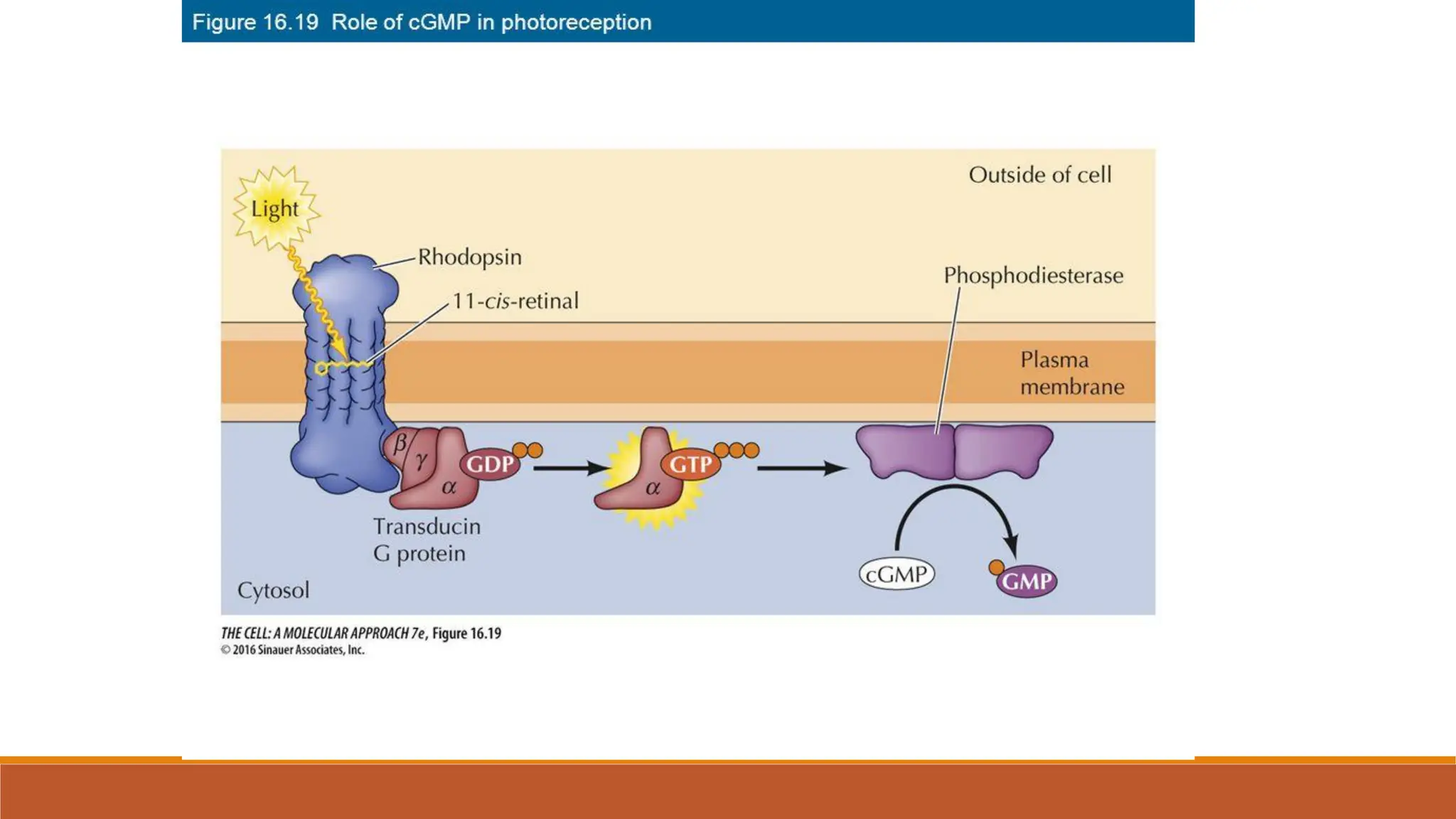
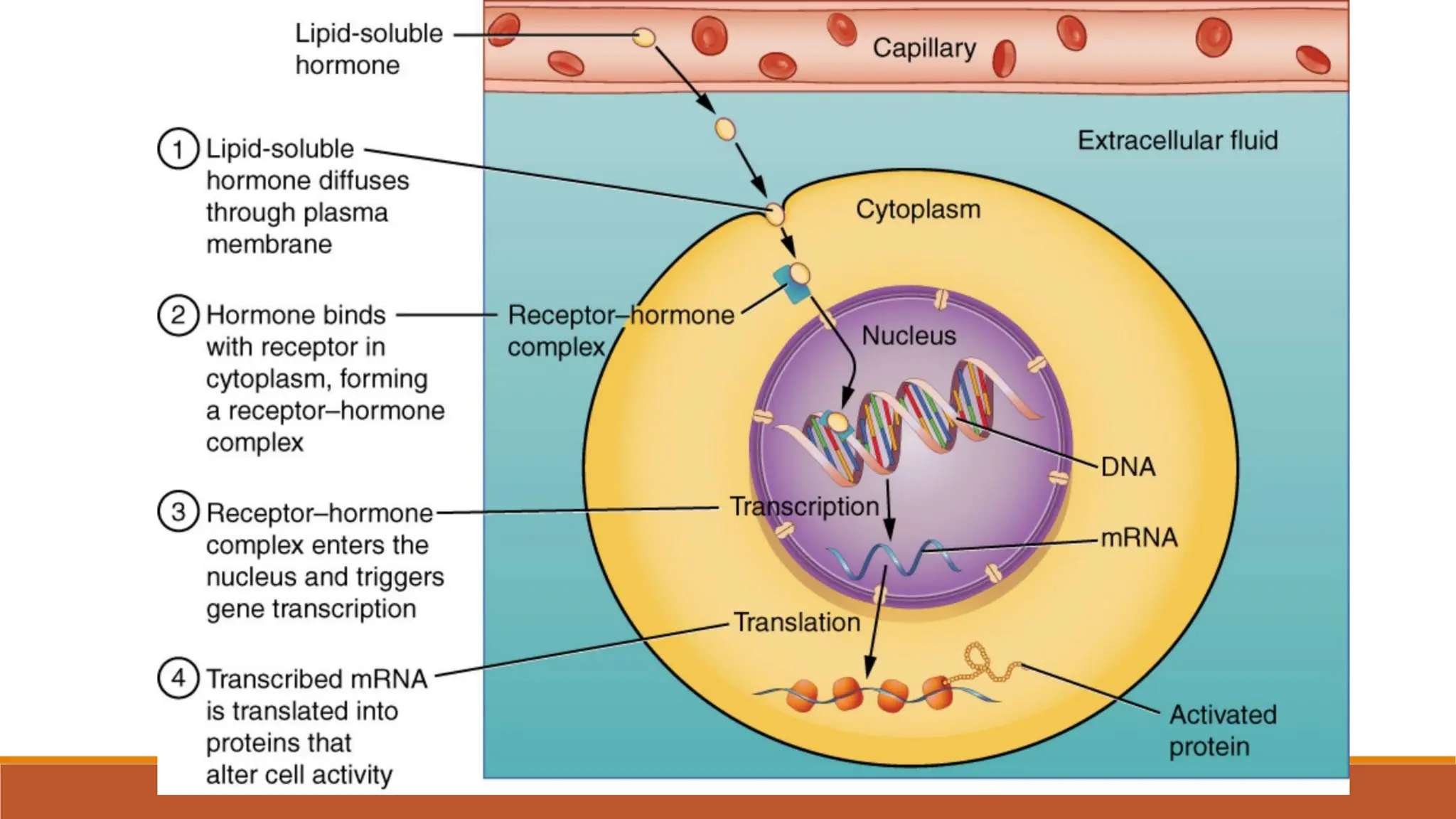
Hormones can act through two main mechanisms: 1) by binding to cell surface receptors which activate intracellular signaling pathways using secondary messengers like cAMP or calcium, or 2) by directly binding to intracellular receptors which then act as transcription factors to regulate gene expression. Some key examples of the cell surface receptor pathway include hormones like glucagon that increase cAMP levels via G protein coupled receptors or hormones like TRH that increase intracellular calcium levels. The intracellular receptor pathway is used by hormones like steroid hormones.