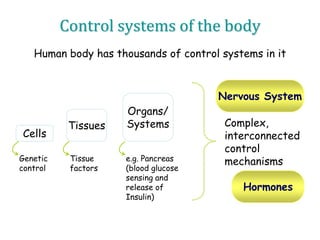
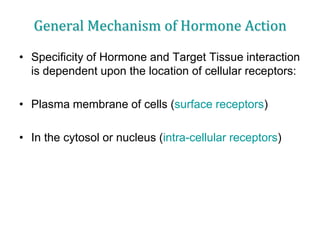
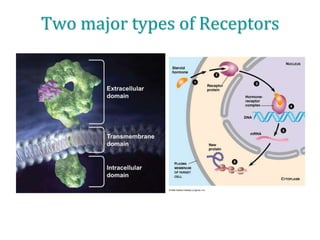
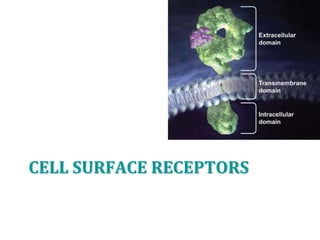
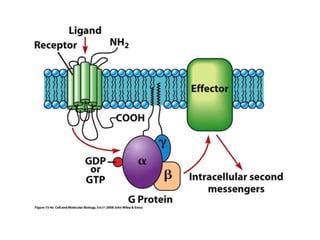
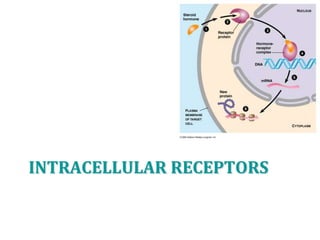
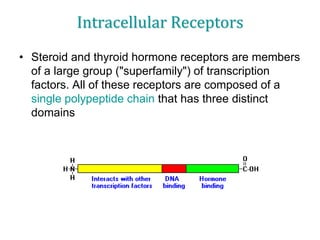
1. The document outlines different types of cellular receptors including cell surface receptors like G protein-coupled receptors and tyrosine kinase receptors, as well as intracellular receptors.
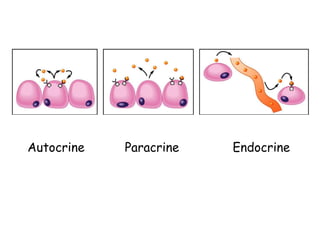
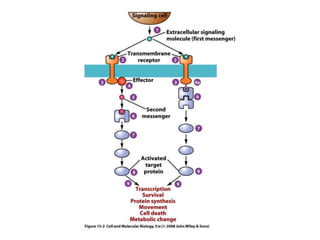
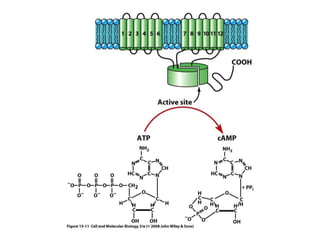
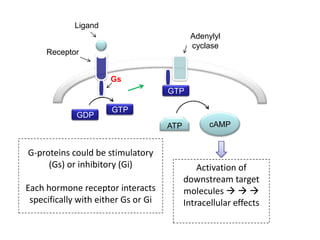
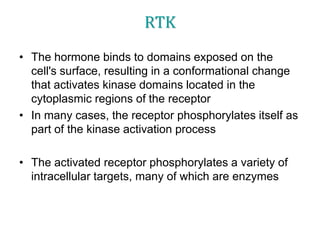
2. It provides examples of hormone signaling pathways, noting that hormones activate receptors which then trigger intracellular second messenger systems like cAMP, calcium, or phosphorylation to produce cellular effects.
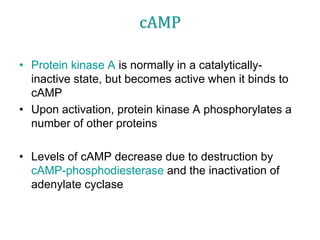
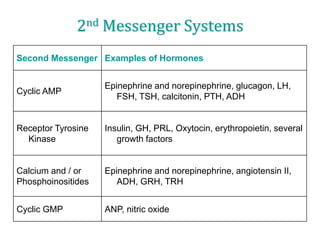
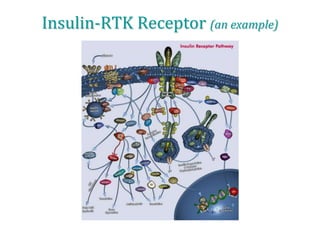
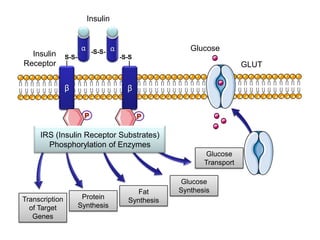
3. The mechanism of insulin signaling is described as an example of receptor tyrosine kinase activation, showing how insulin binding leads to phosphorylation of intracellular targets and downstream effects on processes like glucose uptake and fat/protein synthesis.