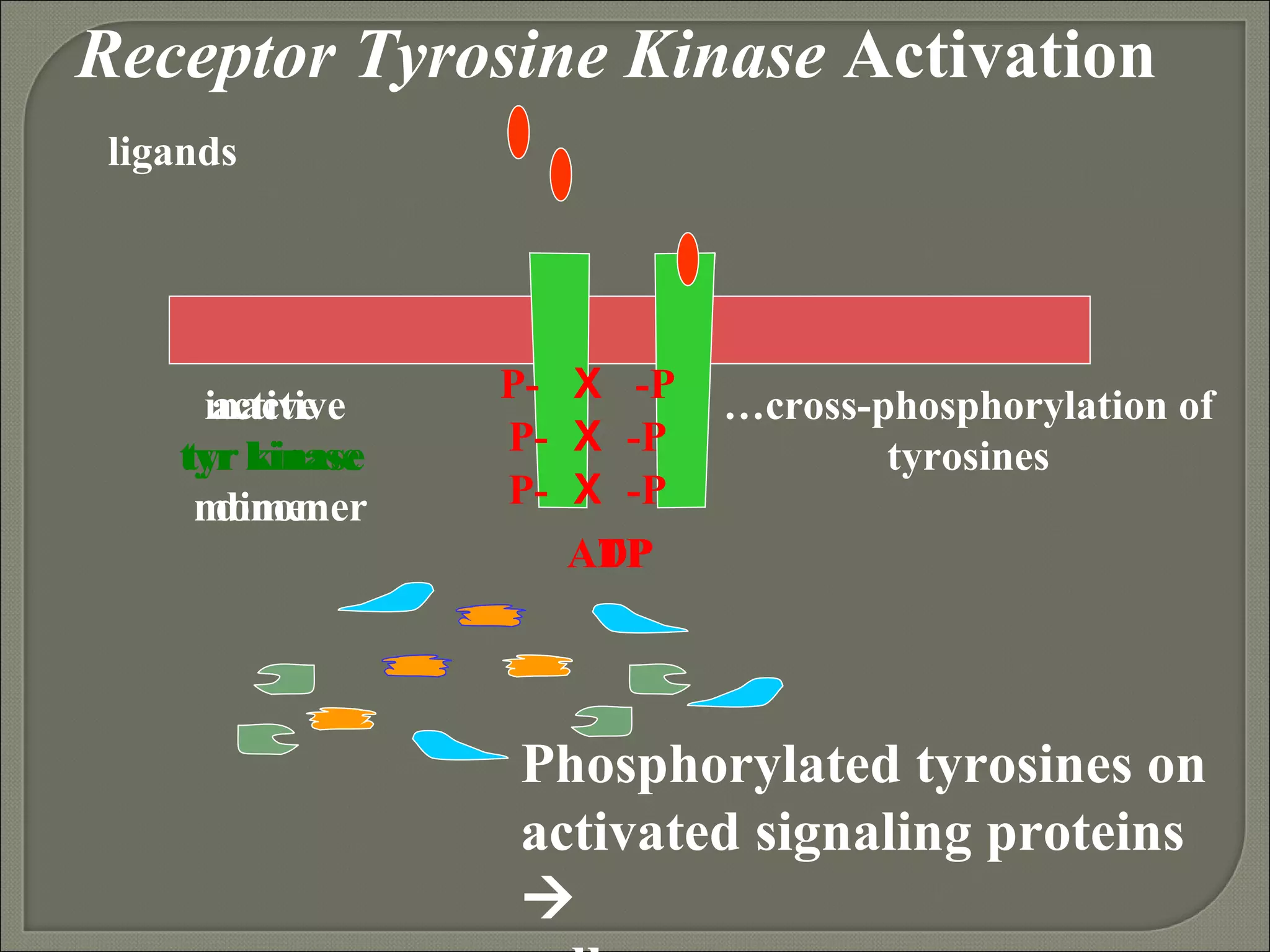
The document discusses receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), a class of cell surface receptors that possess intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity. RTKs are activated through ligand binding and dimerization, which leads to autophosphorylation and downstream signaling. This signaling involves phosphorylation of proteins by RTKs and recruitment of adapter proteins, and results in cellular responses like cell division, differentiation, and motility. Common to all RTKs are an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain, and regulatory domains.