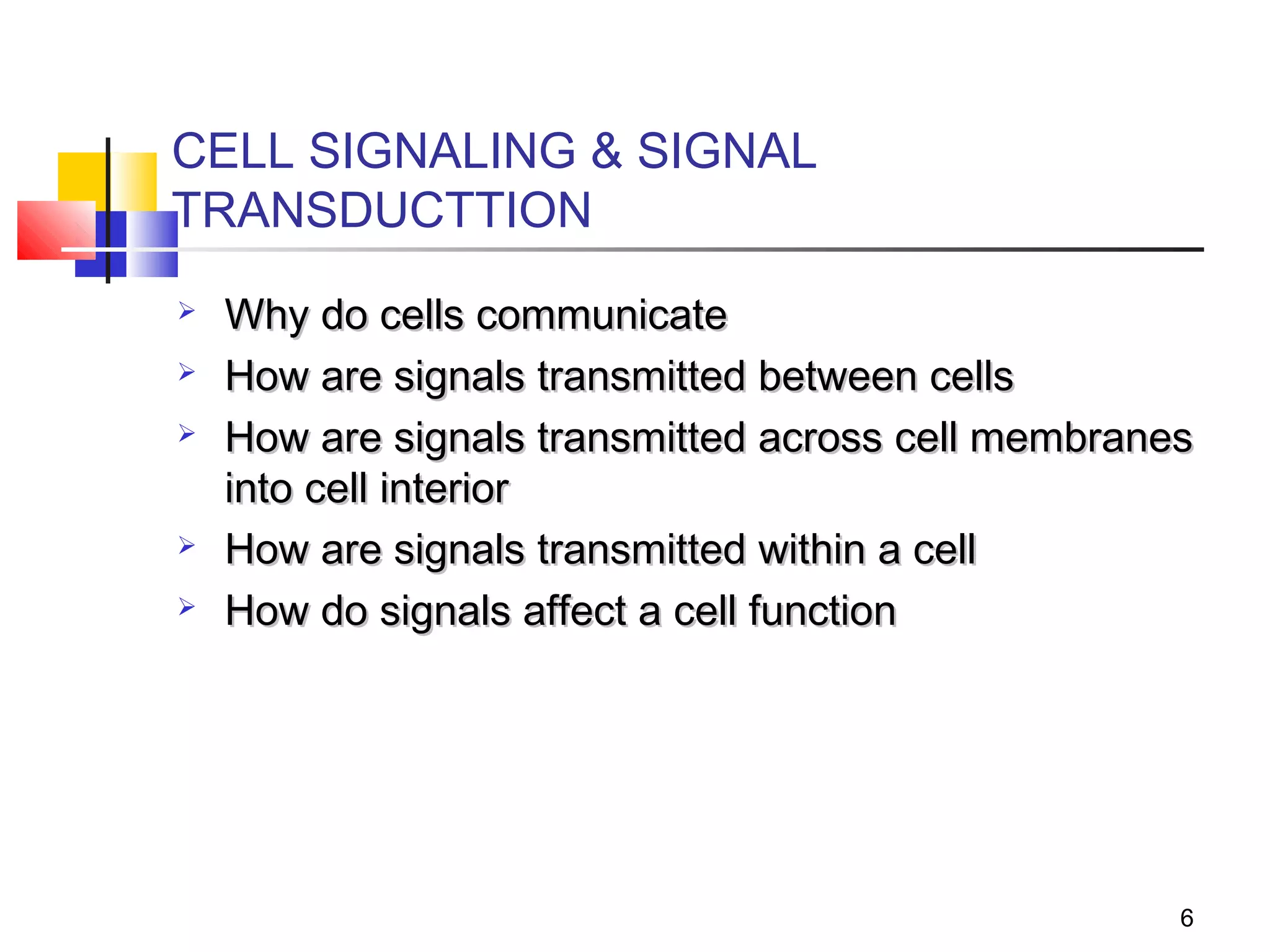
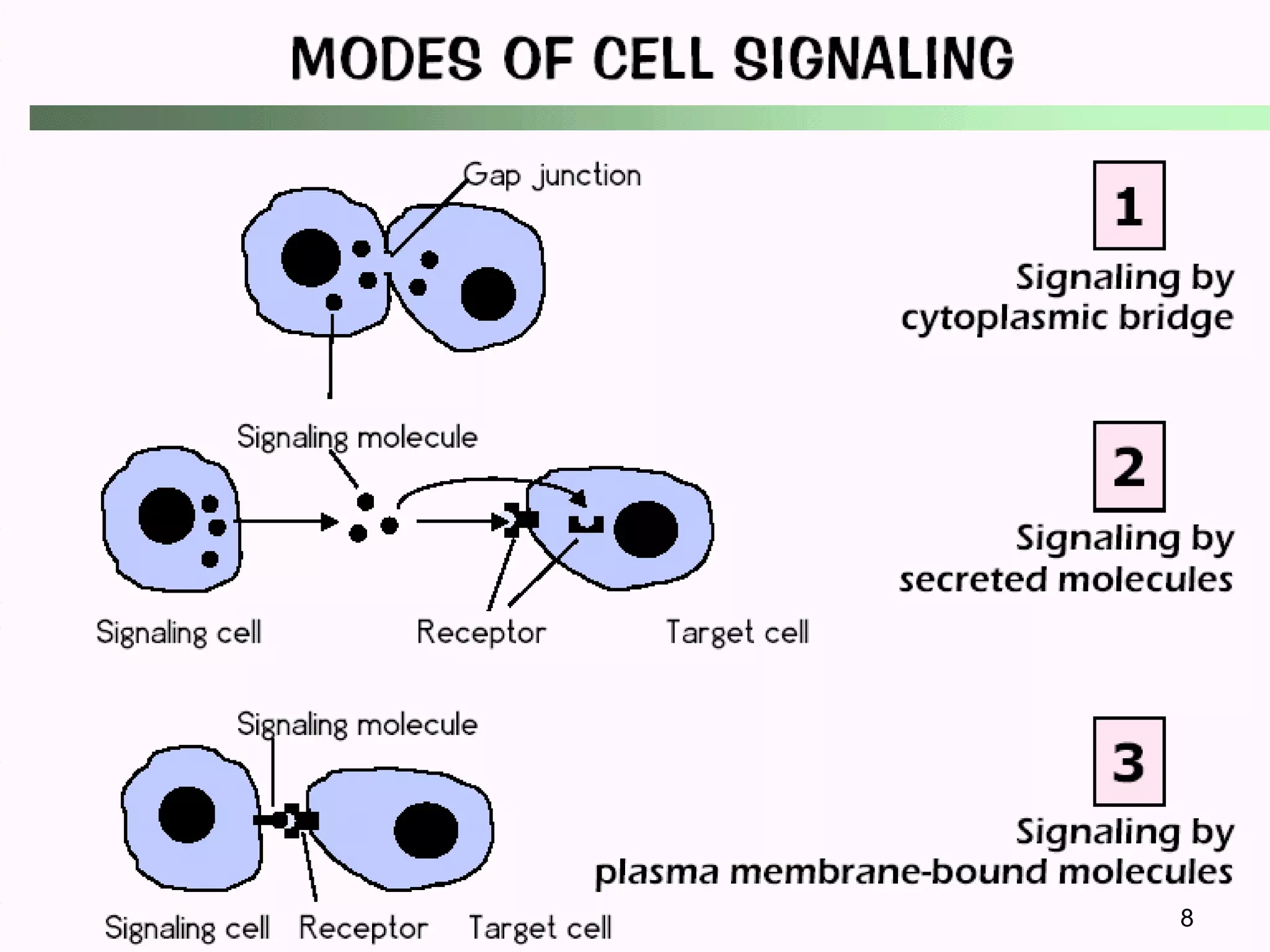
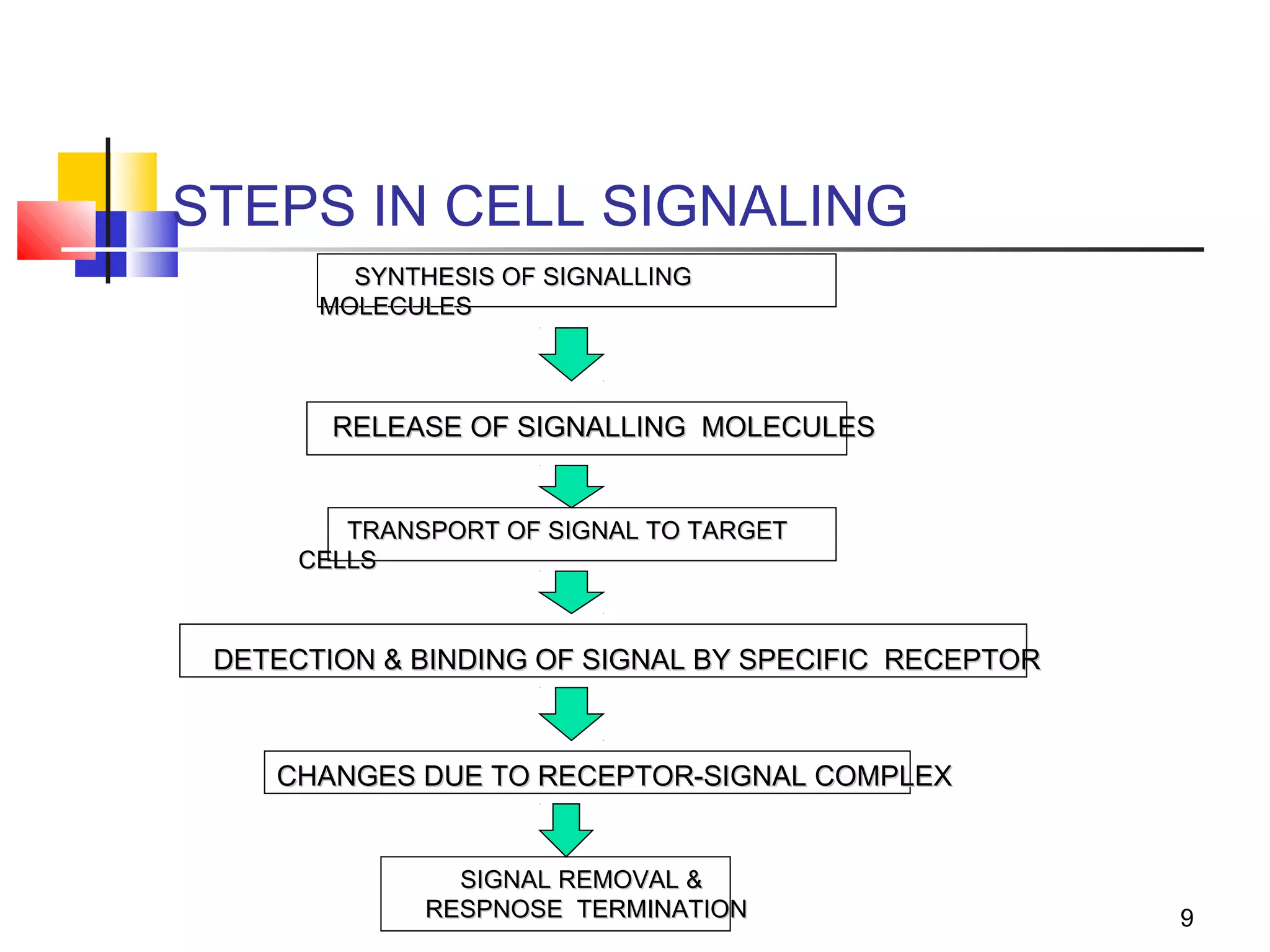
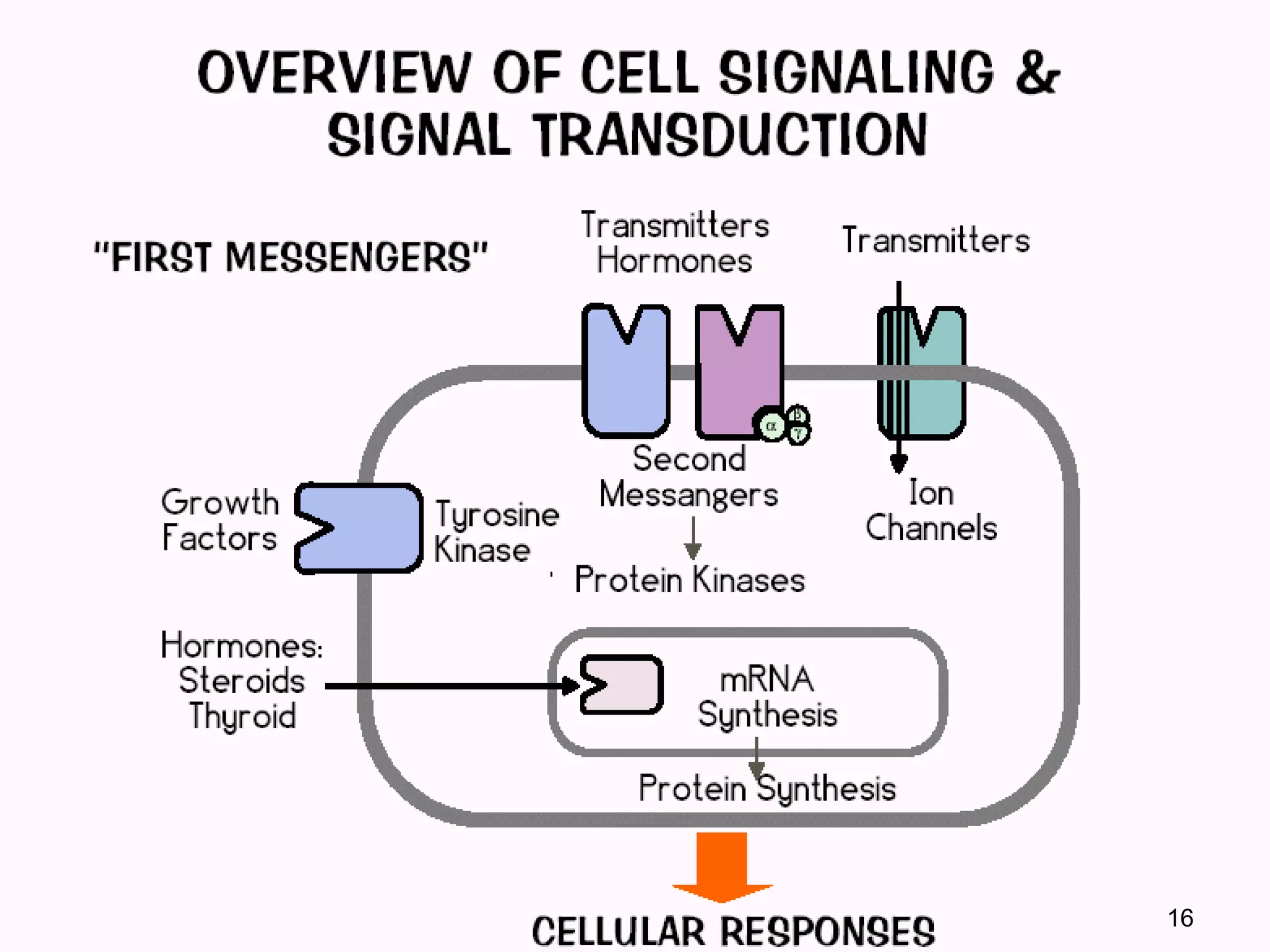
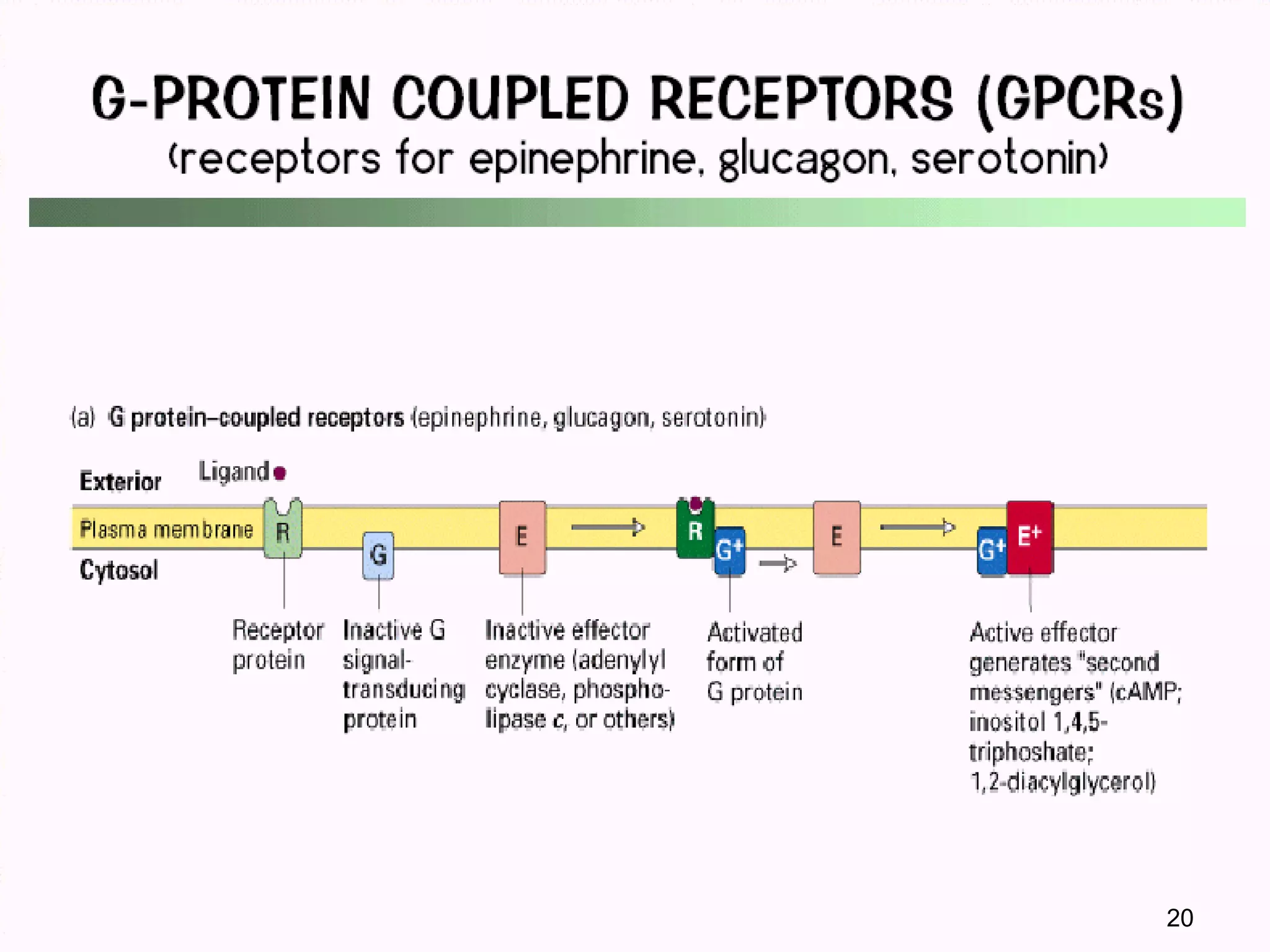
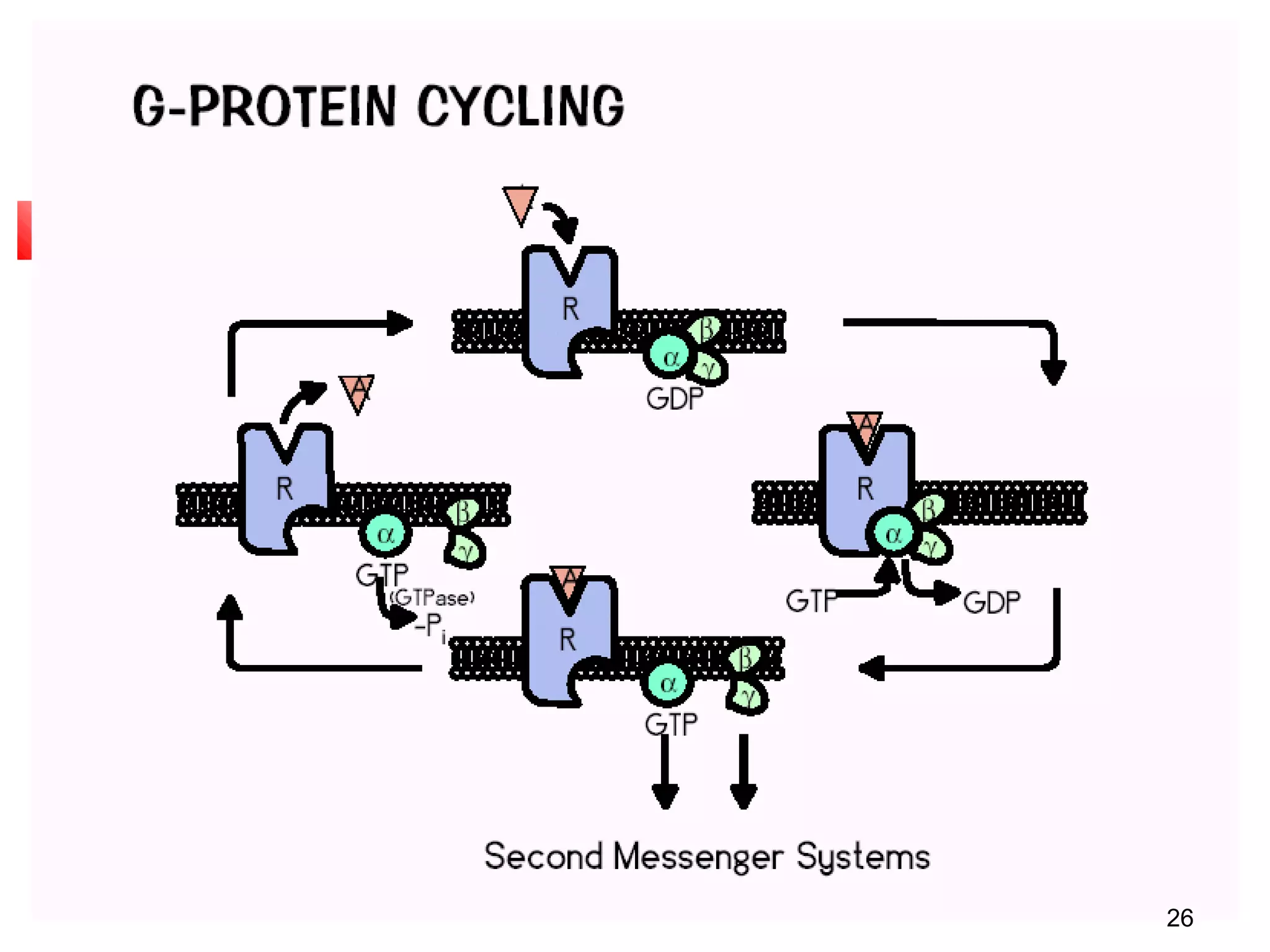
Cells communicate through signaling molecules that are detected by receptors on other cells. Signals are transmitted across the cell membrane by signal transduction pathways and cause changes in cell function. Signals may target nearby (paracrine), distant (endocrine), or adjacent (juxtacrine) cells. Ion channels in the cell membrane are important for signal transduction and are classified by their method of gating, such as ligand-gated channels that open in response to neurotransmitters.