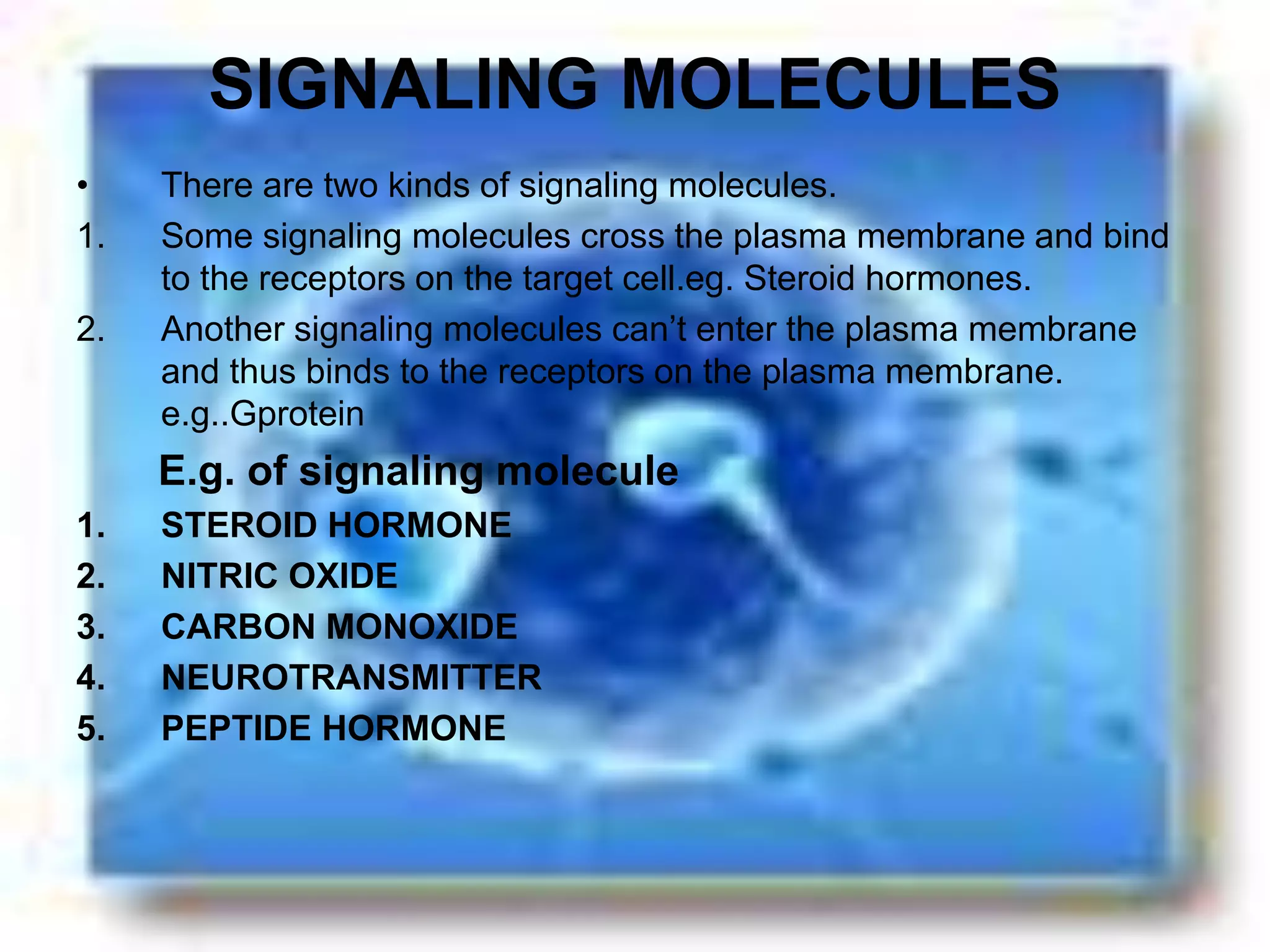
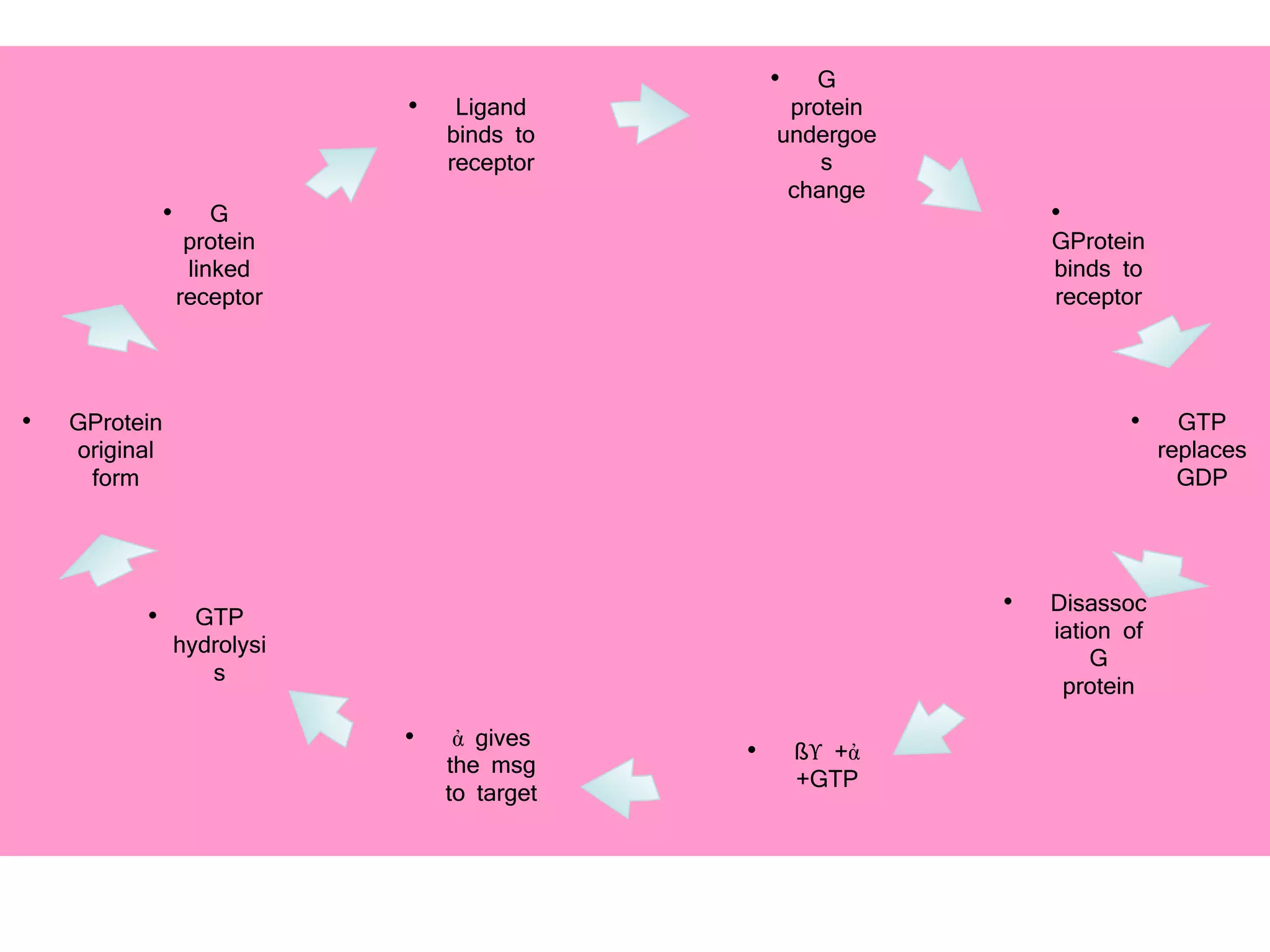
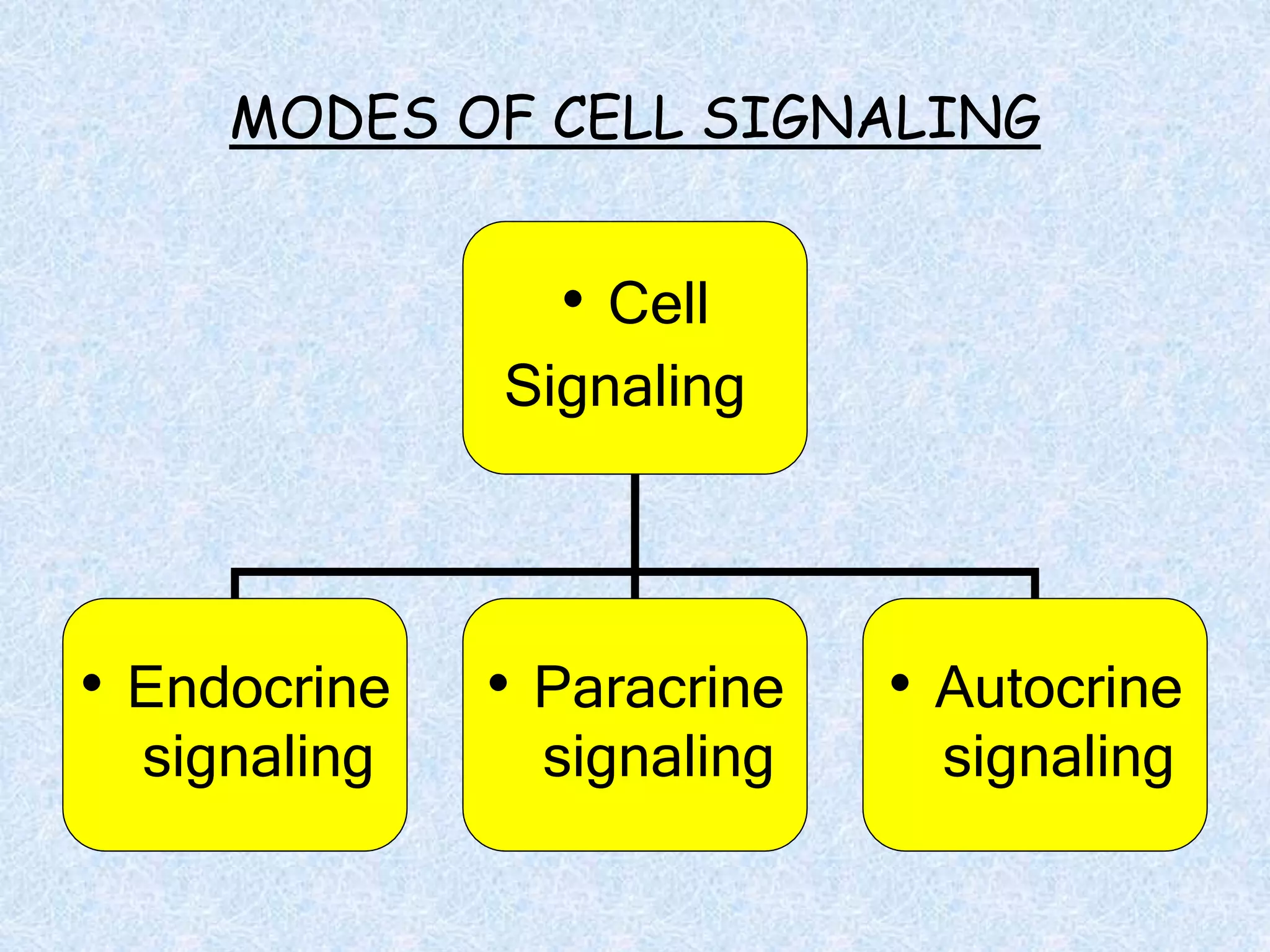
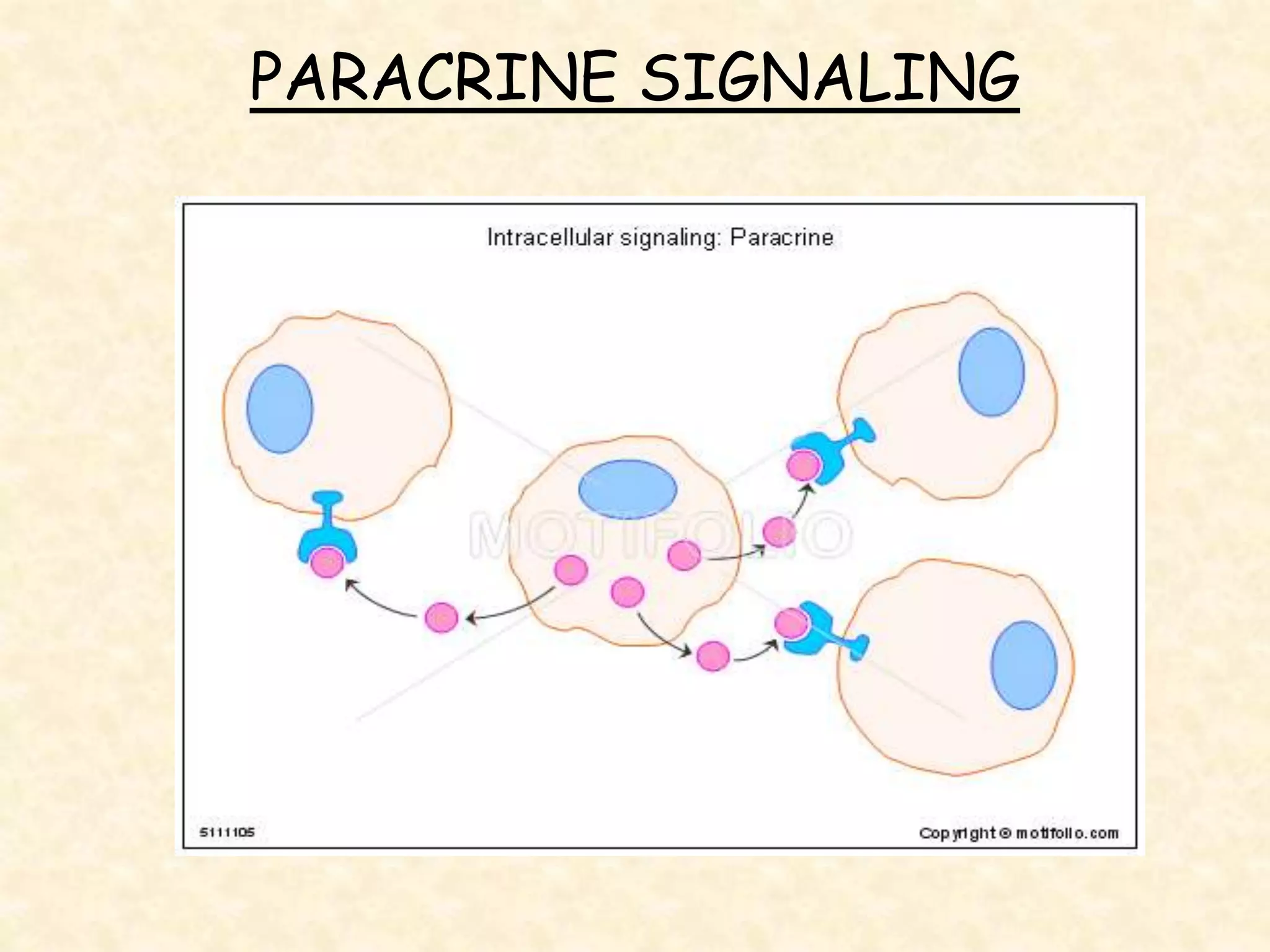
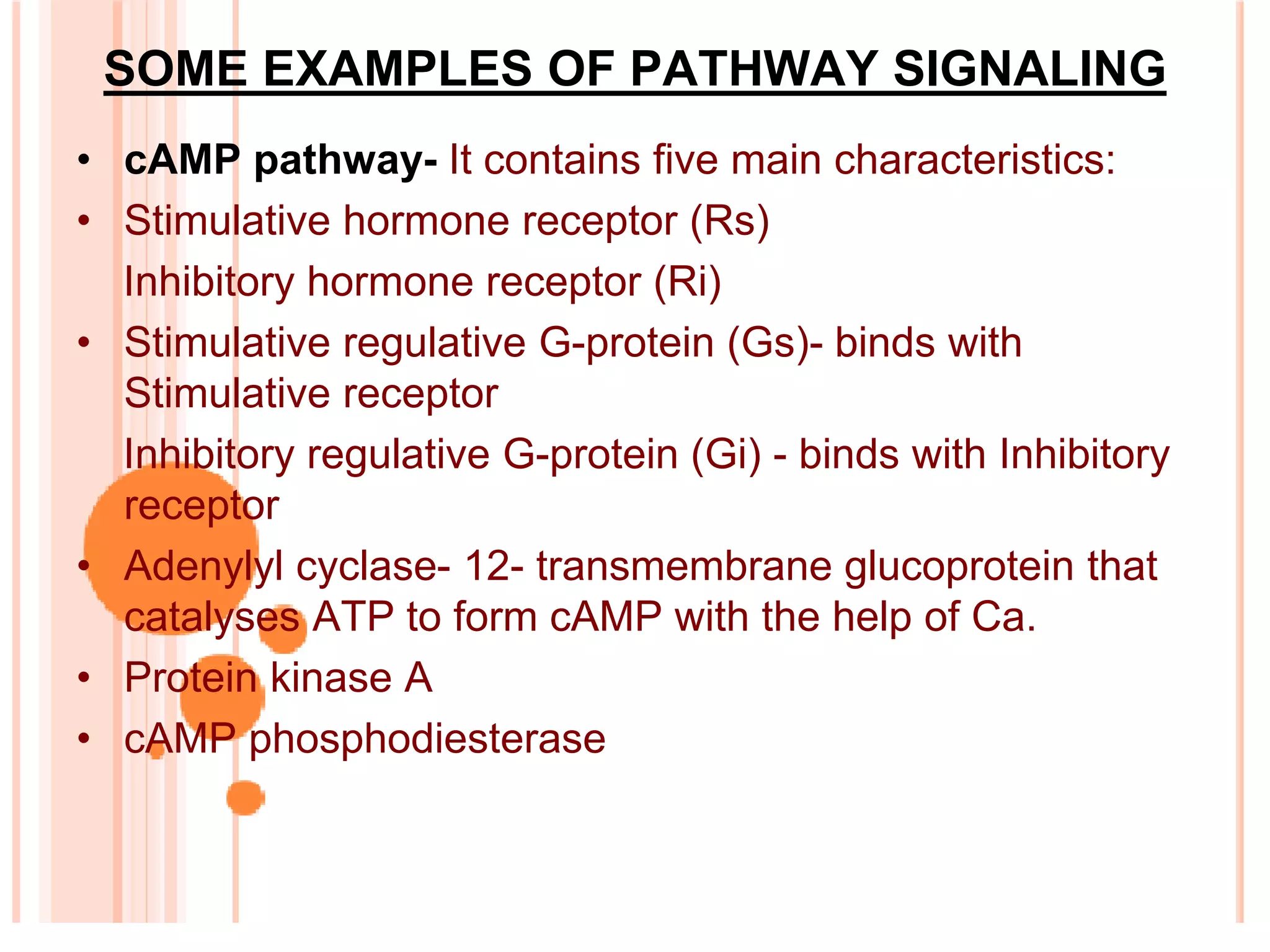
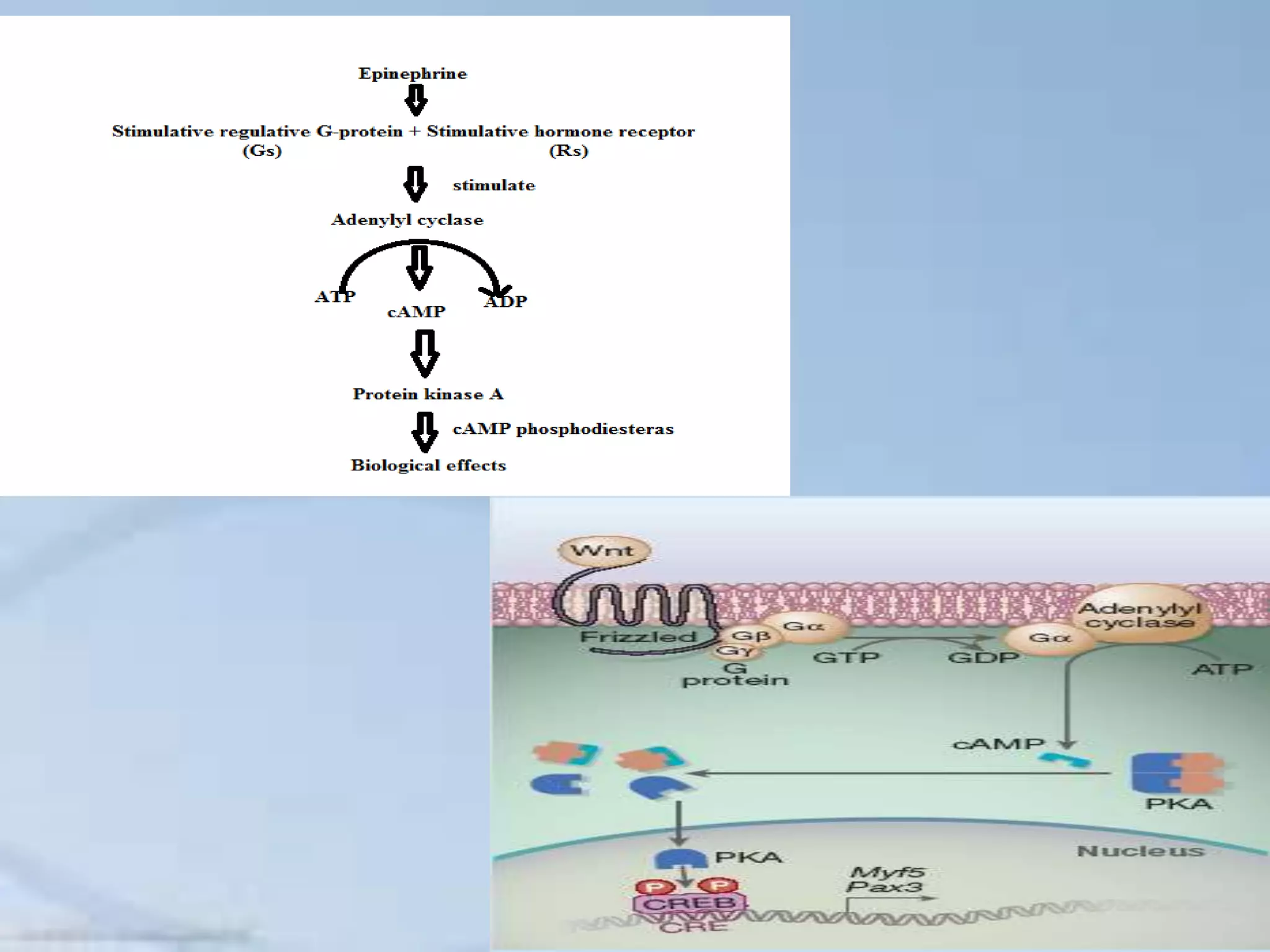
The document provides an overview of signal transduction, describing it as the process where extracellular signaling molecules activate membrane receptors, leading to intracellular responses. It covers fundamental elements including ligands, receptor types, and various signaling pathways such as G-protein coupled receptors and second messengers like calcium ions and nitric oxide. The significance of signal transduction in cellular communication, disease implications, and potential applications in synthetic drug development and artificial tissue is also highlighted.