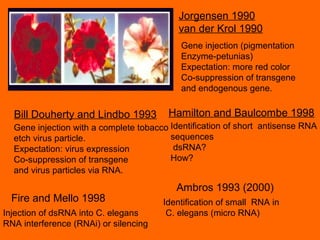
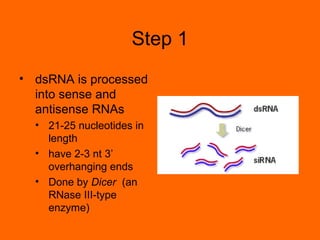
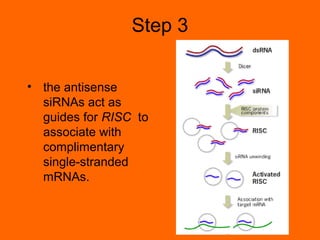
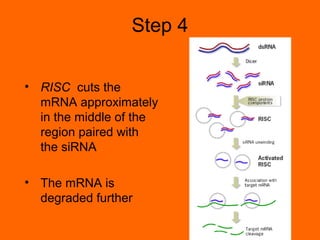
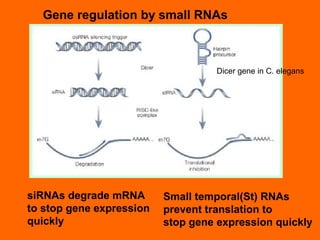
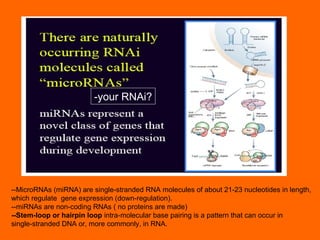
RNA interference is a cellular mechanism that uses small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to degrade unwanted RNAs in the cytoplasm. The mechanism involves introducing double-stranded RNA that is processed by an enzyme into siRNAs. These siRNAs then guide another protein complex to cleave homologous messenger RNA, preventing its translation and silencing gene expression in a potent and specific manner.