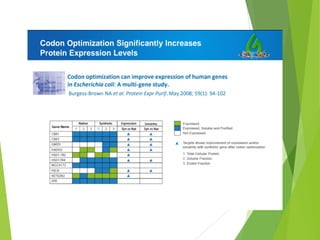
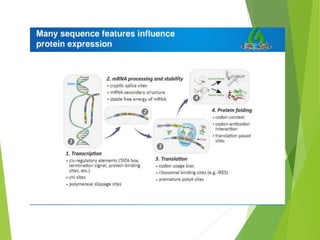
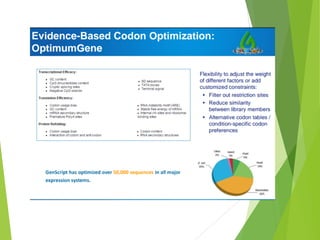
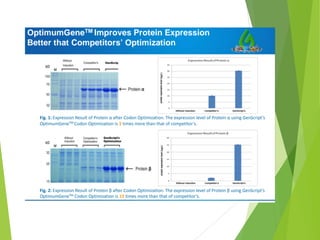
The document discusses vector engineering and codon optimization essential for maximizing the expression of heterologous genes in different host systems. It details the components required in expression vectors for prokaryotic and eukaryotic hosts, emphasizing the importance of promoters and fusion proteins. Additionally, it covers the significance of codon optimization in achieving high-level expression by addressing factors like tRNA abundance and mRNA structure.