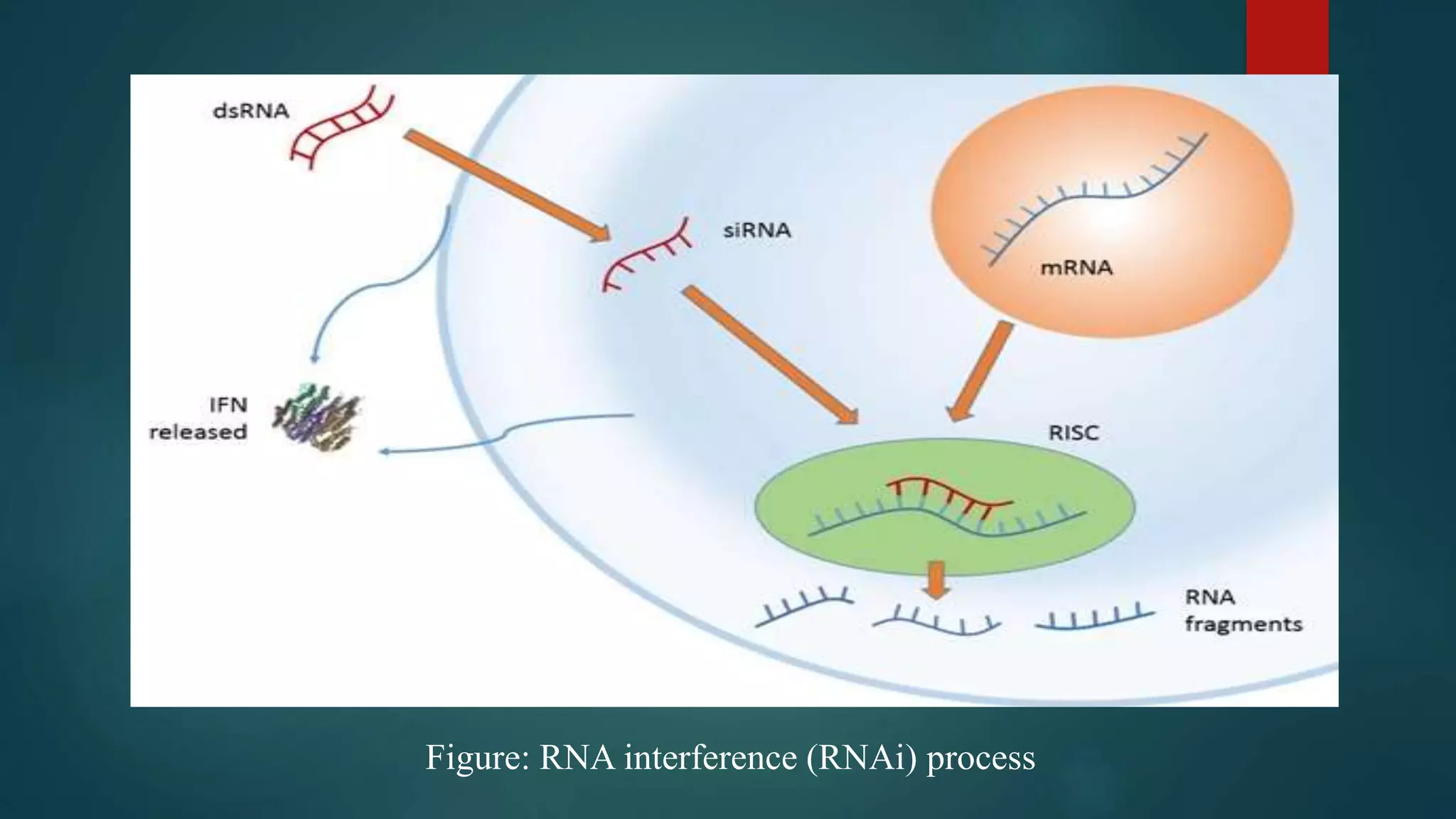
This document provides an overview of gene silencing, including its history, mechanisms, types, and applications. Gene silencing aims to reduce or eliminate protein production from a gene. There are two main types - transcriptional gene silencing modifies the gene, while post-transcriptional gene silencing uses double-stranded RNA to suppress gene expression. Key mechanisms include antisense oligonucleotides, ribozymes, and RNA interference. Gene silencing has advantages like being cost-effective and specific, and applications in treating diseases, developing resistant crops, and analyzing unknown genes.