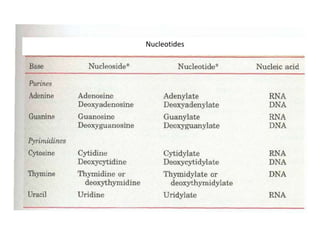
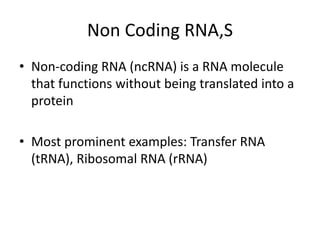
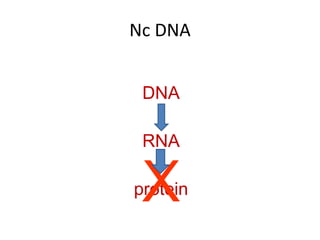
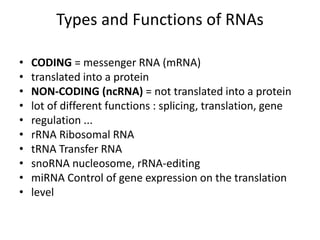
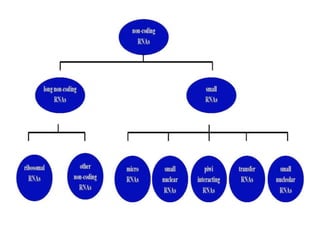
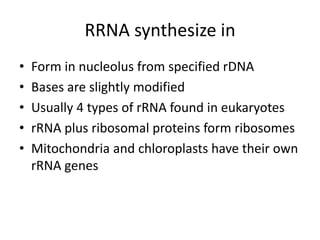
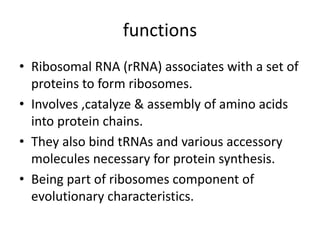
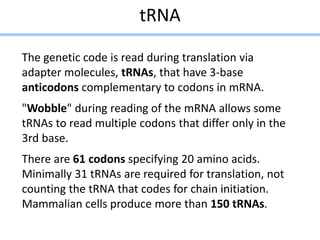
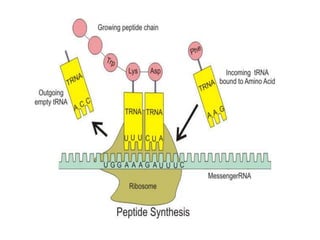
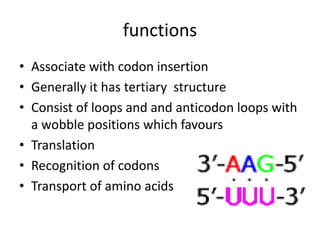
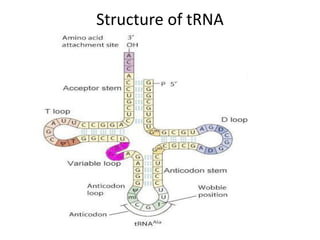
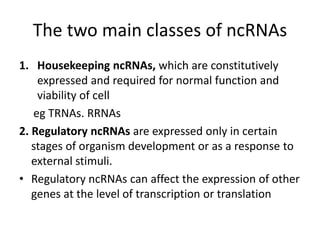
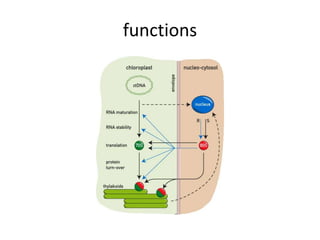
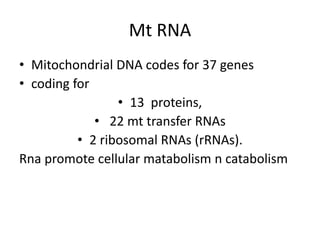
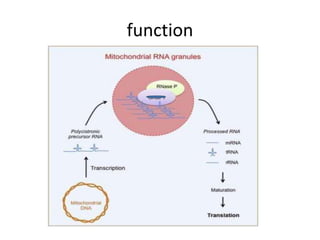
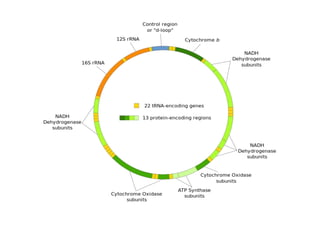
RNA serves various essential functions in biology. There are two main types: coding RNA (mRNA) which is translated into proteins, and non-coding RNA (ncRNA) which has regulatory functions but is not translated. Major ncRNAs include tRNA, which transports amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis, and rRNA, which along with proteins makes up the ribosome and catalyzes peptide bond formation. NcRNAs can regulate genes at the transcription or translation level. In eukaryotes, the majority of genomic transcripts are ncRNAs with diverse roles in splicing, translation, and gene expression control.