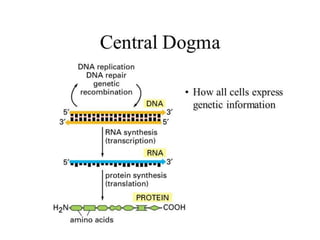
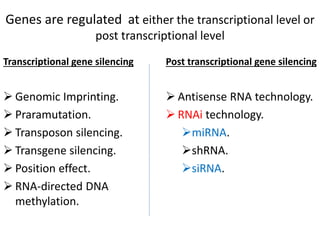
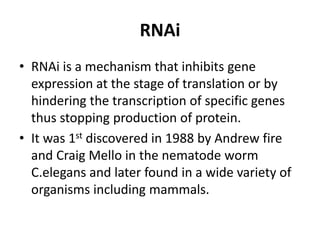
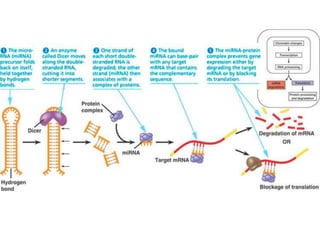
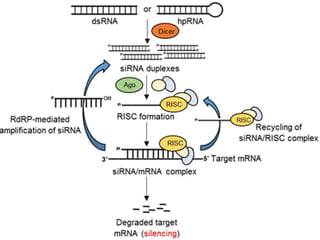
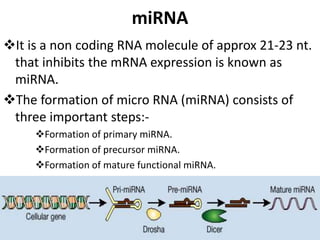
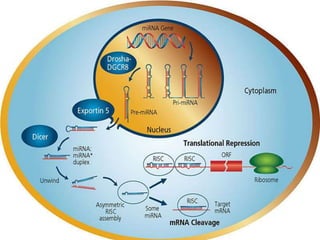
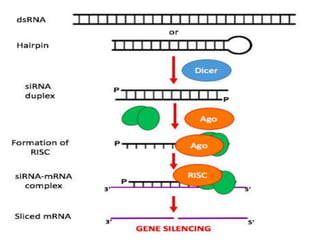
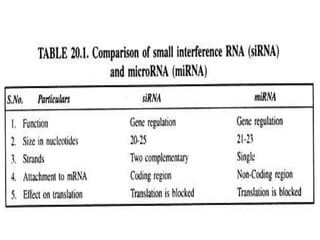
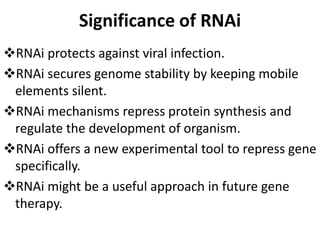
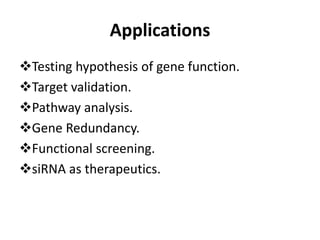
This document provides an overview of siRNA and miRNA. It defines siRNA as short interfering RNA that is 20-25 base pairs long and similar to miRNA. miRNA is defined as a non-coding RNA molecule around 21-23 nucleotides that inhibits mRNA expression. Both siRNA and miRNA operate in the RNA interference pathway by being processed by the enzyme Dicer and interfering with gene expression by degrading complementary mRNA. The document also reviews the mechanisms and significance of RNAi, including its role in protecting against viruses, maintaining genome stability, and offering a new experimental tool to repress genes specifically.