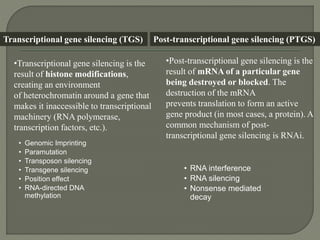
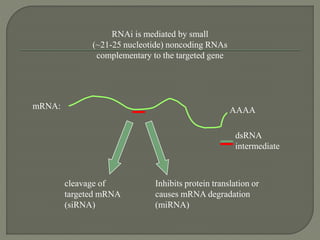
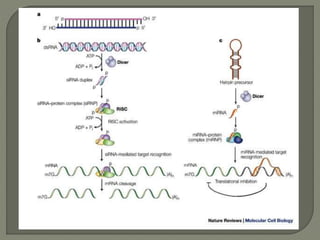
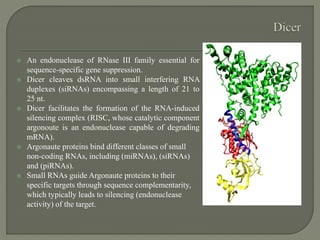
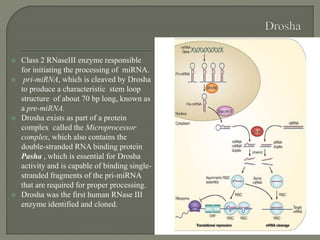
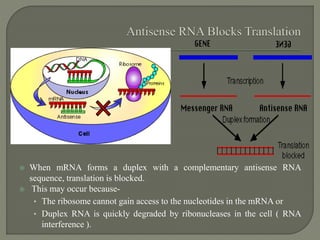
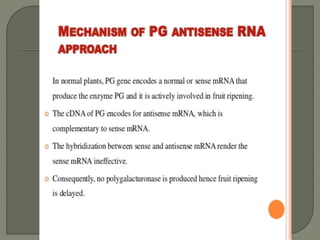
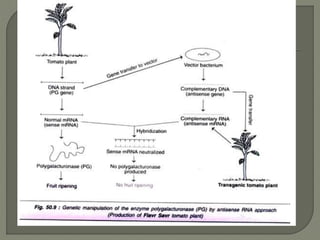
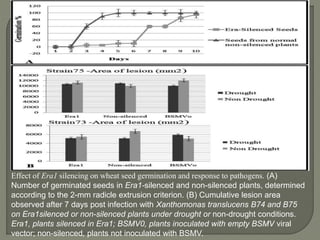
Gene silencing is the process of switching off specific genes through mechanisms like transcriptional gene silencing and post-transcriptional gene silencing, which are regulated by small RNA molecules such as miRNAs and siRNAs. This technology has numerous applications in plant biotechnology, including enhancing nutritional content, extending shelf life, and reducing allergenic properties in crops like tomatoes and apples. RNA interference (RNAi) plays a critical role in these processes, allowing for targeted gene regulation to improve crop traits and mitigate risks associated with food allergies.