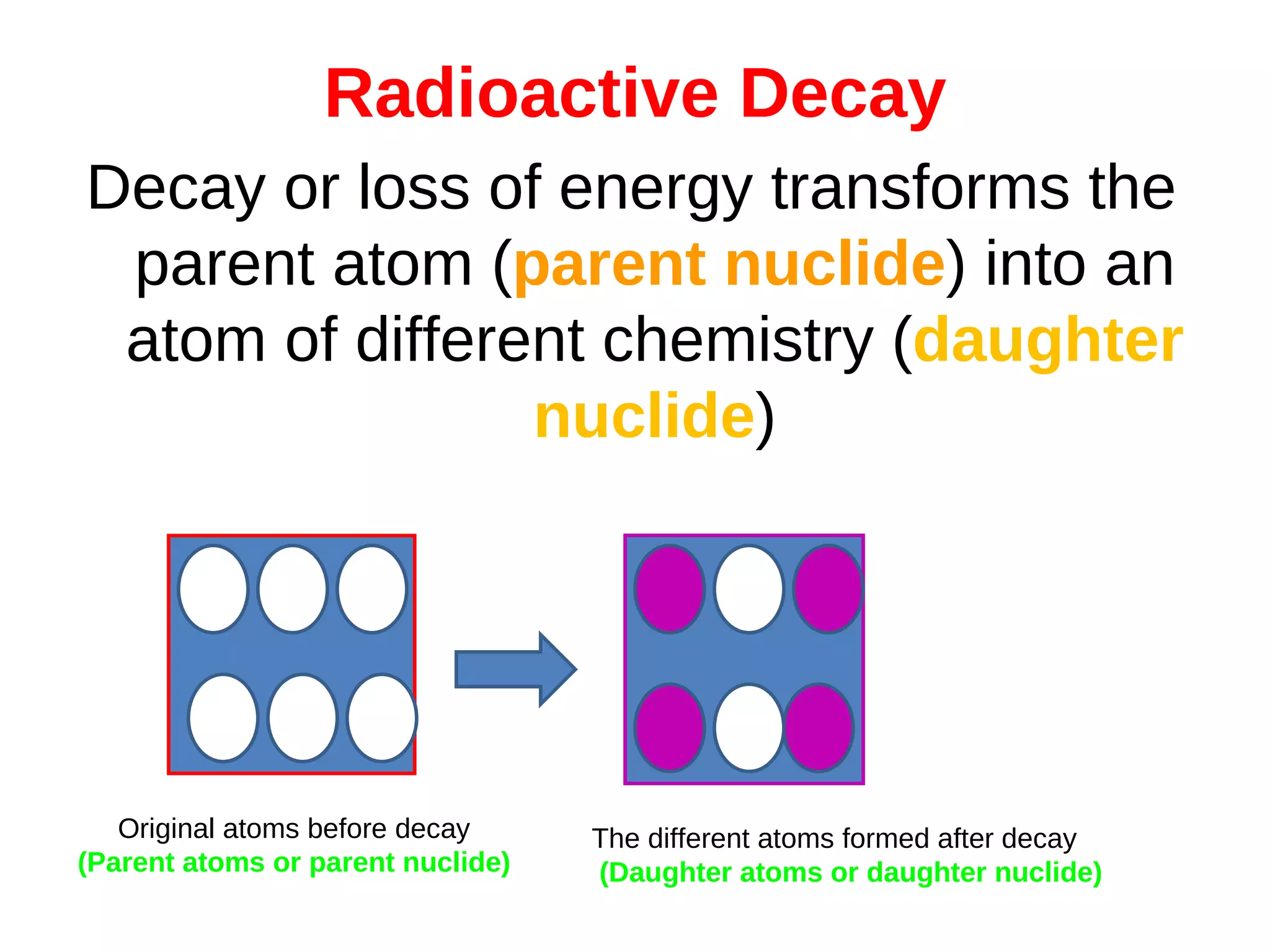
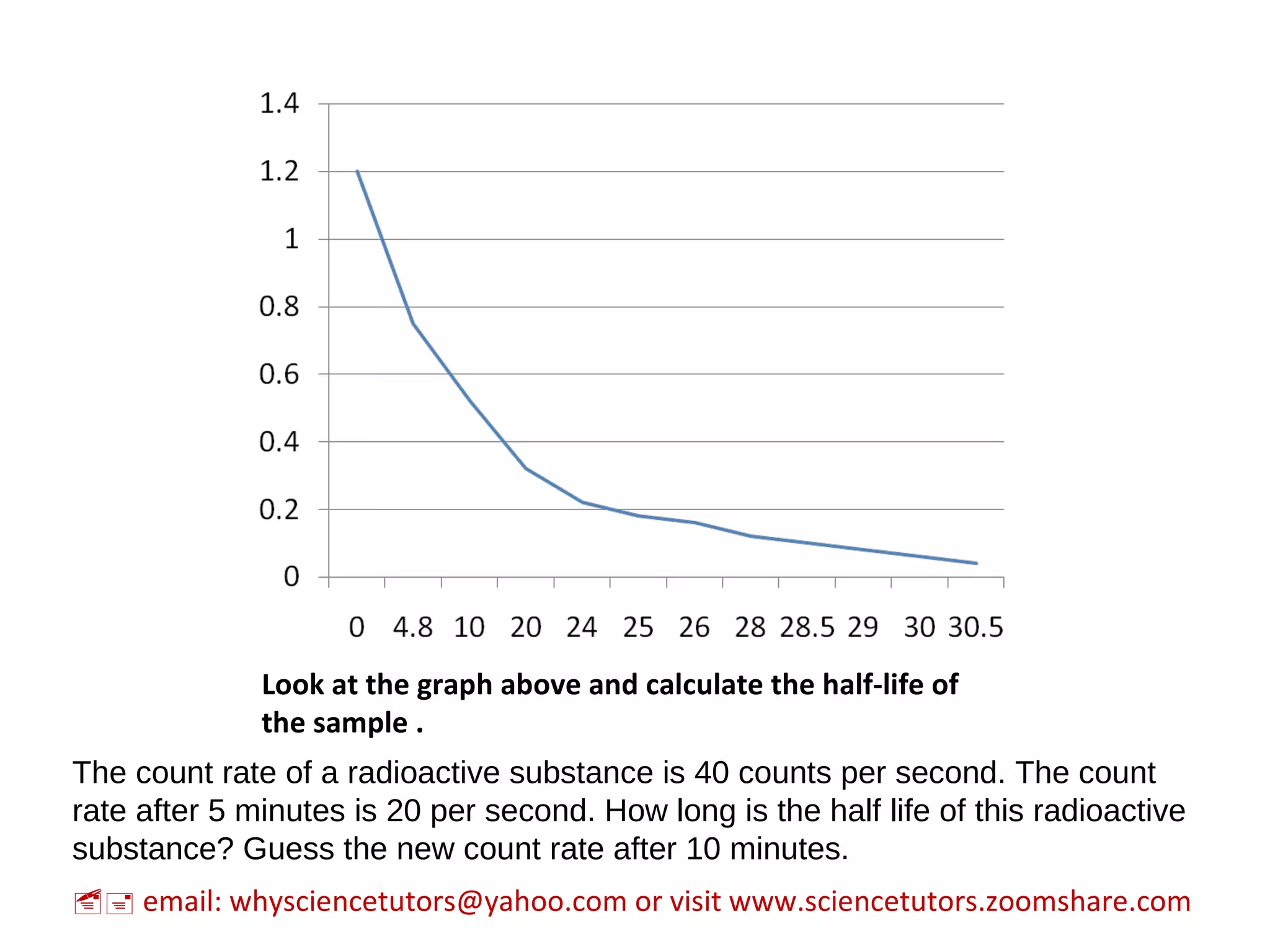
Radioactive decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy through the emission of ionizing particles, transforming into a different atom called a daughter nuclide. The document discusses concepts such as half-life, which measures the time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay, and the varying types of decay, including alpha, beta, and gamma. Additional information includes how to calculate count rates and the unpredictability of the exact moment an atom will decay.