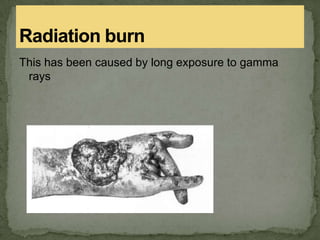
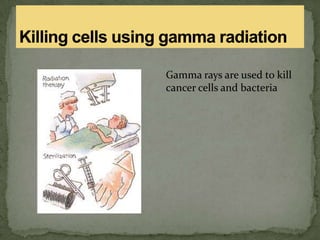
This document discusses radioactive isotopes and the different types of radiation they emit when decaying. It explains that unstable atomic nuclei will emit alpha, beta, or gamma radiation to become stable. Alpha radiation is emitted as a helium nucleus, beta as a high-speed electron, and gamma as a high-energy electromagnetic wave. It describes the properties and interactions of each type of radiation, and how they can damage cells and potentially cause cancer if absorbed in the body. Examples are given of uses of radioisotopes and radiation such as electricity generation, sterilization, and food irradiation.