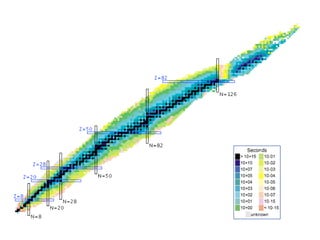
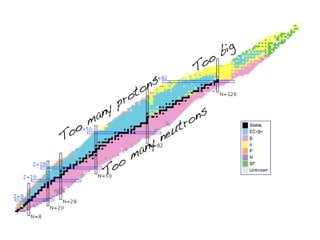
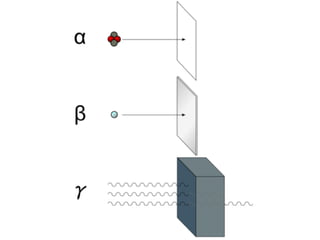
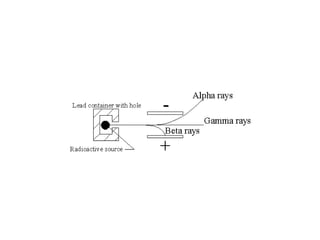
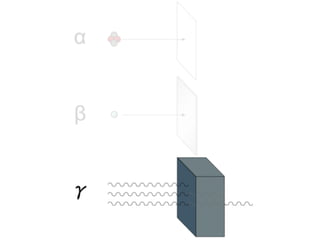
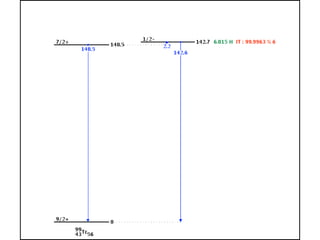
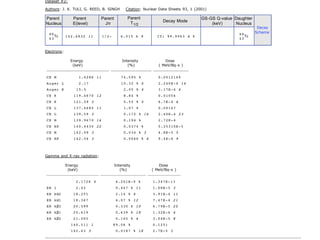
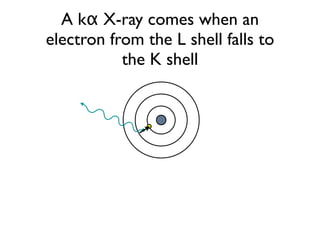
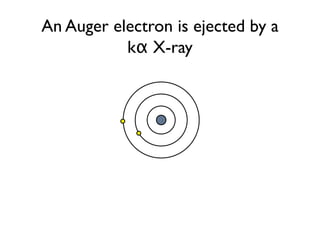
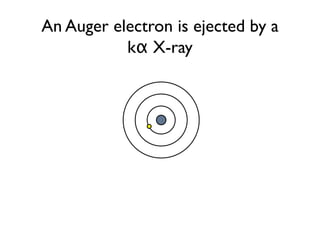
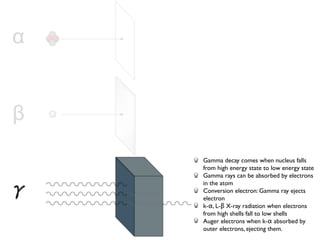
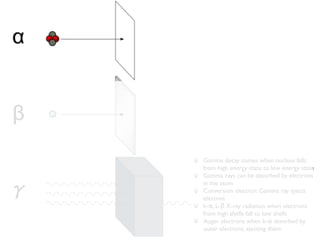
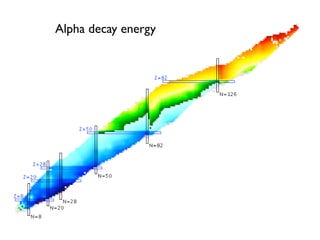
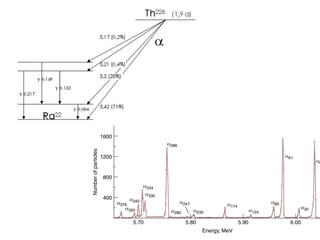
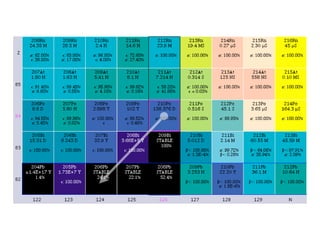
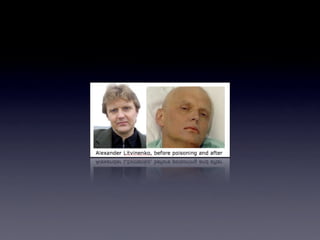
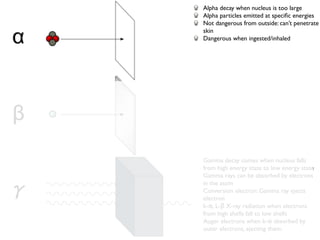
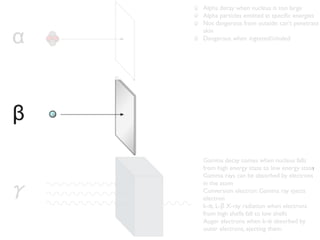
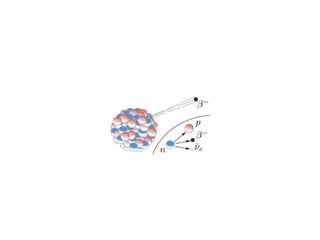
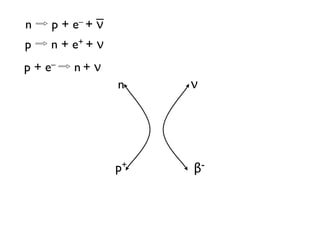
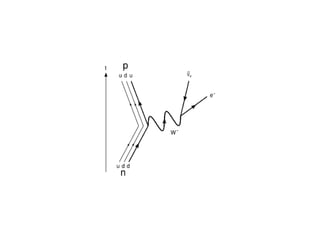
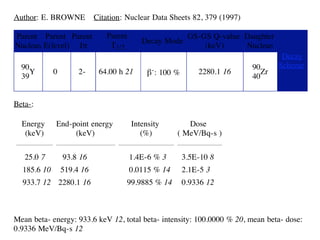
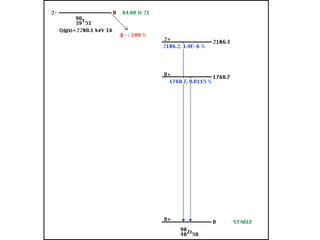
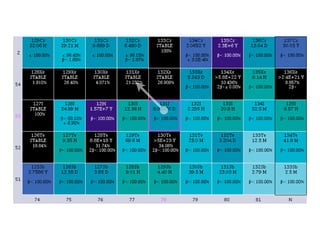
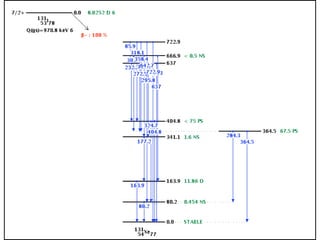
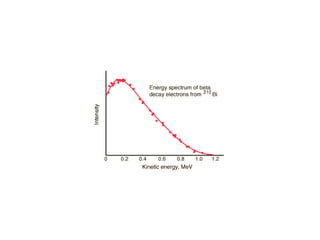
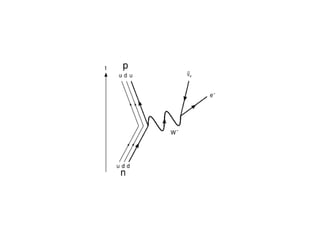
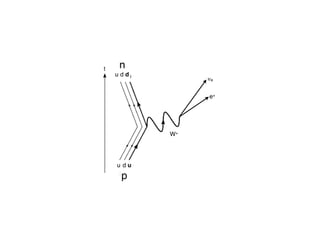
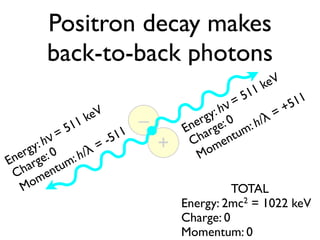
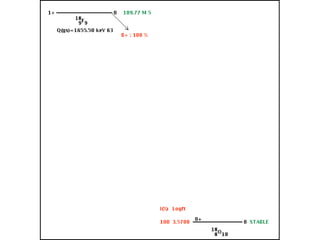
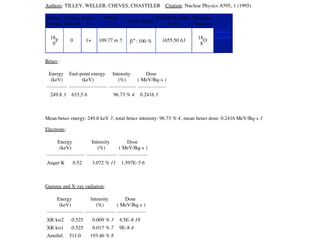
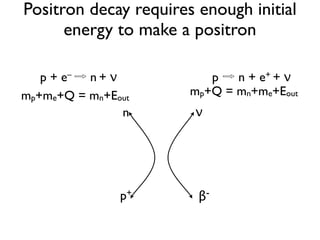
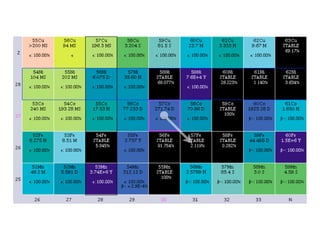
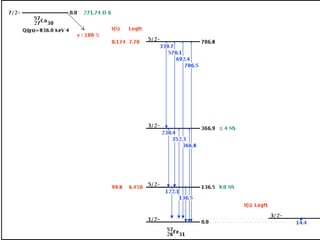
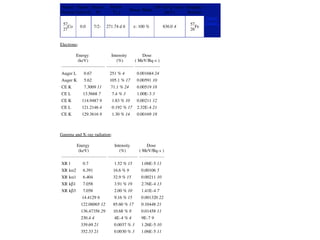
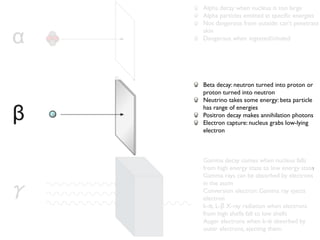
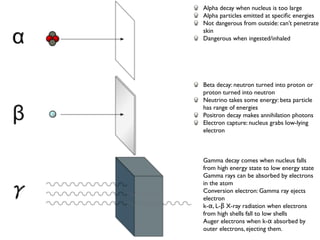
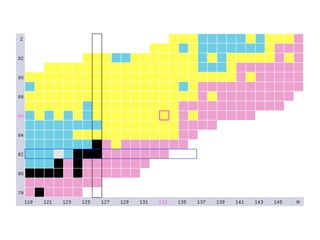
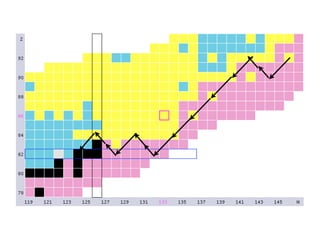
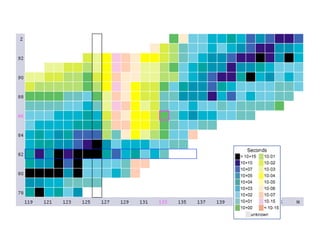
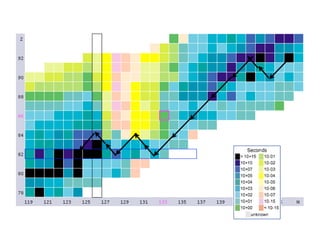
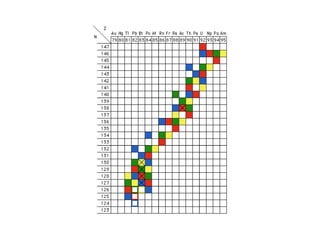
The document provides detailed information on various types of radioactive decay, including alpha, beta, and gamma decay processes, alongside relevant datasets with energy levels, decay modes, and half-lives. It highlights the interactions of emitted particles such as conversion electrons and X-rays, emphasizing their significance and energy characteristics in nuclear reactions. Additionally, it discusses the implications of these decay processes on safety and radiation exposure scenarios.