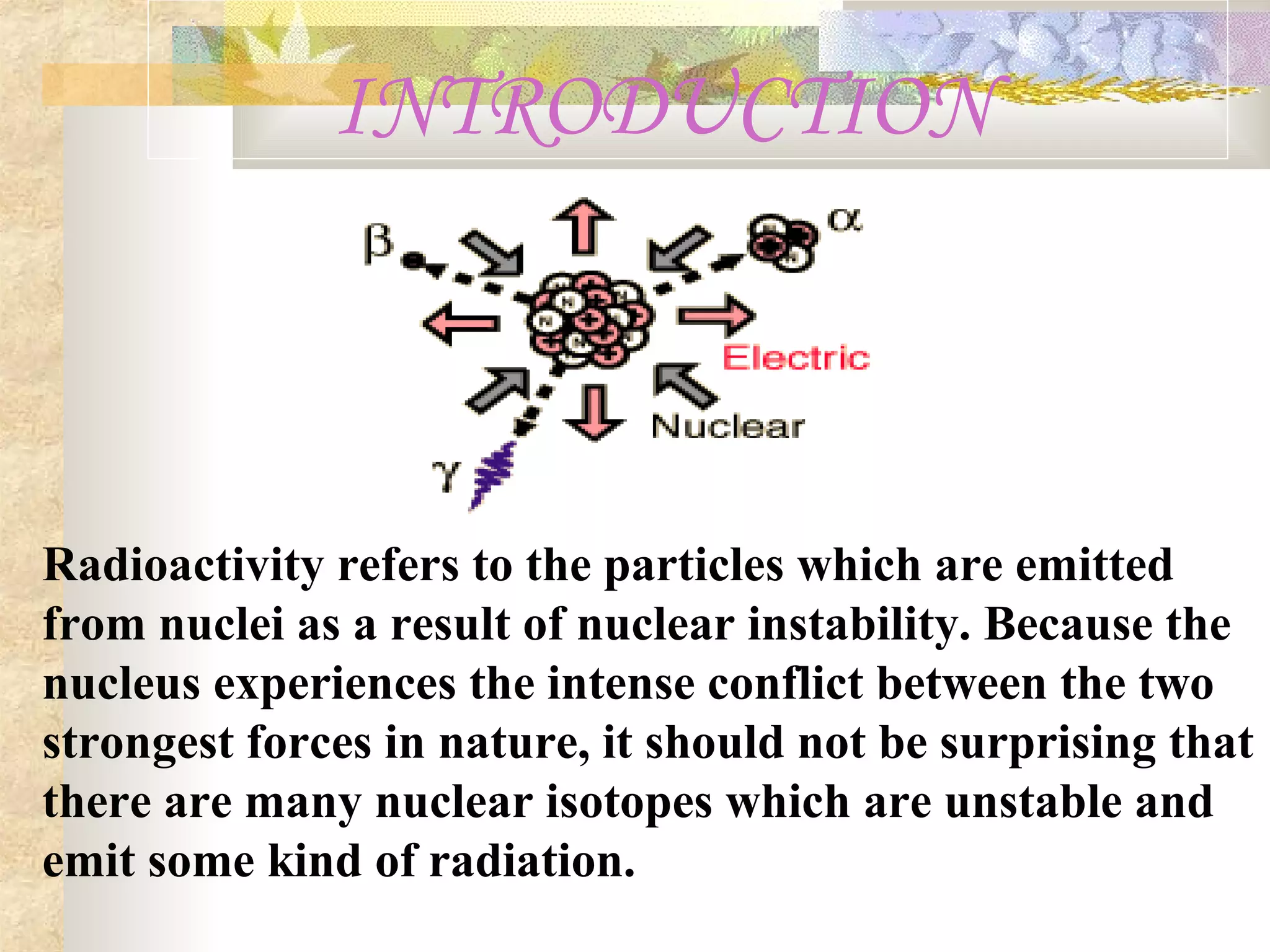
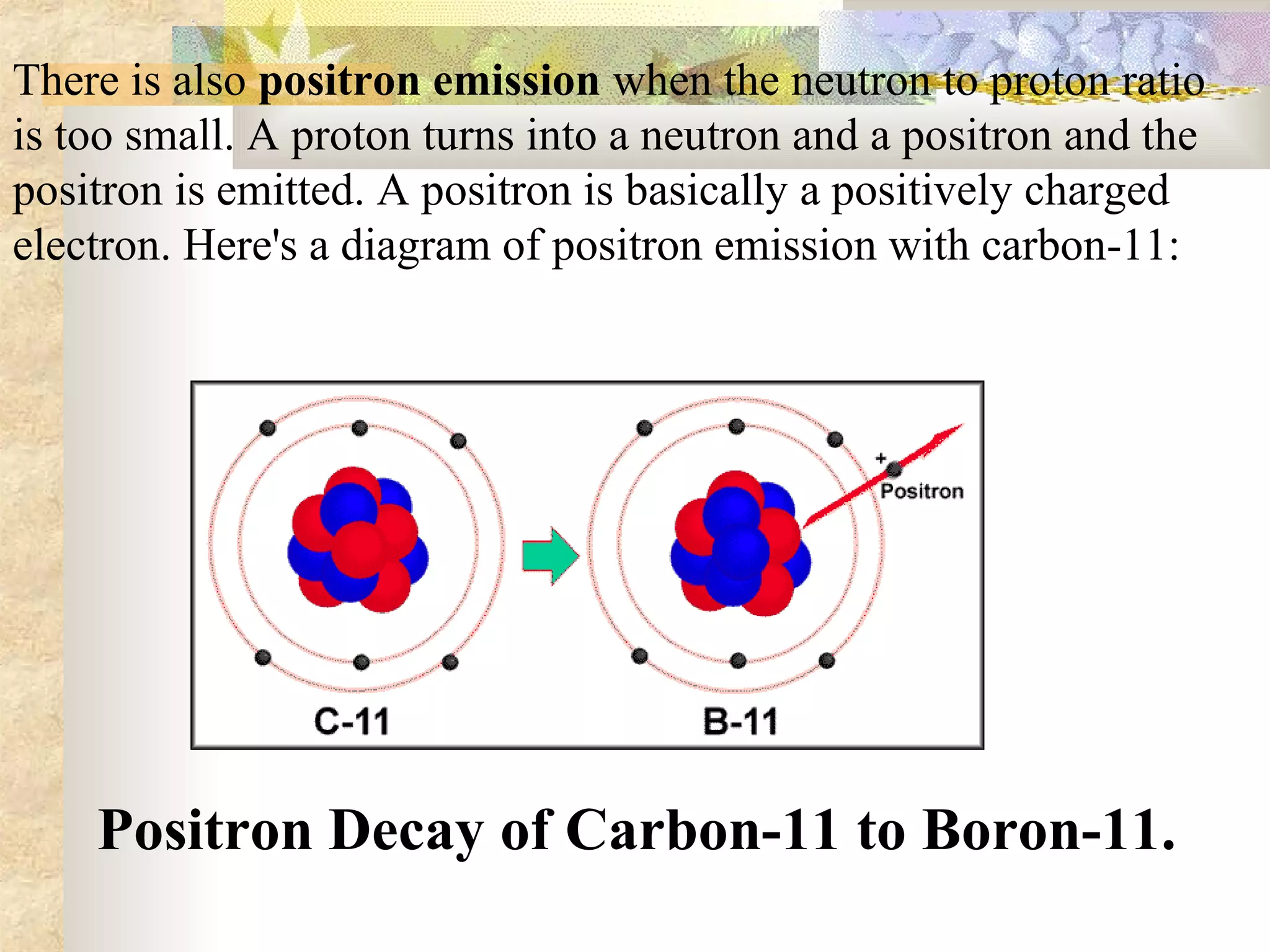
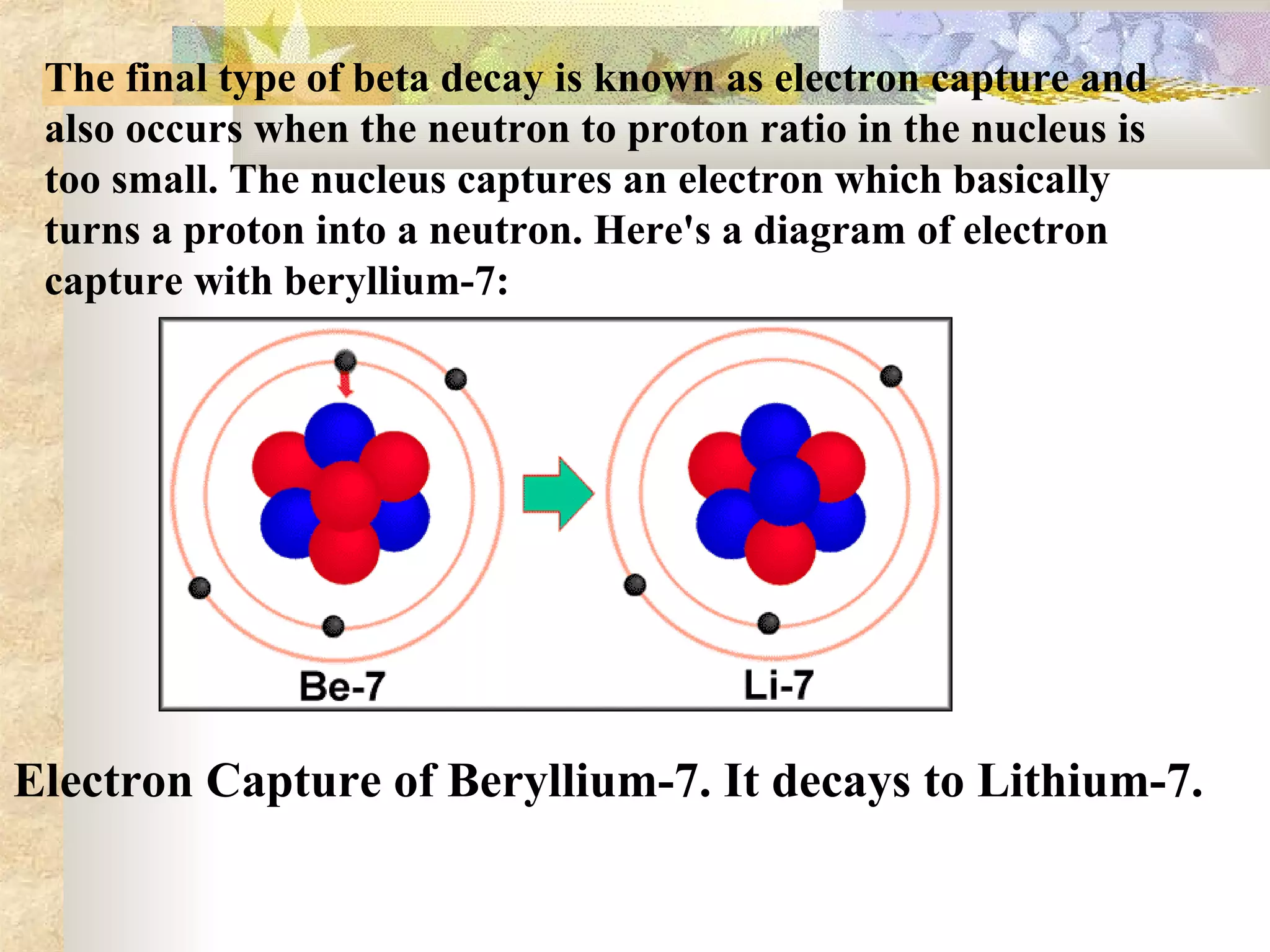
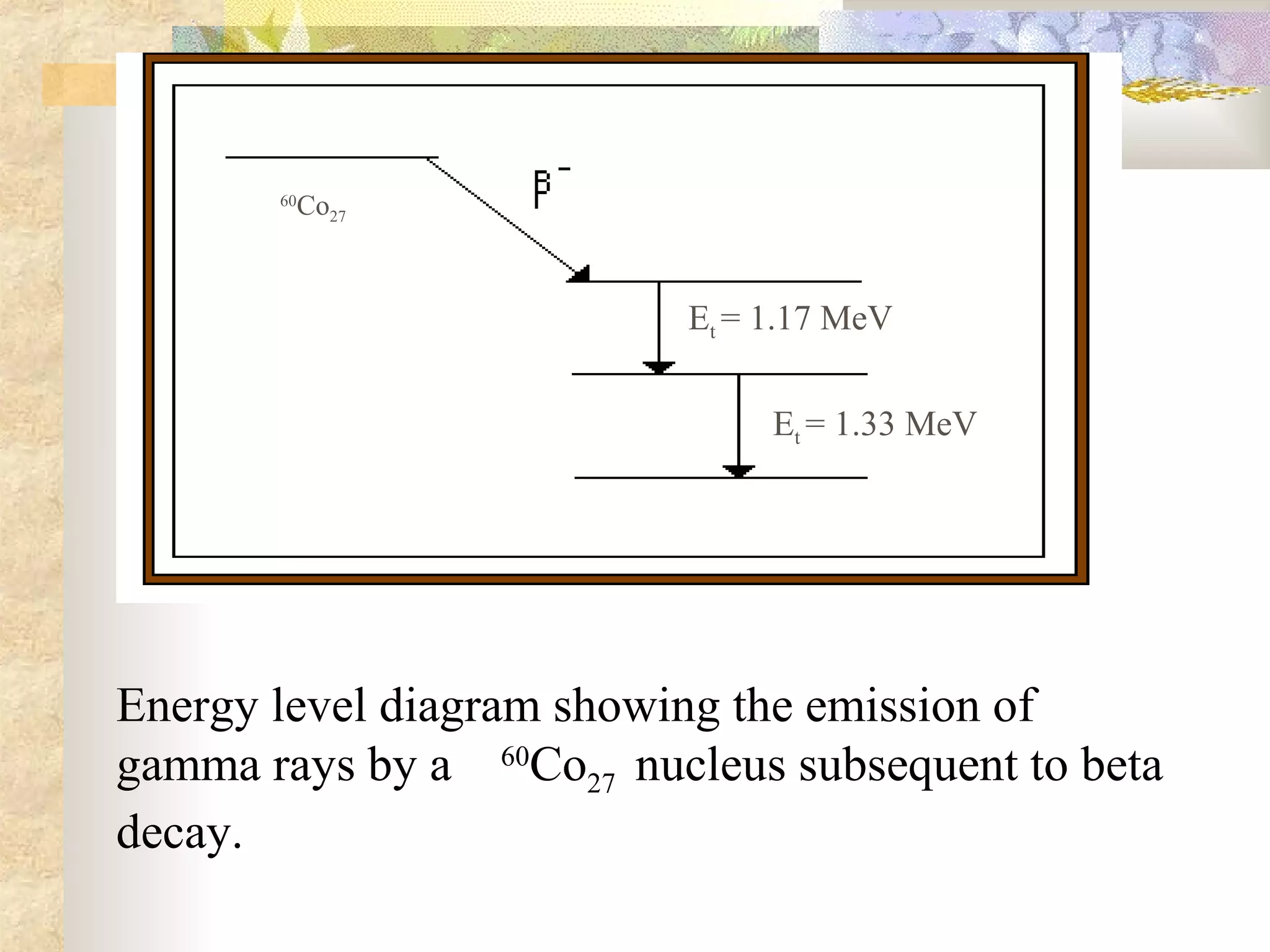
This document summarizes the key aspects of radioactivity covered in a physics project. It discusses the three main types of radioactive decay - alpha, beta, and gamma decay. Alpha decay occurs when a nucleus has too many protons, causing it to emit a helium nucleus. Beta decay involves either a neutron converting to a proton or vice versa, emitting an electron or positron. Gamma decay occurs when a nucleus shifts between energy states by emitting a photon, without changing its composition. The rate of radioactive decay is characterized by the half-life, the time for half of a radioactive sample to decay.