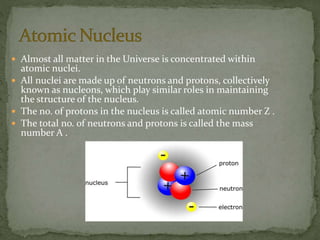
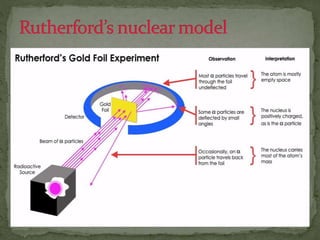
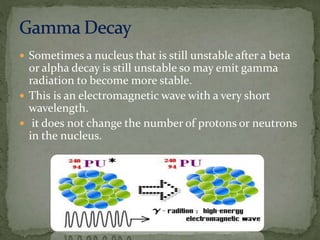
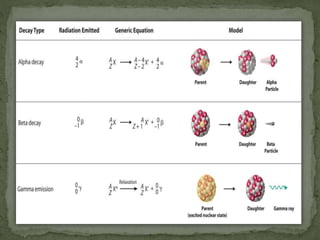
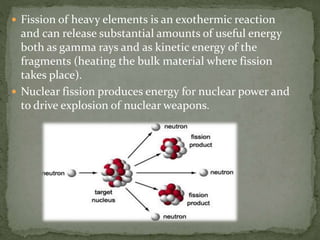
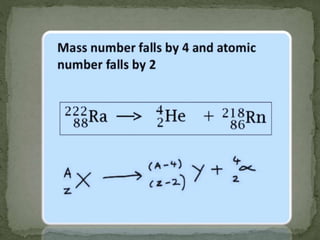Almost all matter in the universe is concentrated within atomic nuclei composed of neutrons and protons. Radioactive decay occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays. The number of protons defines the element, while the total number of protons and neutrons is the mass number. Radioactive emissions are random, but the average rate of decay follows statistical laws defined by half-life.