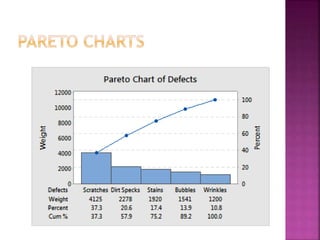
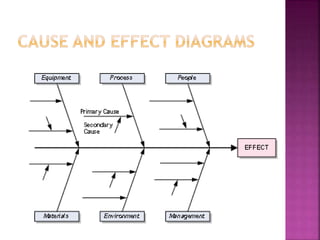
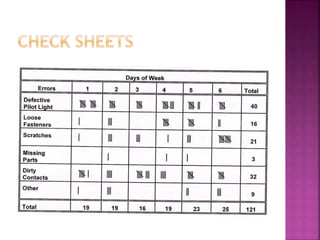
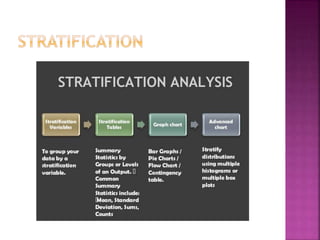
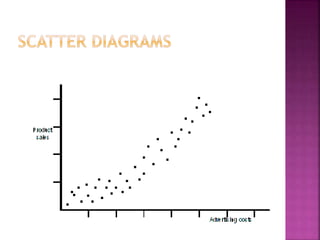
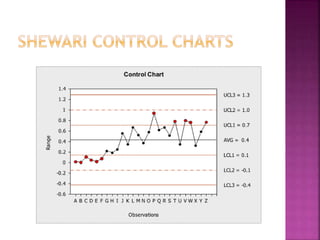
This document discusses quality control and quality assurance. It defines quality as prescribed characteristics present in products and outlines quality control as the process of verifying and correcting quality when deviations are found. Quality control aims to assess quality standards at different production stages, recommend corrective actions, and suggest quality improvements without raising costs. It emphasizes quality in design, processes, personnel selection and training. Total quality control refers to a total commitment to quality in all areas. Quality circles involve employees identifying and solving quality problems. Quality is built in from the start and requires top management commitment and continuous training. Statistical methods like control charts are applied. Quality depends on design, procurement, production, inspection and packaging/handling.