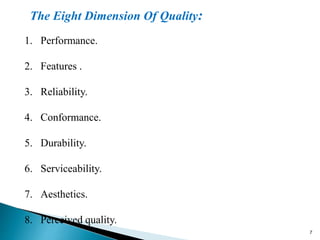
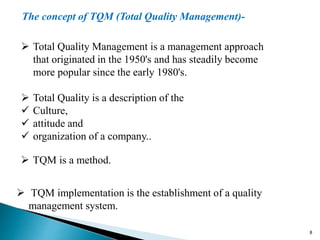
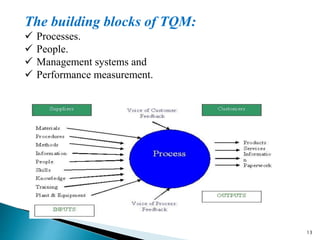
This document provides an overview of total quality management (TQM). It defines TQM as managing an organization holistically to achieve excellence. The objectives of TQM are to provide high-quality products and services to customers, improve processes, prevent defects, help teams make better decisions, and enable continuous improvement. TQM requires a strategic commitment from top management, employee involvement, quality planning, and measuring performance. Barriers to successful TQM implementation include lack of understanding, weak management support, poor communication, and limited resources. Benefits include strengthened competitiveness, higher productivity, reduced costs, improved customer satisfaction and loyalty, and increased profitability.