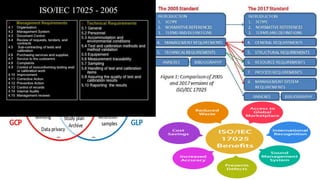
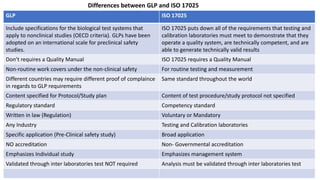
The document provides information about the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and two of its most widely implemented standards: ISO 9001 and ISO 17025. ISO is the world's largest developer of voluntary international standards, with over 20,000 standards covering almost all industries. ISO 9001 helps organizations implement quality management systems, while ISO 17025 provides requirements for competence and impartiality of testing and calibration laboratories. Both standards have been implemented by over a million organizations globally and facilitate international acceptance of certifications.