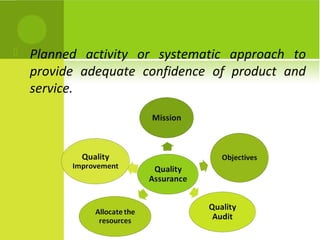
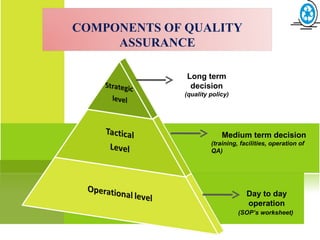
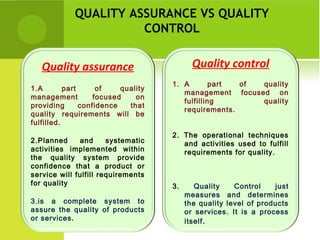
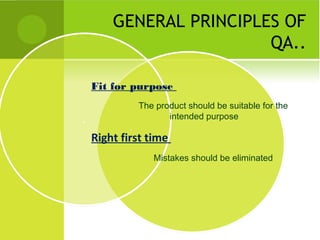
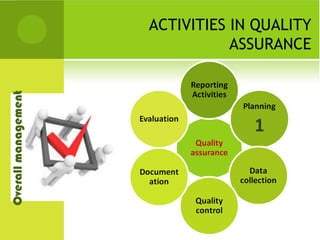
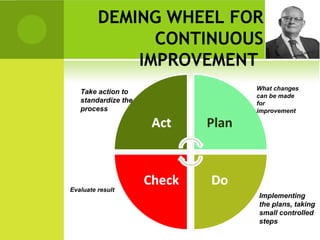
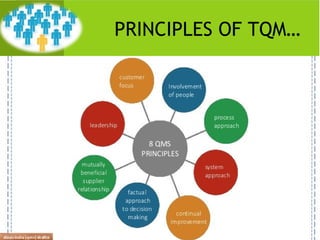
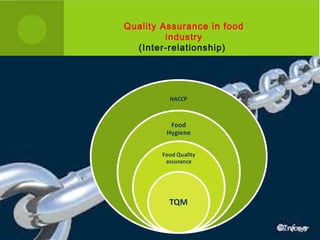
This document provides an overview of quality assurance and related concepts in the food industry. It defines quality assurance and discusses its relationship to total quality management. Key aspects covered include good manufacturing practices (GMP), good laboratory practices (GLP), good agricultural practices (GAP), and sanitary and hygienic practices. GMP, GLP, GAP and hygienic practices all establish guidelines and procedures to ensure food safety and quality throughout the production and processing chain. Total quality management (TQM) is also discussed as a philosophy aimed at continuous improvement of quality to meet customer expectations.