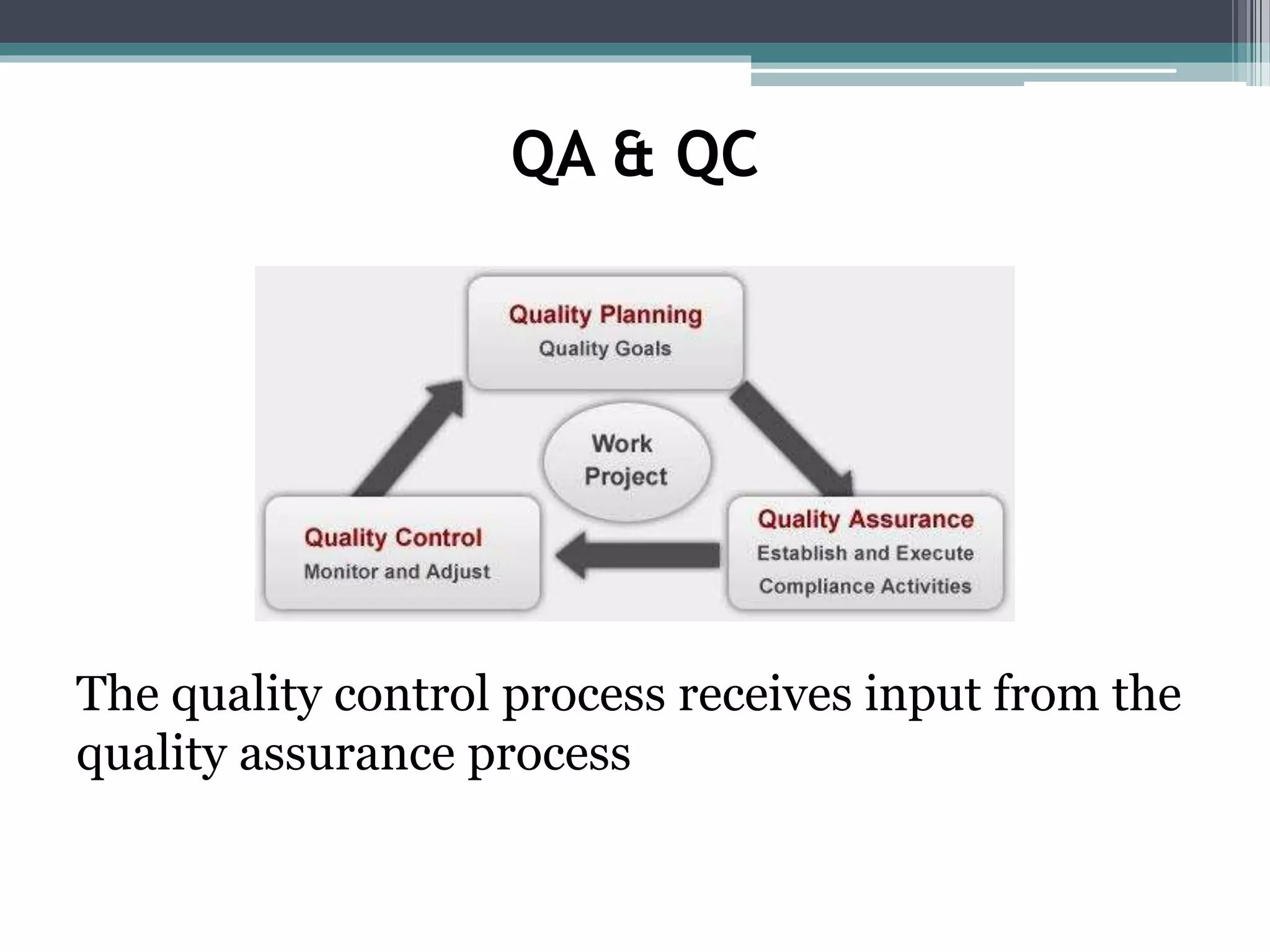
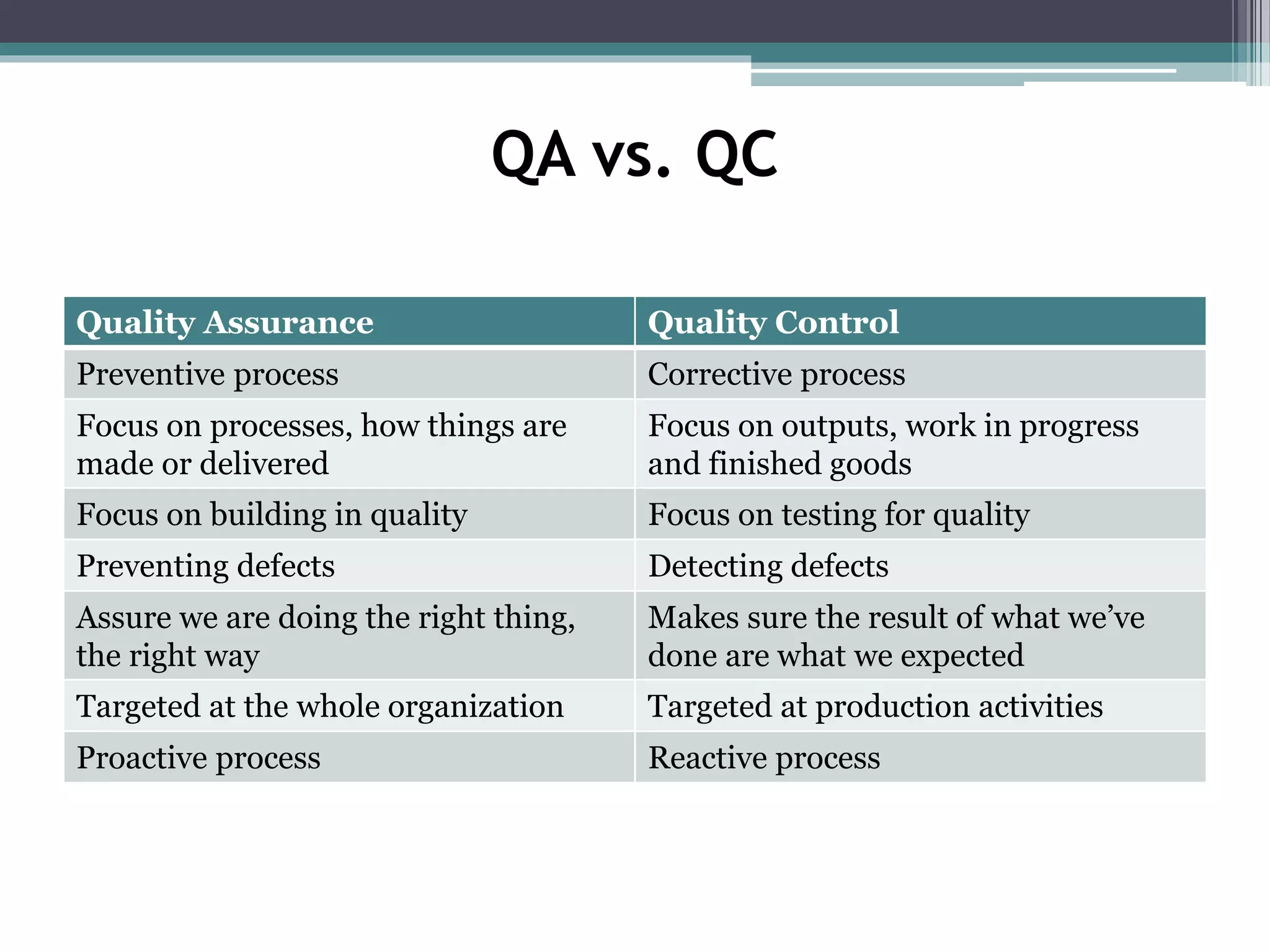
The document discusses quality assurance and quality control. Quality assurance is a proactive process that focuses on processes and preventing defects by understanding requirements upfront and developing plans to meet them. Quality control is reactive and focuses on operational activities like inspection and testing to identify defects and ensure deliverables meet requirements. The quality control process receives input from quality assurance, and if defects are found during quality control, quality assurance will investigate and implement corrective actions to prevent reoccurrence.