Embed presentation
Downloaded 41 times




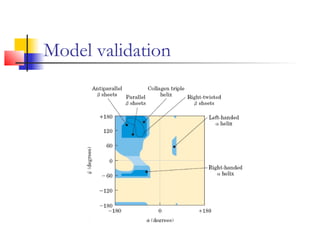


Structurally variable regions like loops, insertions and deletions can complicate protein structure modeling. The structure of an equivalent length segment from a homologous protein provides a guide for modeling missing regions, though the chosen segment may not always fit properly. De novo prediction involves using rotamer libraries of common amino acid conformations to predict side chain positions. Model validation checks the stereochemical accuracy, packing quality, and folding reliability of the predicted structure.









