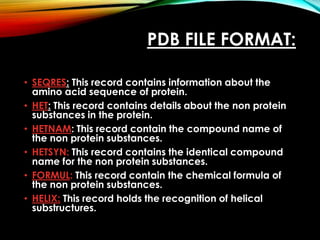
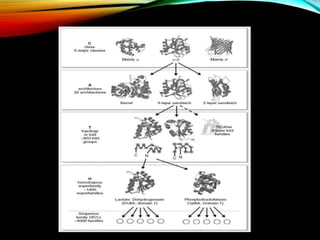
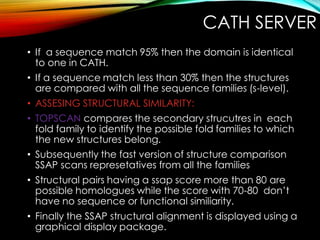
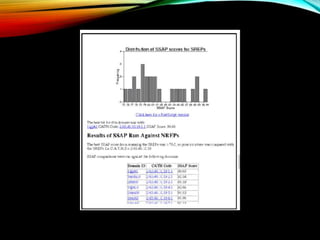
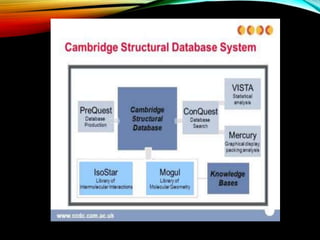
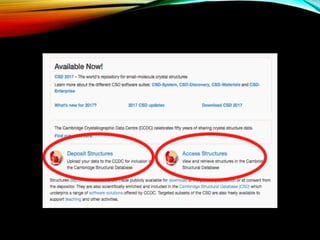
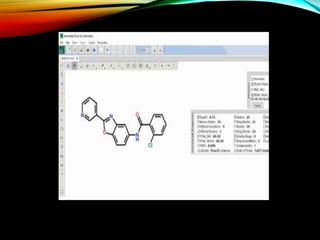
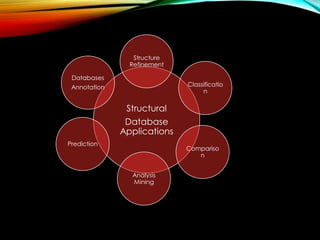
Structural databases like PDB, CSD, and CATH contain 3D structural information of proteins, small molecules, and macromolecules determined through techniques like X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy. These databases provide bibliographic data, atomic coordinates, and other details for each entry. PDB contains protein structures, CSD contains organic and metal-organic structures, and CATH classifies protein domains hierarchically. Structural databases have wide applications in structure prediction, analysis, mining, comparison, classification, structure refinement, and database annotation.