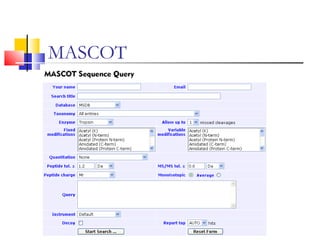
This document provides information on various computational tools and methods for protein identification, characterization, and structure prediction. It discusses tools that use amino acid composition, sequence alignment, peptide mass fingerprinting, and physico-chemical properties to identify proteins. It also describes methods such as Chou-Fasman, GOR, and neural networks that predict protein secondary structure and properties based on amino acid order, propensities, and probabilities.