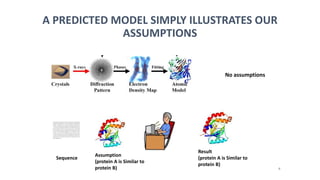
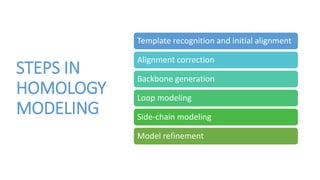
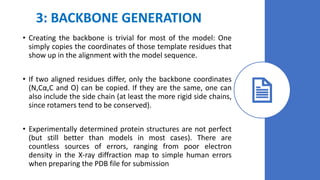
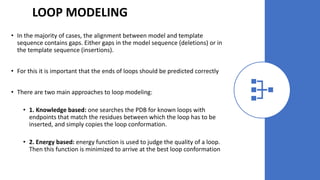
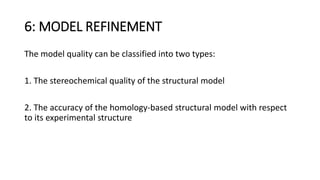
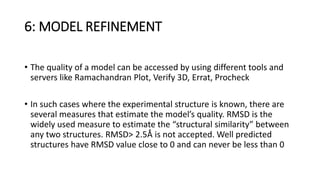
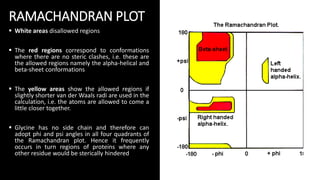
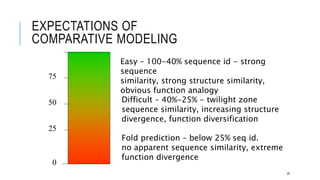
The document discusses protein modeling, which involves predicting the 3D structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence using computational methods. It describes why computational modeling is necessary, as experimental techniques like X-ray crystallography and NMR are often slow and many proteins do not crystallize well. The main methods covered are homology modeling, threading, and ab initio modeling. Key steps in homology modeling include template recognition, alignment, backbone generation, loop modeling, side chain modeling, and model refinement. Validation tools like Ramachandran plots, Verify3D, and ERRAT are also summarized.