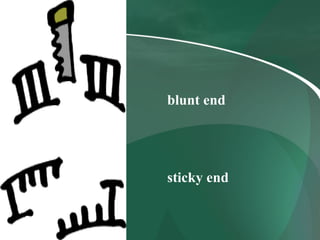
Restriction enzymes are proteins that cut DNA at specific recognition sequences. There are three main types of restriction enzymes. Type I enzymes require cofactors and have three subunits. Type II enzymes recognize palindromic sequences and are the most commonly used. They cut DNA into blunt or sticky ends. Type III enzymes recognize two separate sequences and cut further from the recognition site. Restriction enzymes are important tools in biotechnology and DNA manipulation.