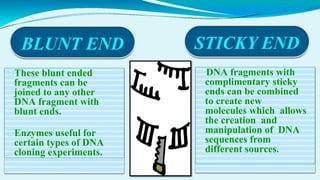
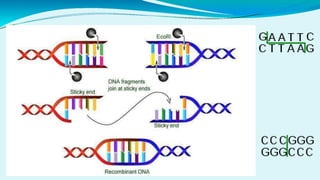
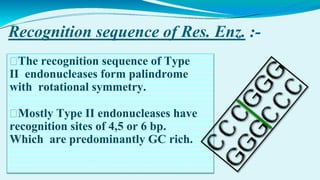
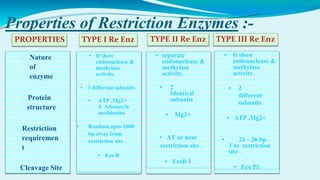
This document provides information on restriction enzymes, including their discovery, types, subunits, nomenclature, recognition sequences, properties, and applications. Restriction enzymes are bacterial enzymes that cut DNA at specific recognition sequences. There are three main types: Type I cut DNA randomly far from recognition sites and modify DNA through methylation. Type II cut within or near recognition sites and are used widely in gene cloning and manipulation. Type III have properties between Types I and II.