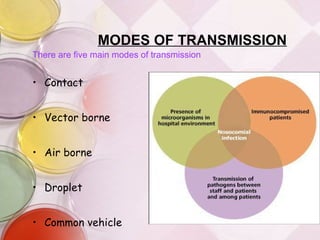
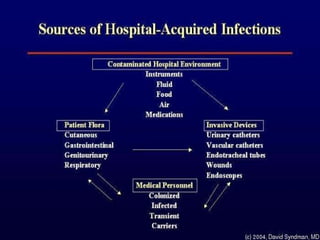
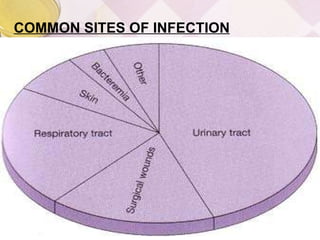
Nosocomial infections, also known as hospital-acquired infections, can develop 48 hours or more after hospital admission or within 30 days after discharge. They are caused by four main factors - crowded hospital conditions, new microorganisms, increasing number of immune-compromised patients, and increasing bacterial resistance. The most common modes of transmission are contact, droplet, vector-borne, airborne, and common vehicle. Common sites of infection include the urinary tract, lungs, bloodstream, and surgical sites. Prevention methods focus on isolation, sterilization, proper hand hygiene, and use of protective equipment like gloves and aprons.