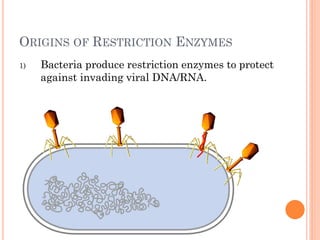
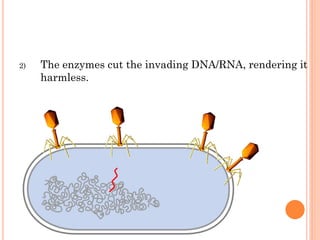
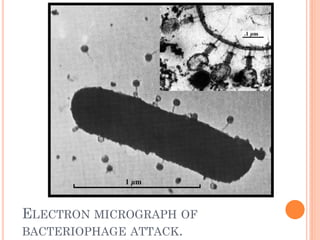
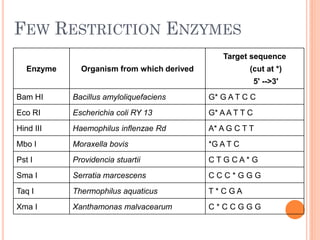
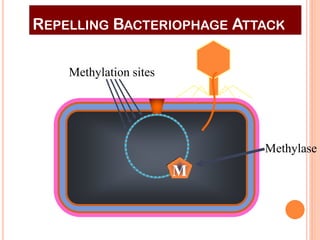
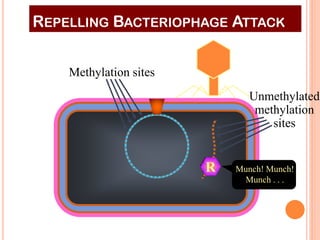
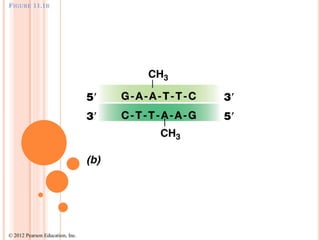
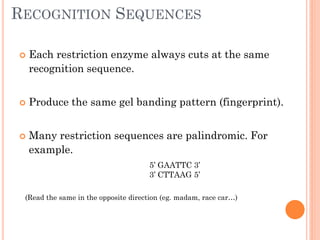
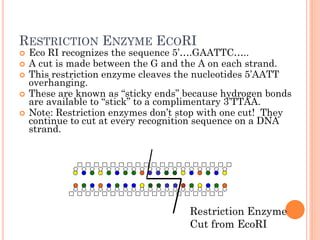
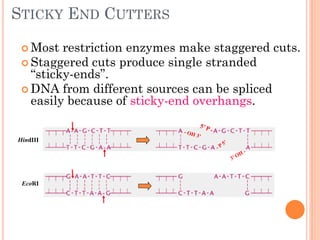
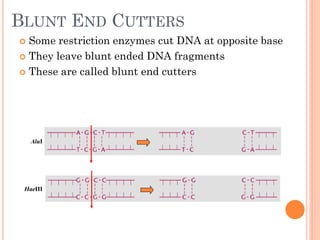
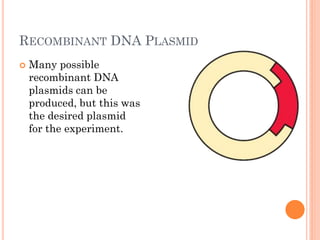
This document discusses restriction enzymes, which are proteins produced by bacteria to protect their DNA from viruses. Restriction enzymes recognize specific DNA sequences and cut the DNA at those sites. There are four main types of restriction enzymes. Type II enzymes cut DNA at or near their recognition sequences and are commonly used in genetic engineering to cut and combine DNA from different sources. This allows scientists to create recombinant DNA by splicing genes from one organism into another, enabling applications like producing pharmaceuticals in bacteria.