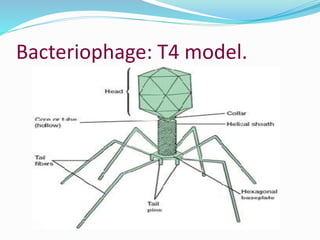
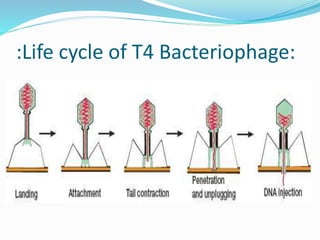
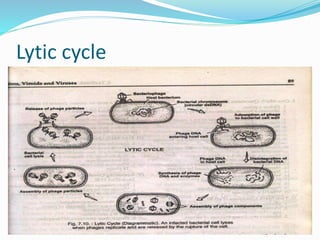
Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria. They were discovered in the early 20th century and come in diverse structural forms. Bacteriophages have a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein coat. They undergo either a lytic cycle that results in host cell lysis or a lysogenic cycle where the phage DNA integrates into the host chromosome. The lysogenic cycle can confer new properties on the host bacteria through lysogenic conversion. Bacteriophages play important roles in bacterial evolution, epidemiology, and have applications in genetic engineering and controlling bacterial growth.