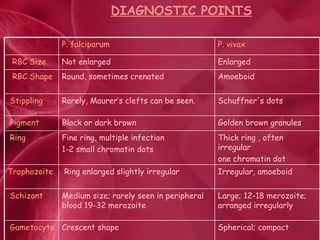
Malaria is a mosquito-borne parasitic disease caused by Plasmodium parasites and transmitted through the bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes. There are four Plasmodium species that cause malaria in humans: P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae. The parasite's life cycle involves the mosquito as a vector and human host. Laboratory diagnosis of malaria is usually done by microscopic examination of blood smears to identify the parasite stages in red blood cells.