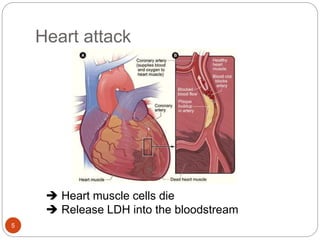
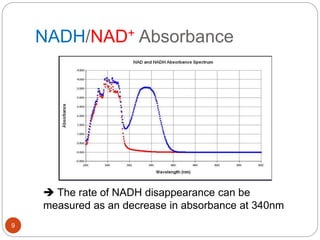
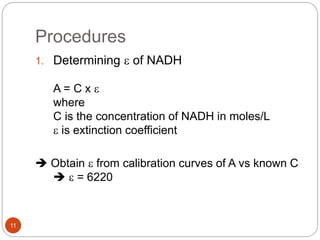
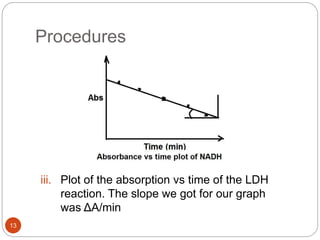
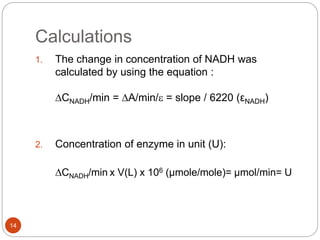
The document discusses the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) blood test used for heart attack victims. LDH is an enzyme found in most body cells that is released when cells are damaged or die. An LDH blood test can detect elevated levels after a heart attack, indicating heart muscle cell death. The test is most useful within 12-24 hours of a heart attack. Higher-than-normal total LDH combined with higher LDH-1 than LDH-2 isoenzymes suggests a heart attack. The LDH level is measured using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer to detect the decrease in absorbance of NADH at 340nm as LDH converts pyruvate to lactate.