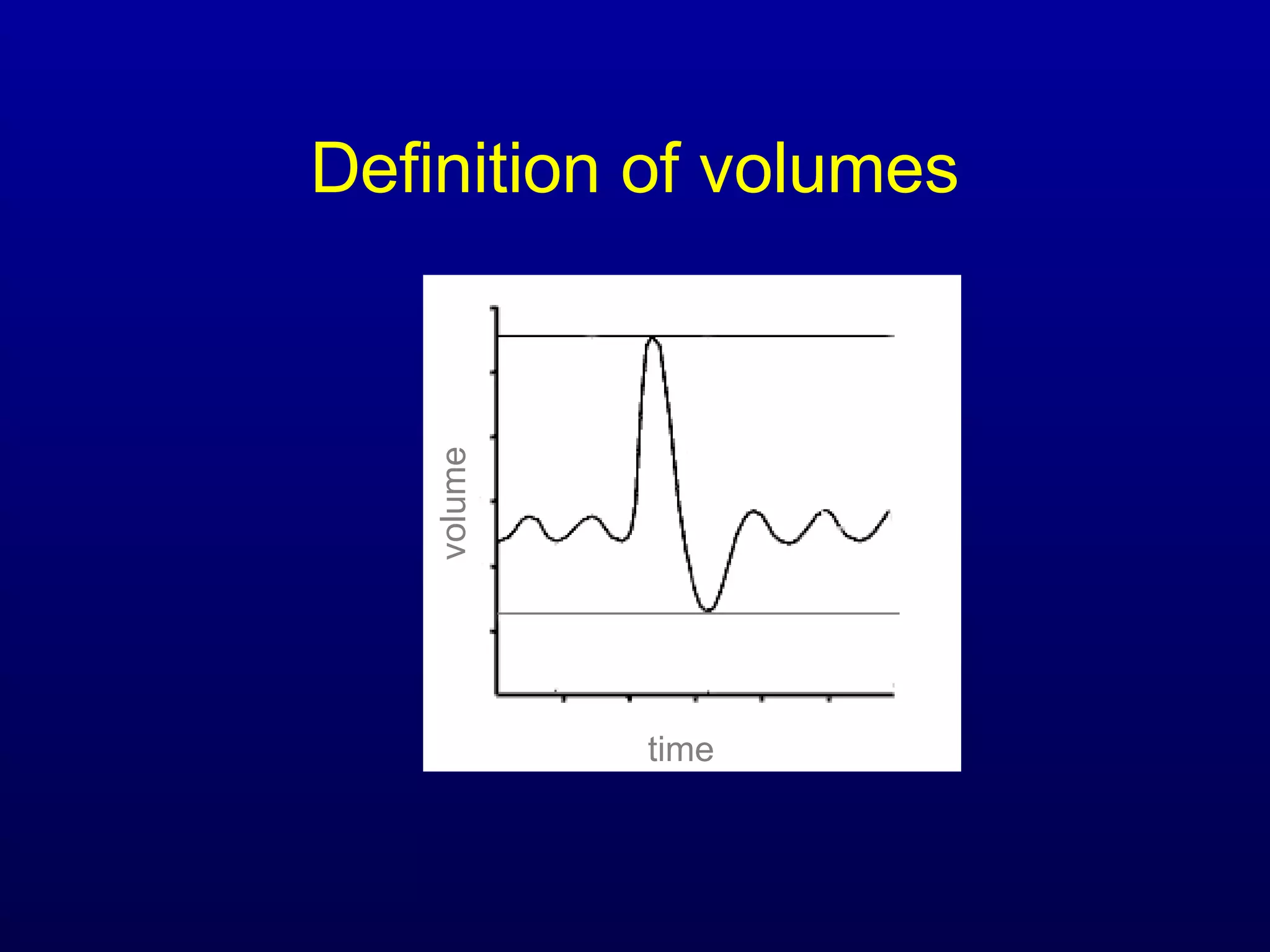
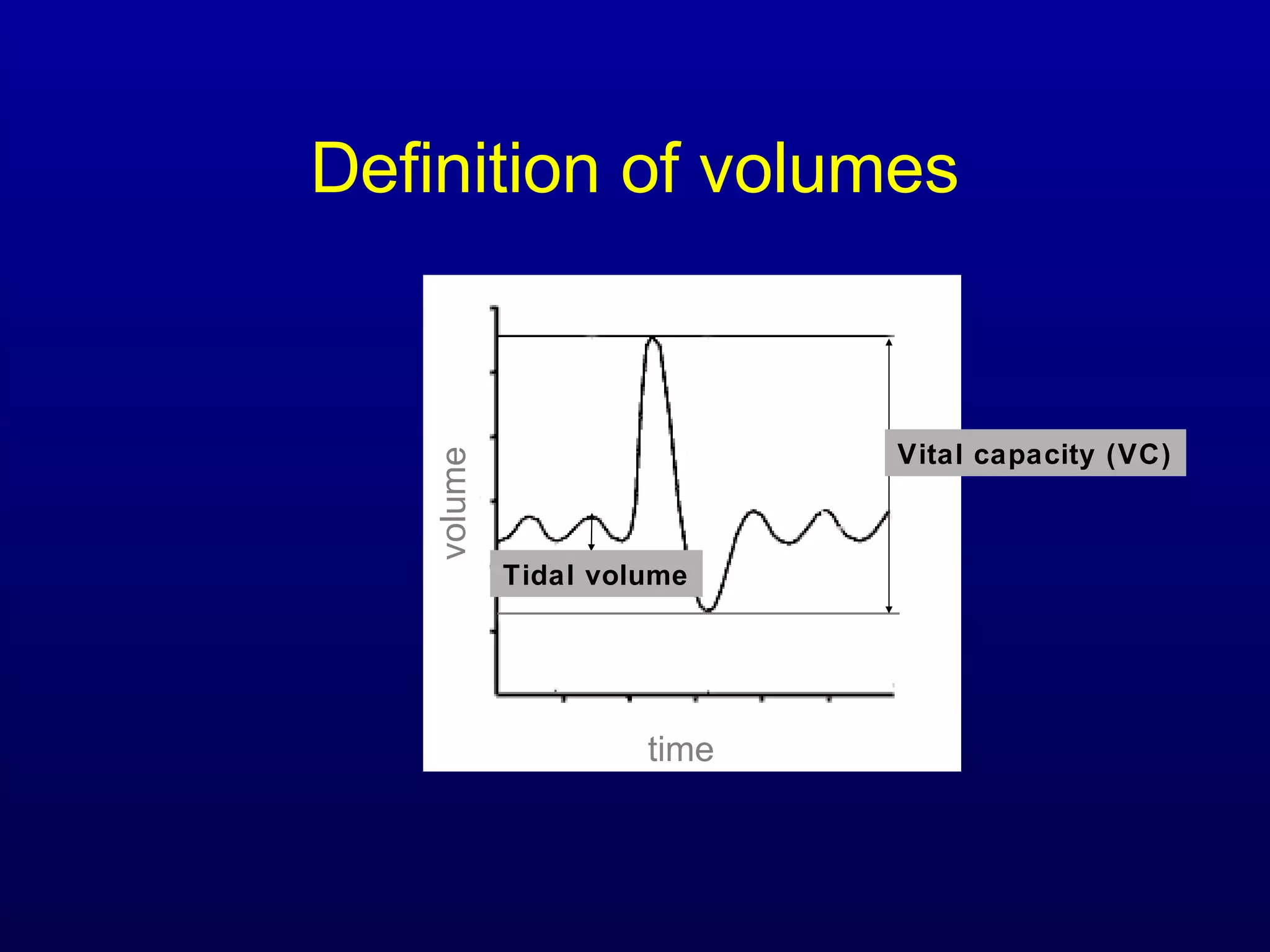
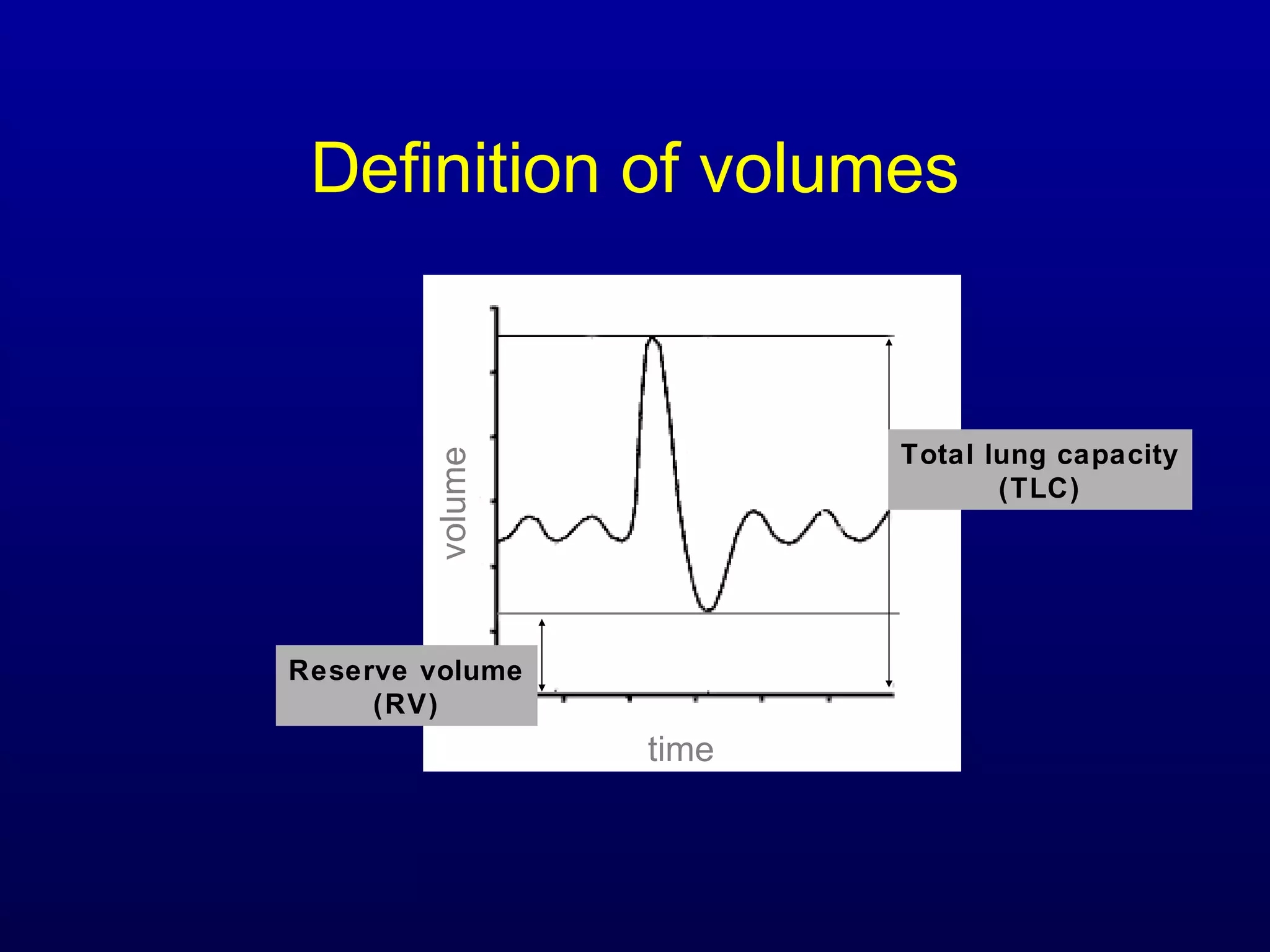
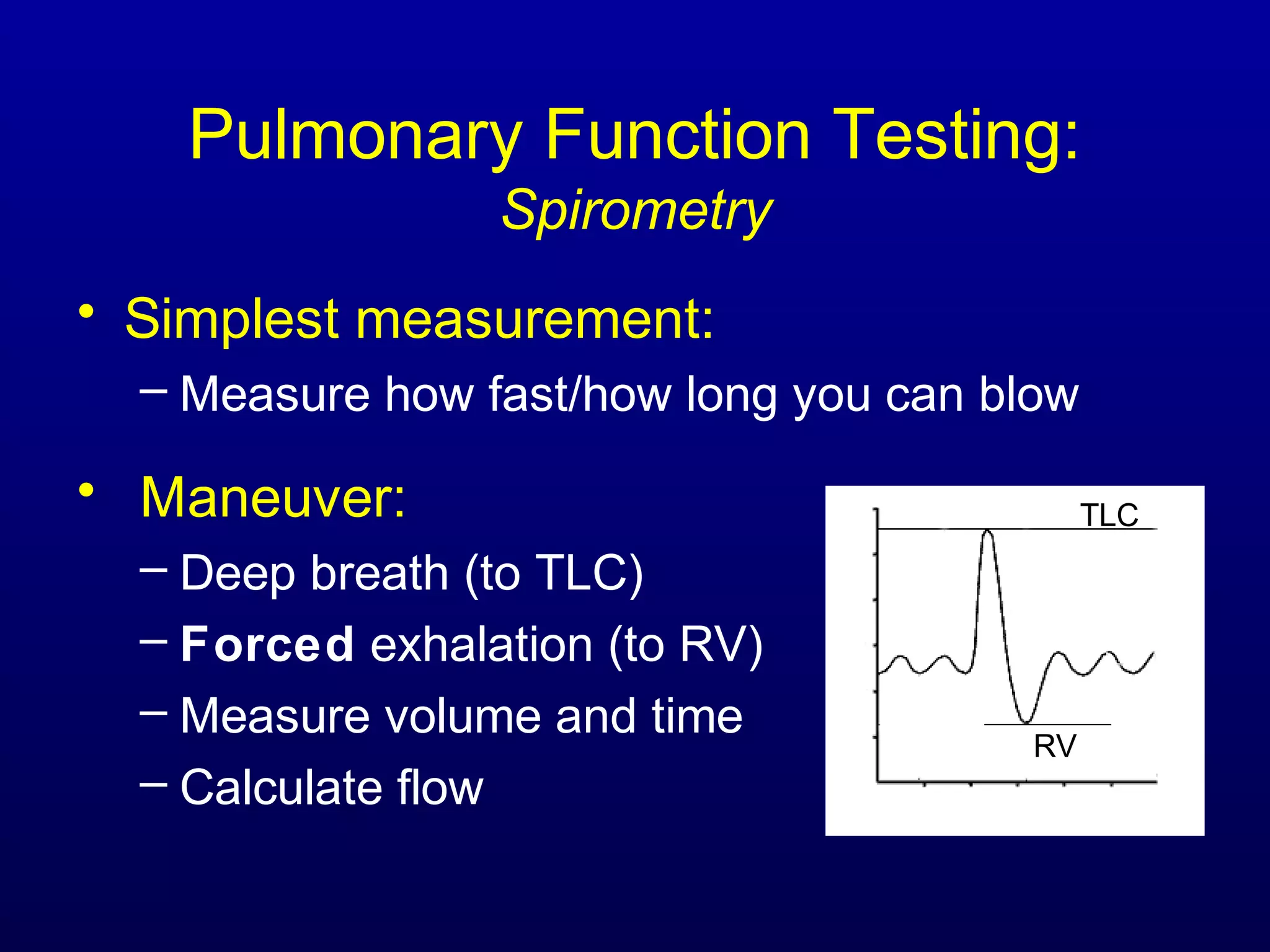
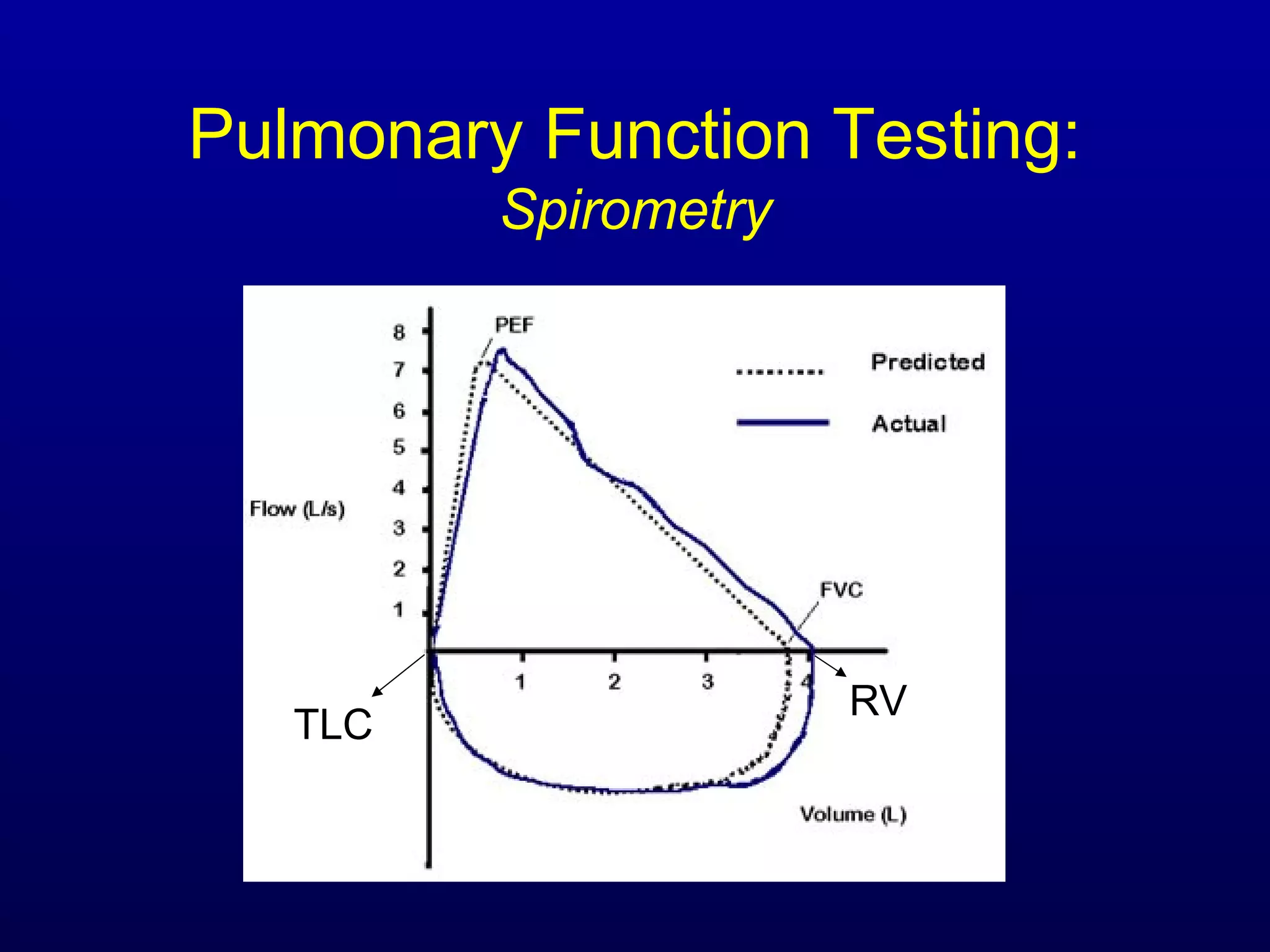
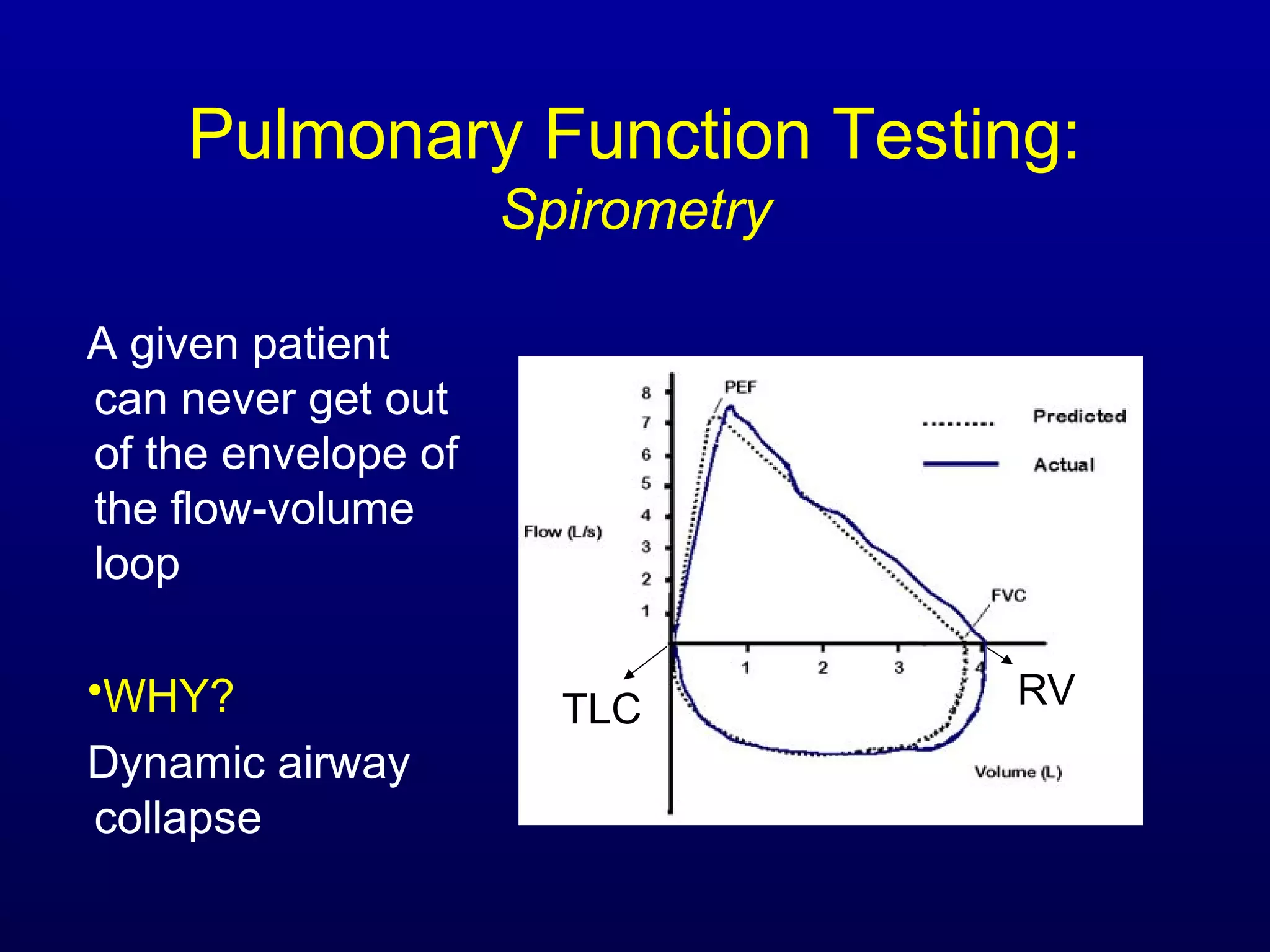
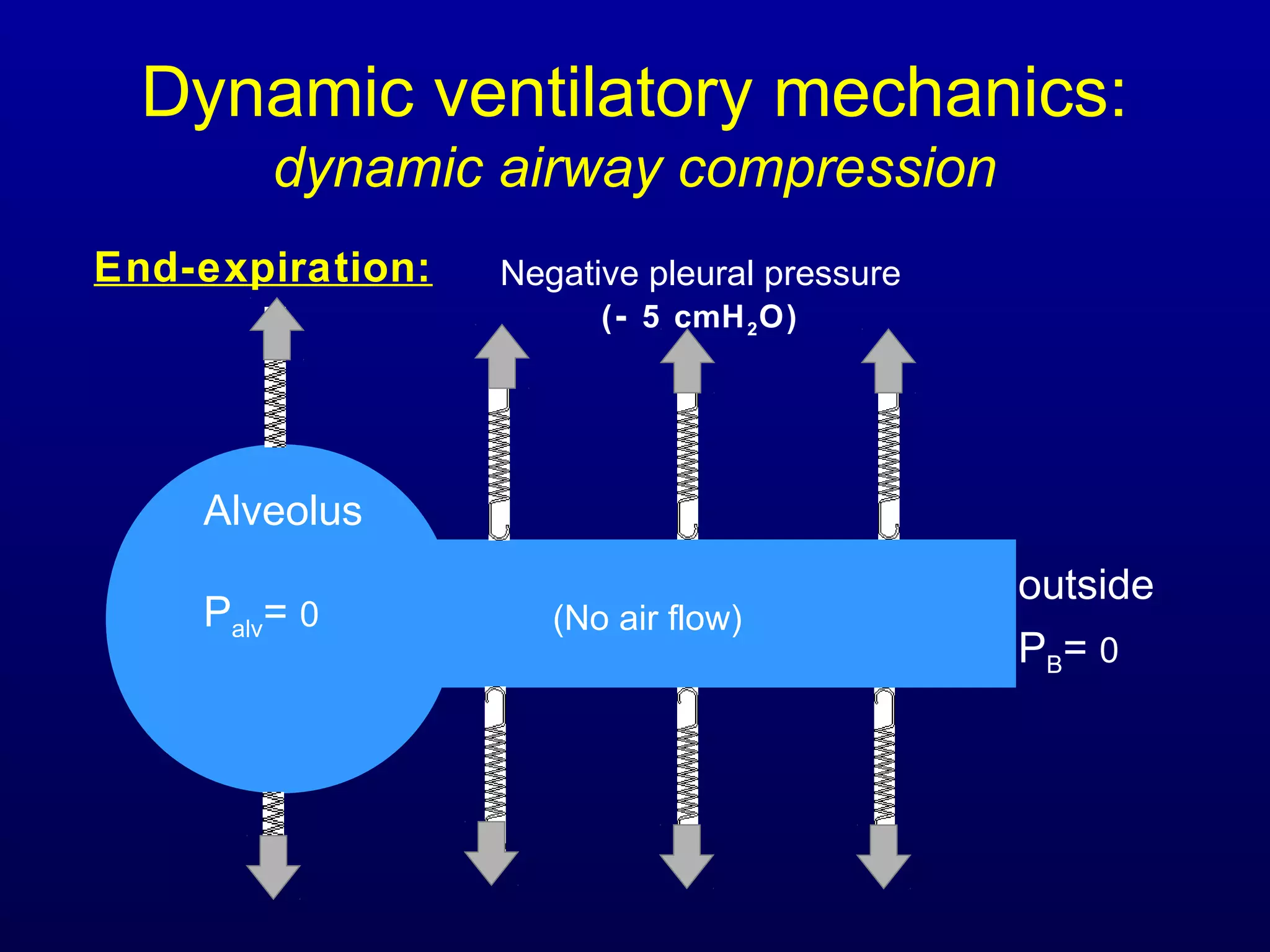
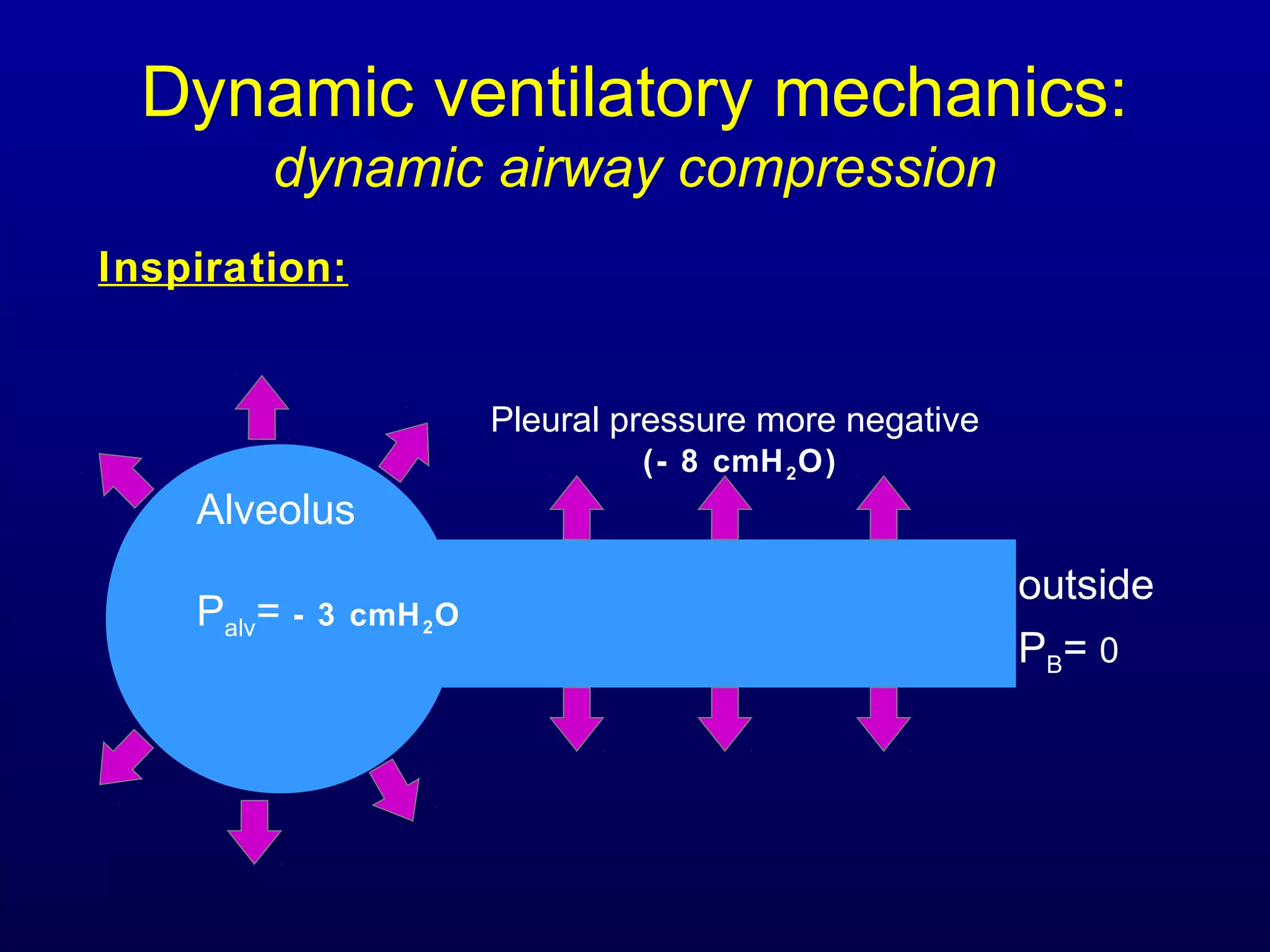
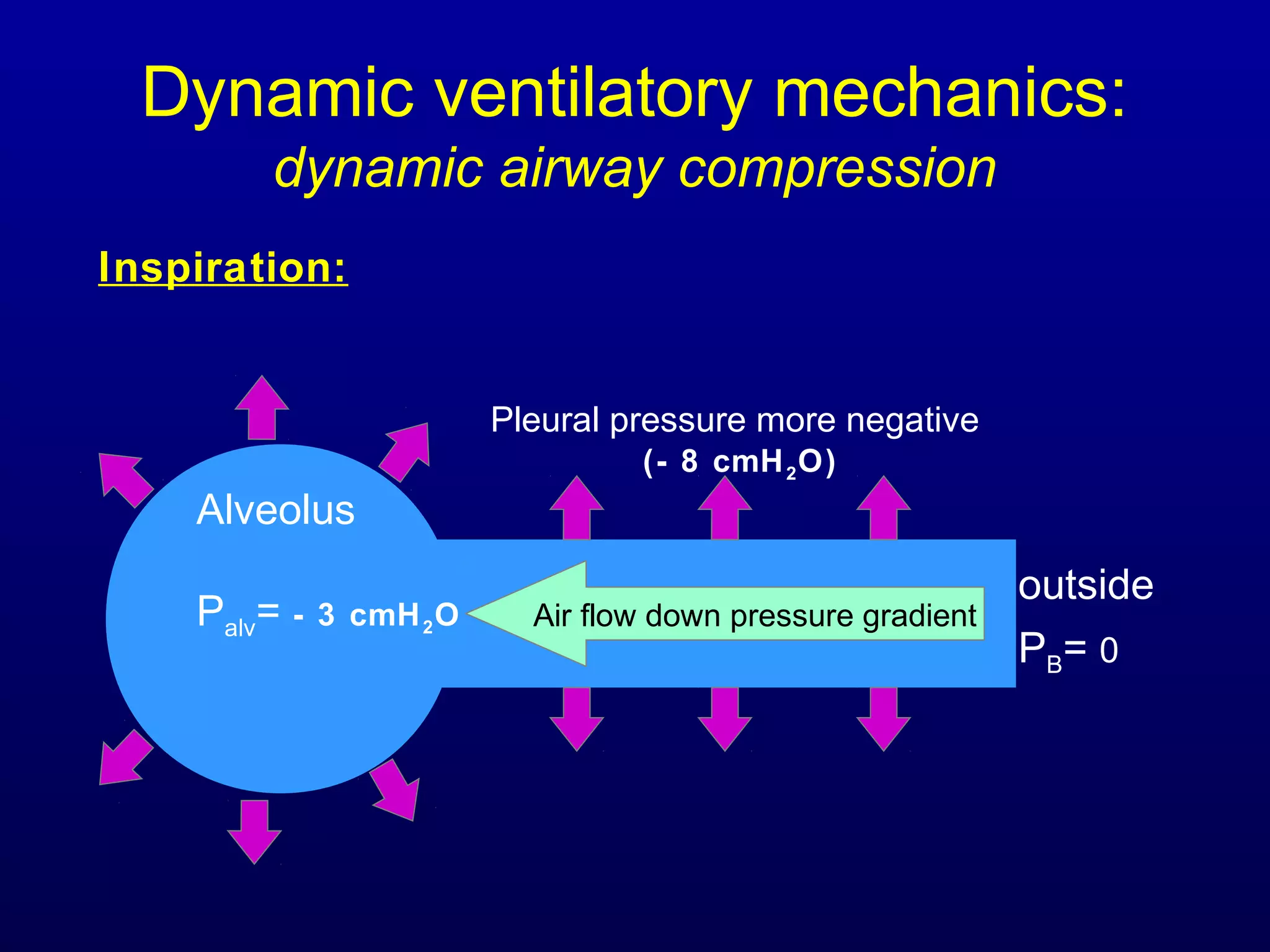
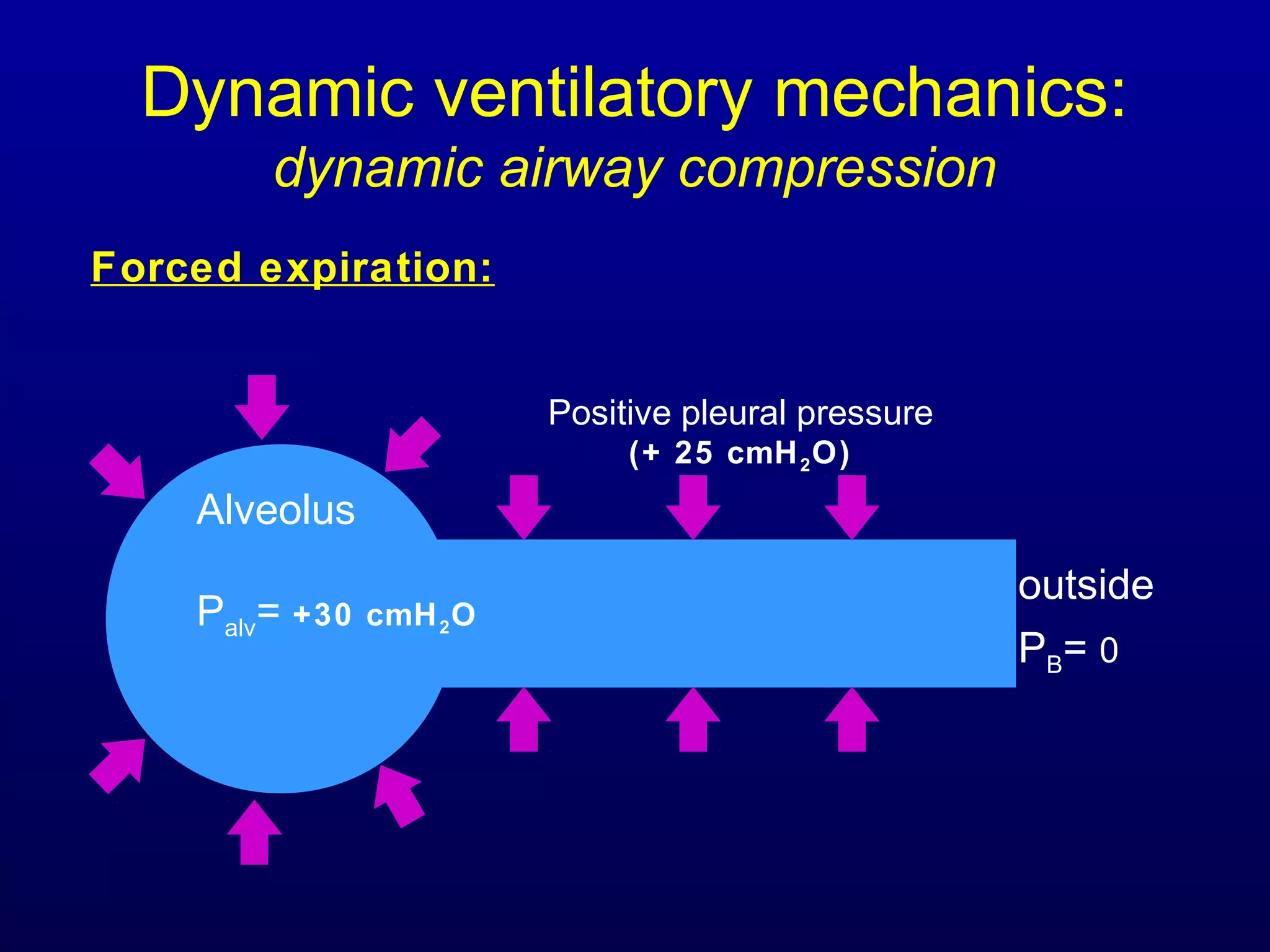
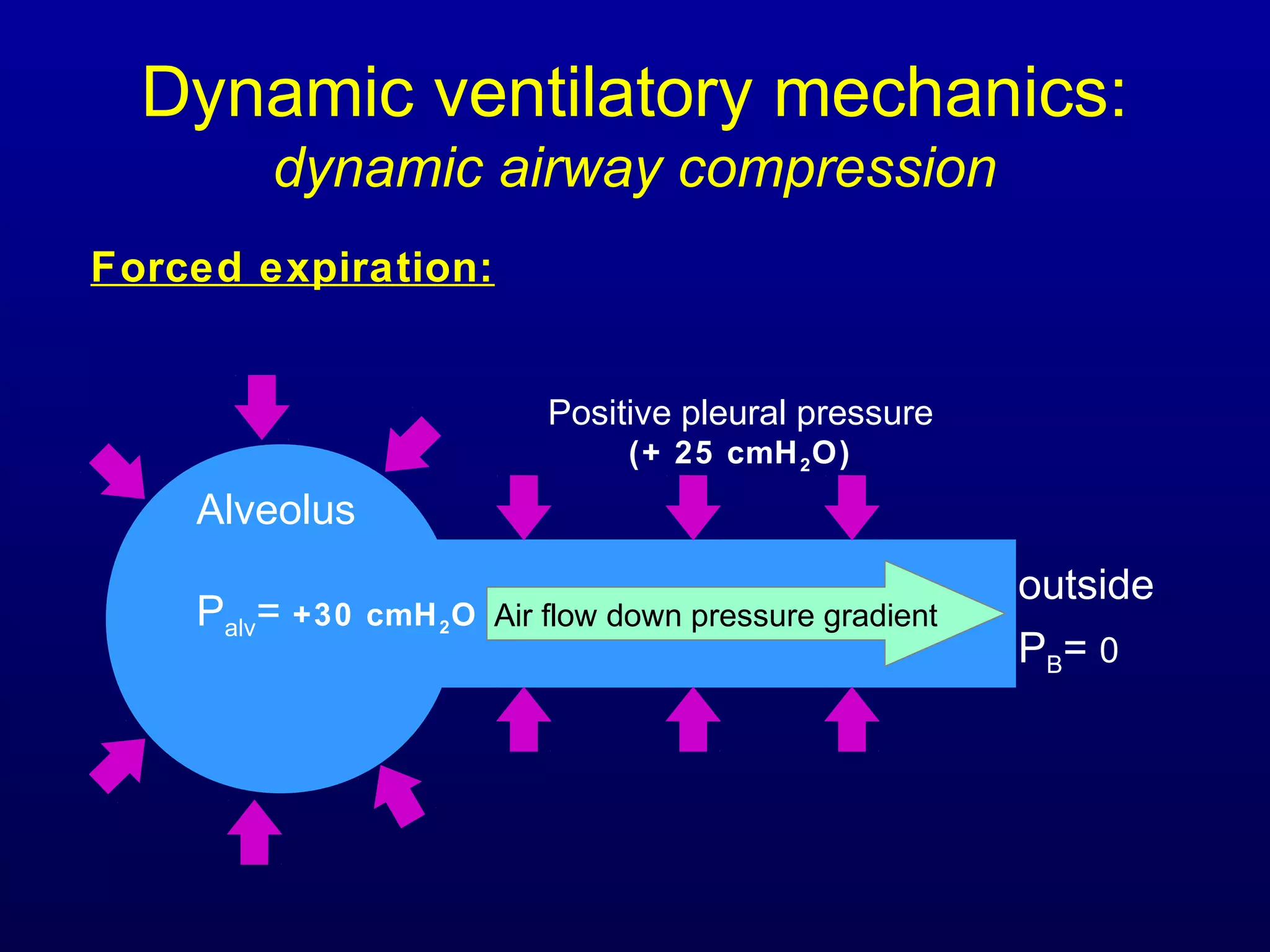
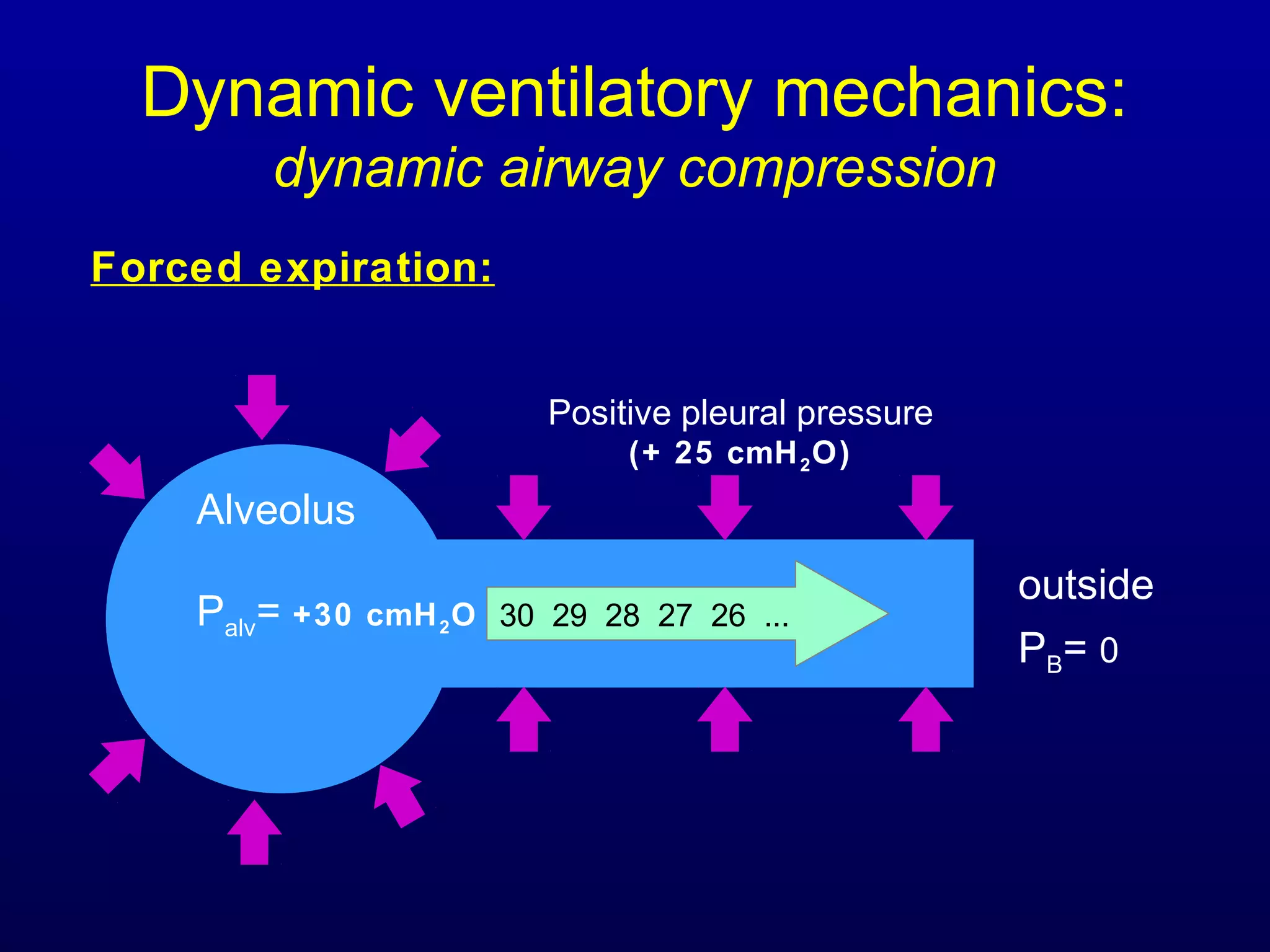
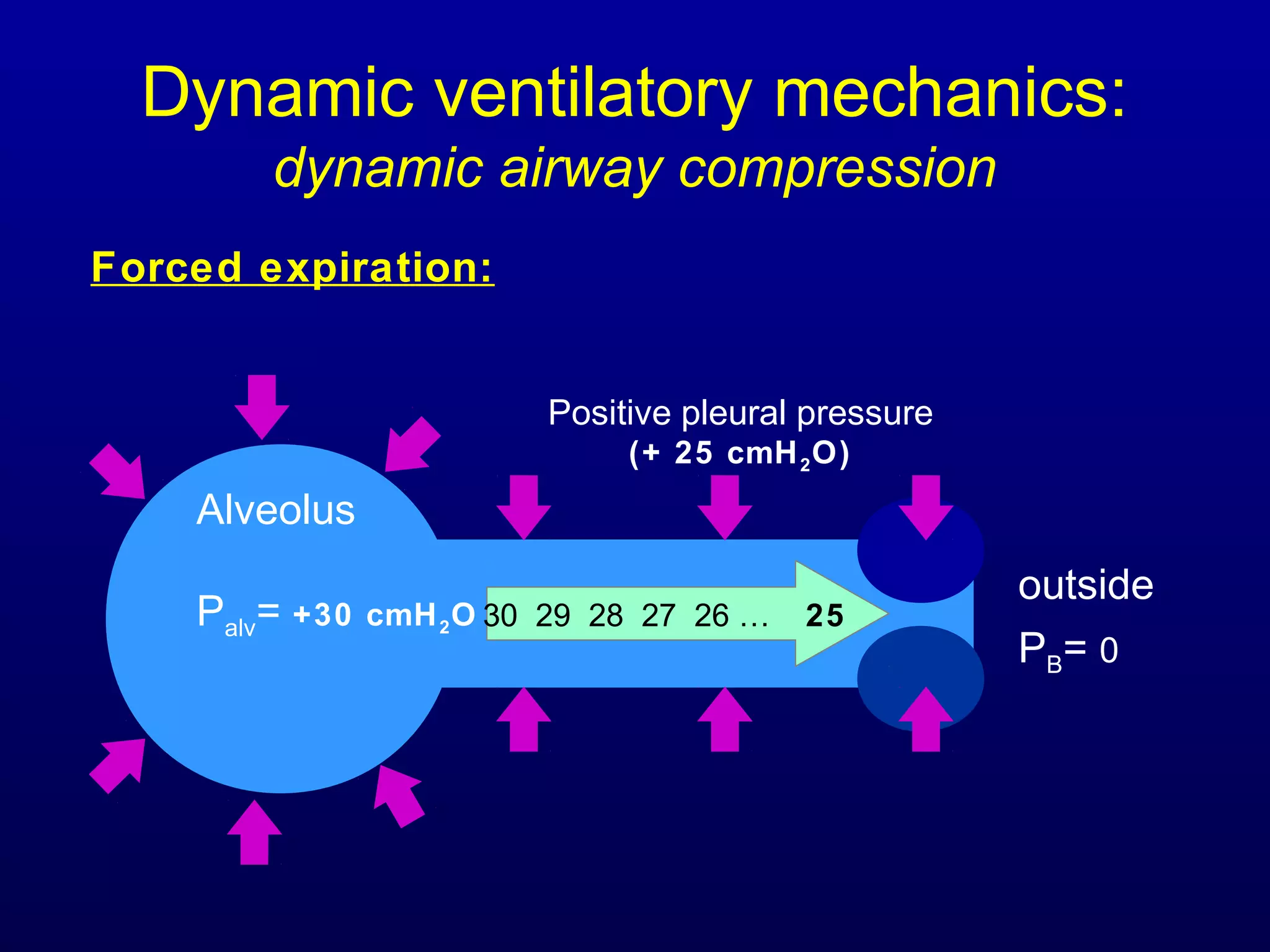
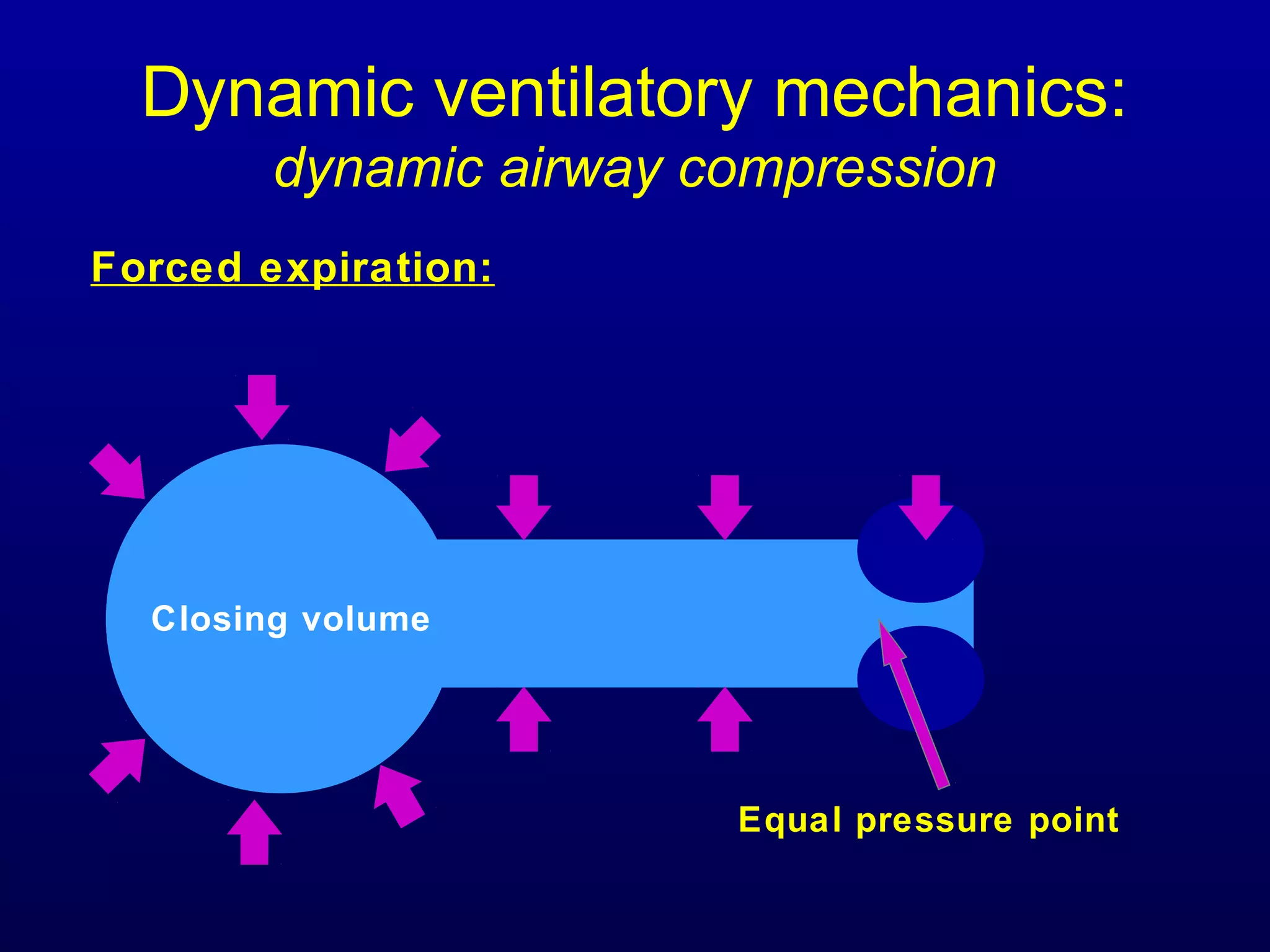
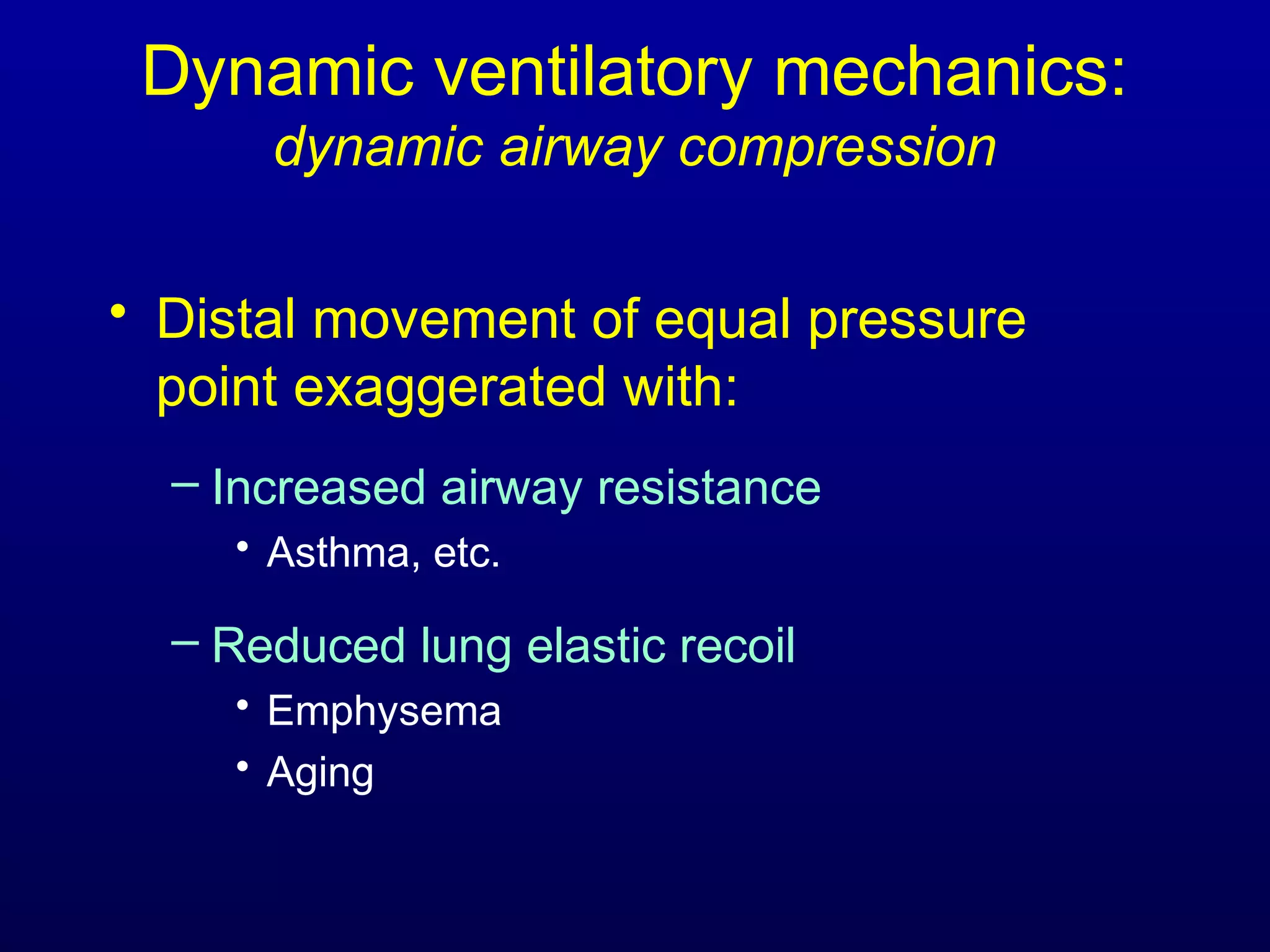
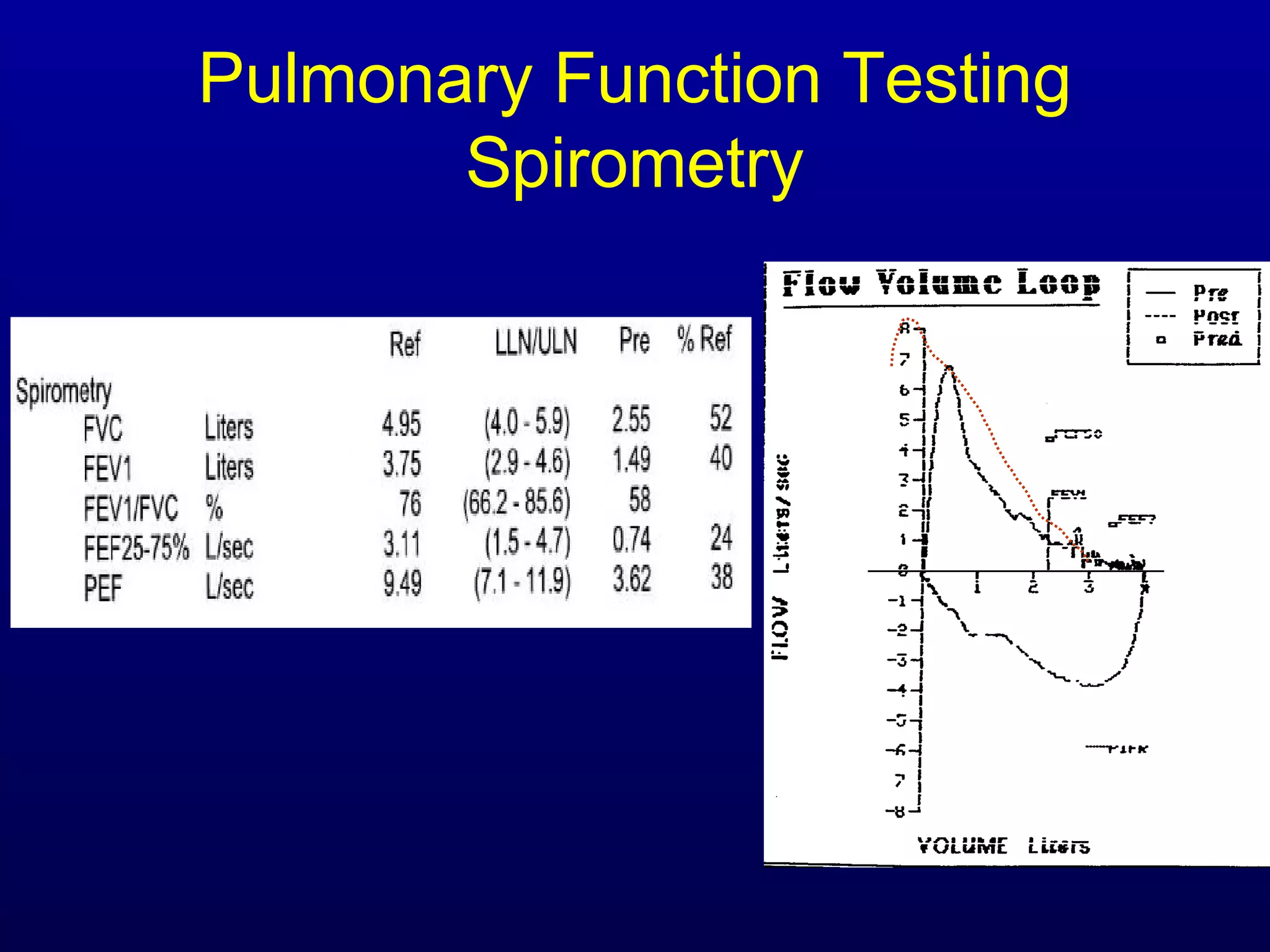
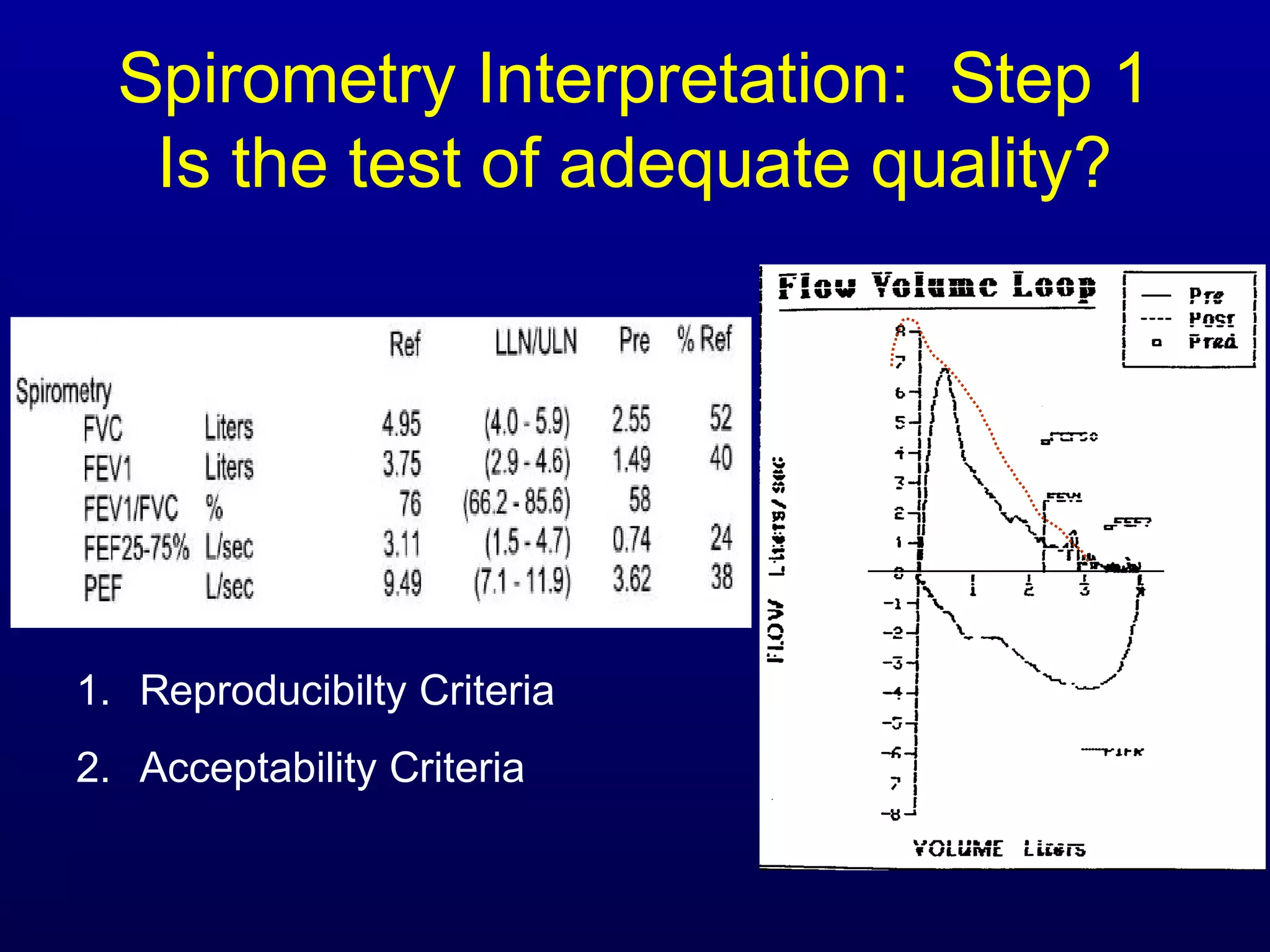
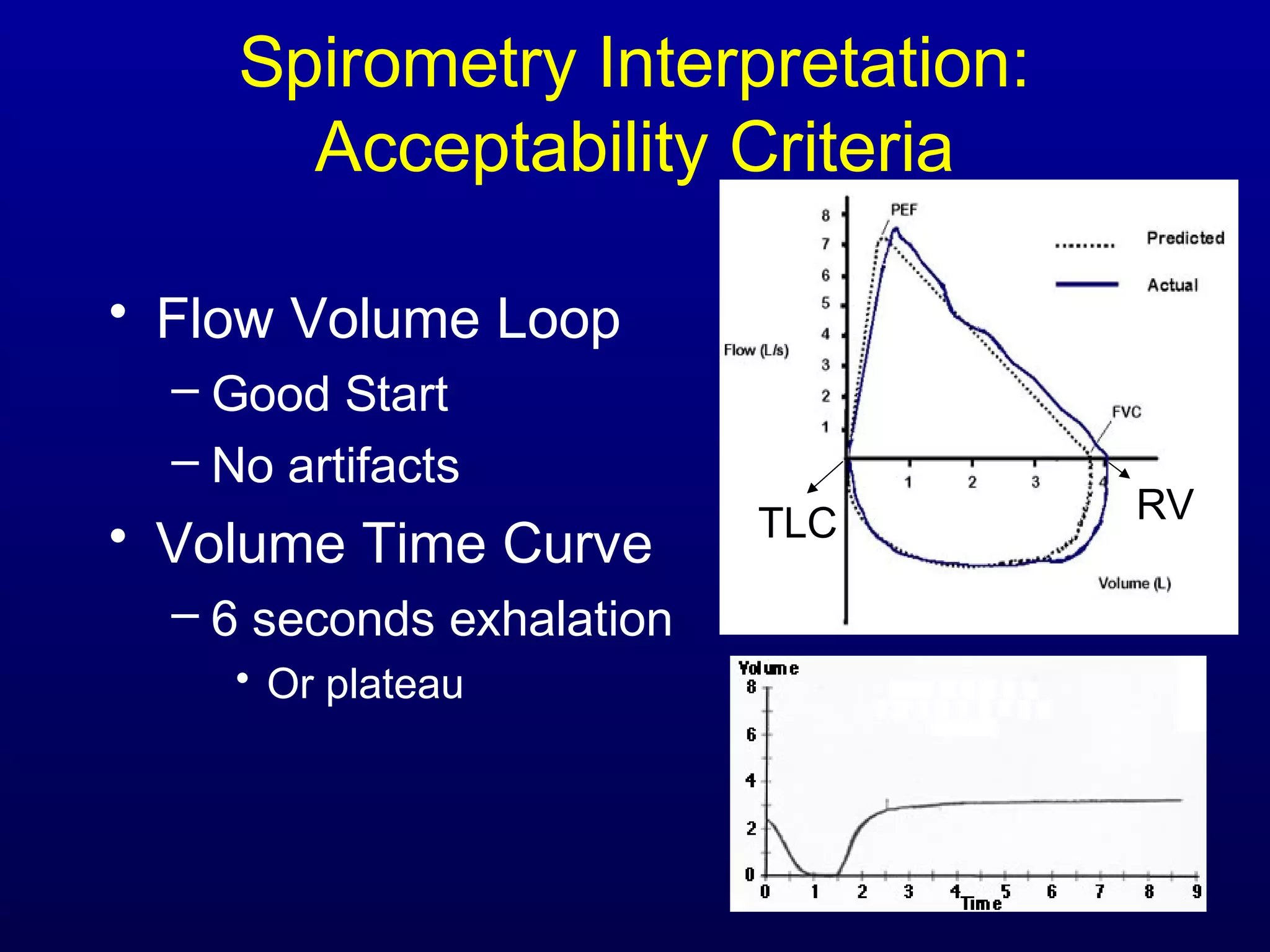
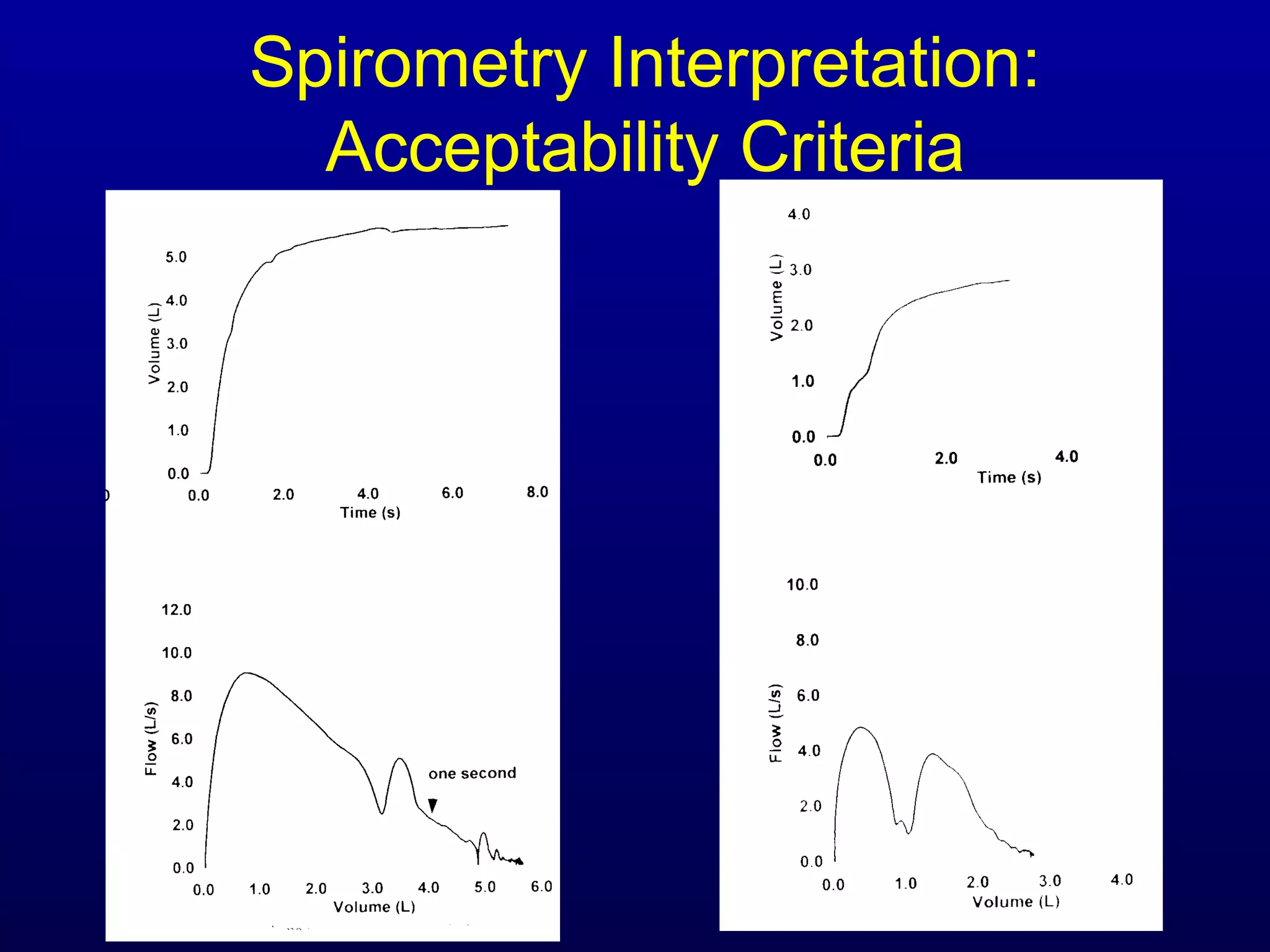
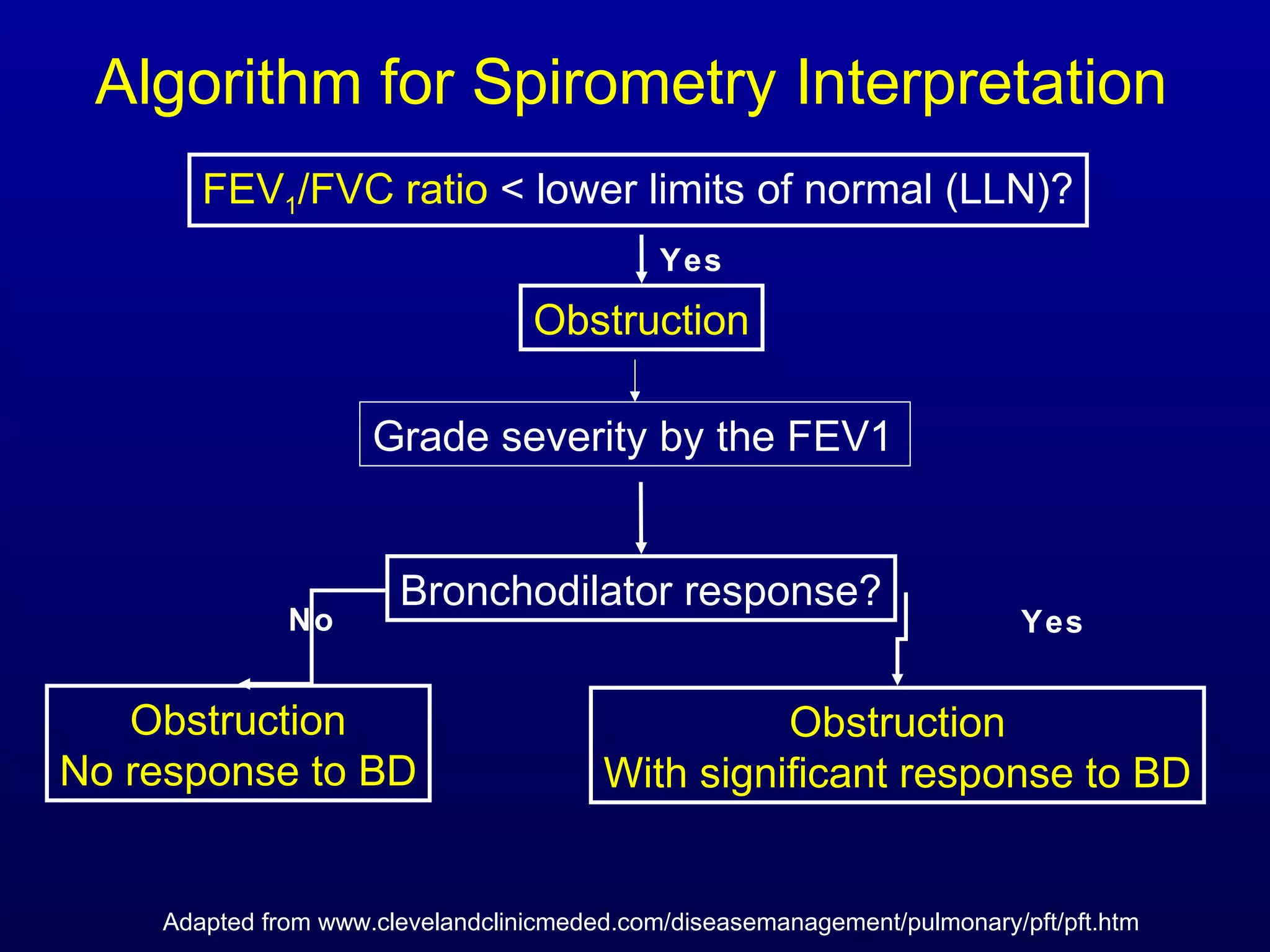
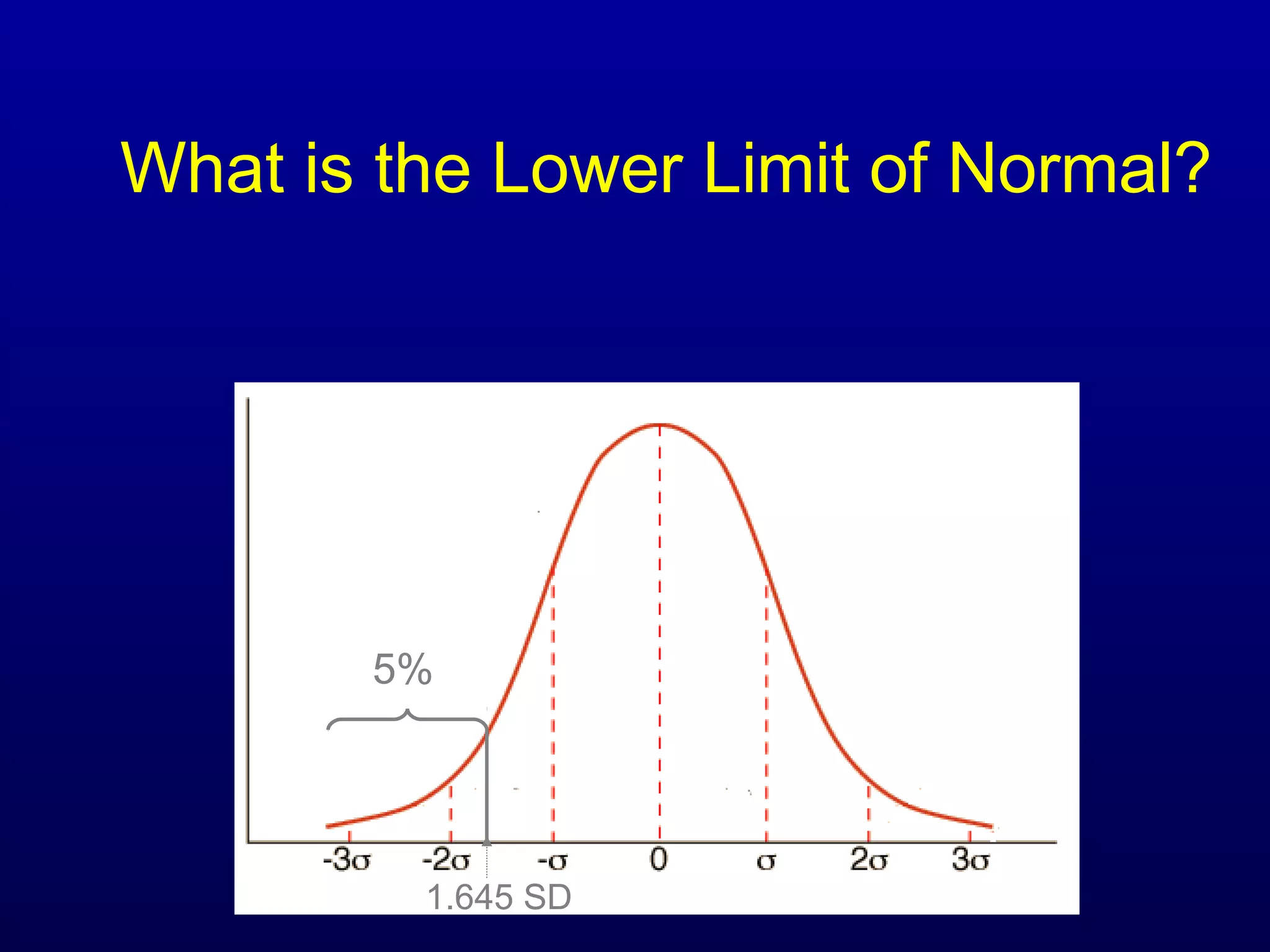
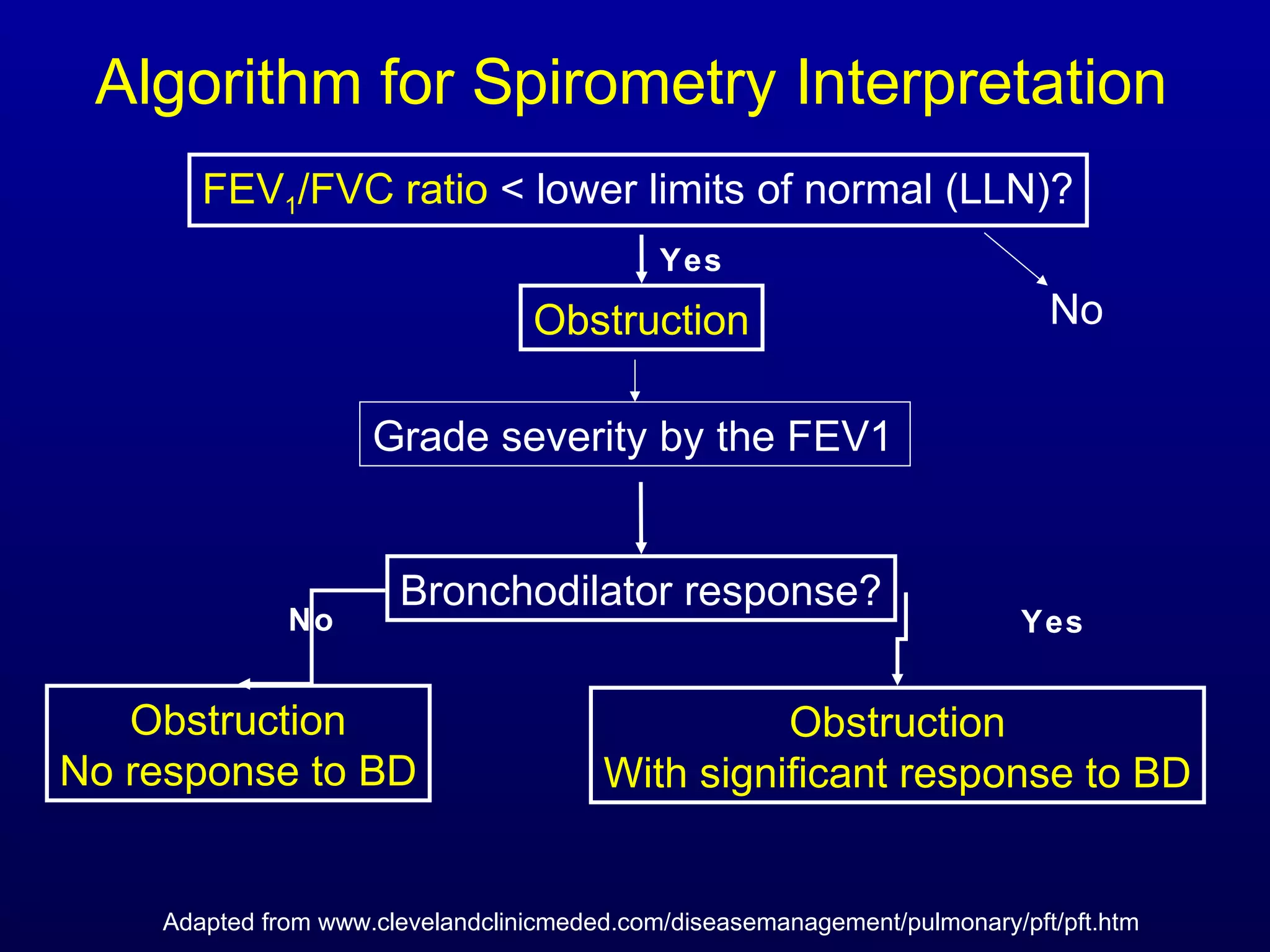
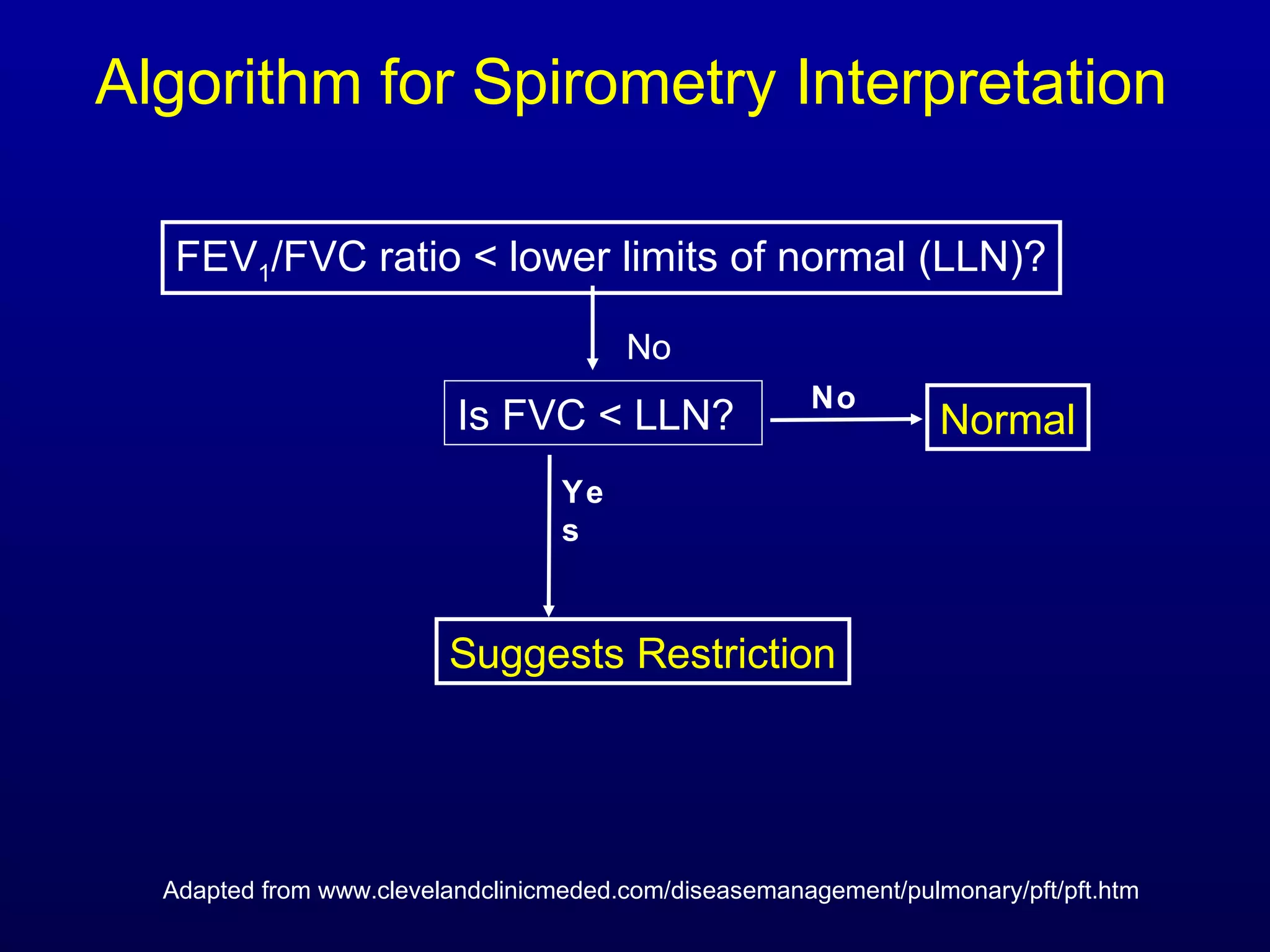
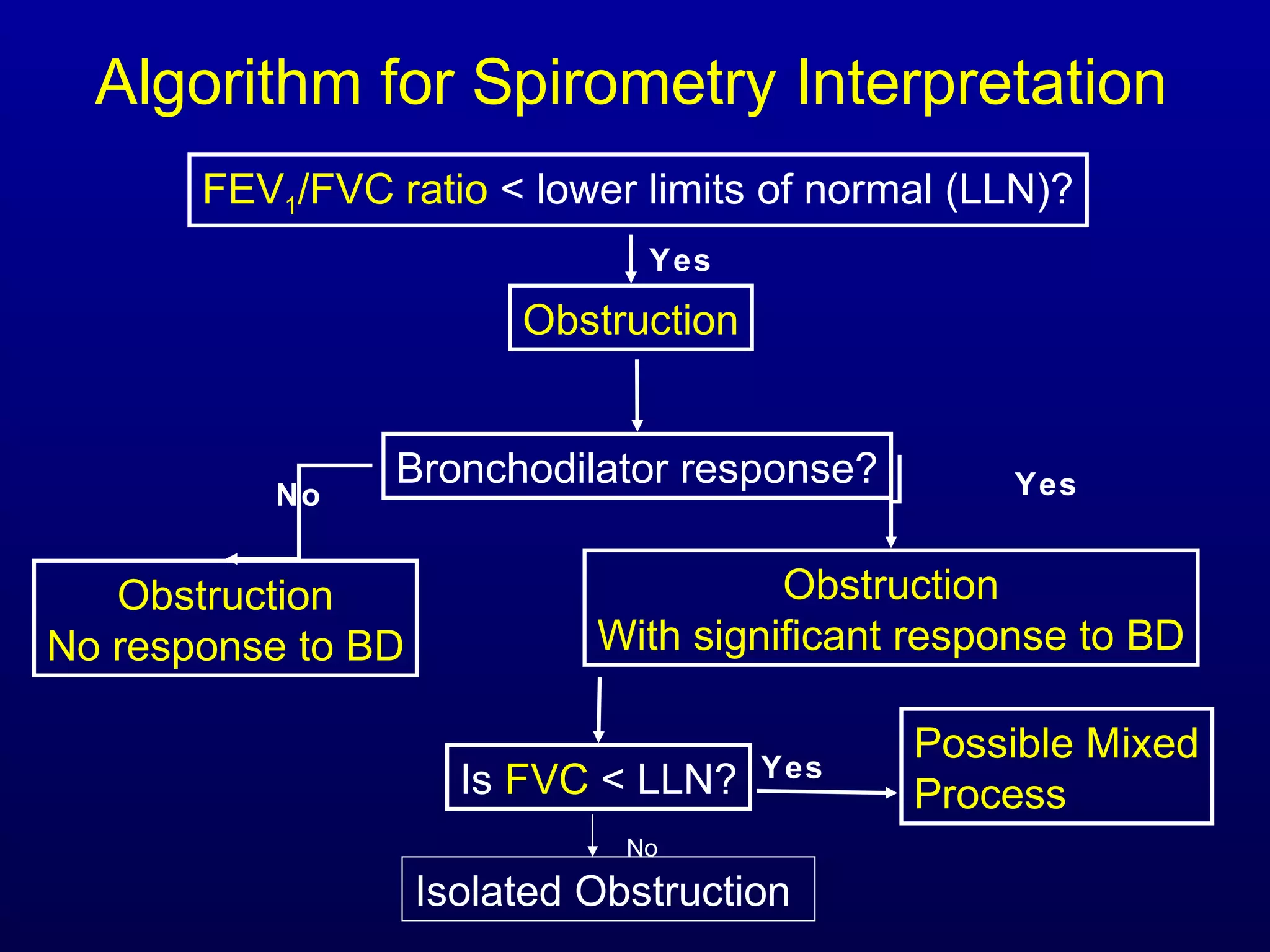
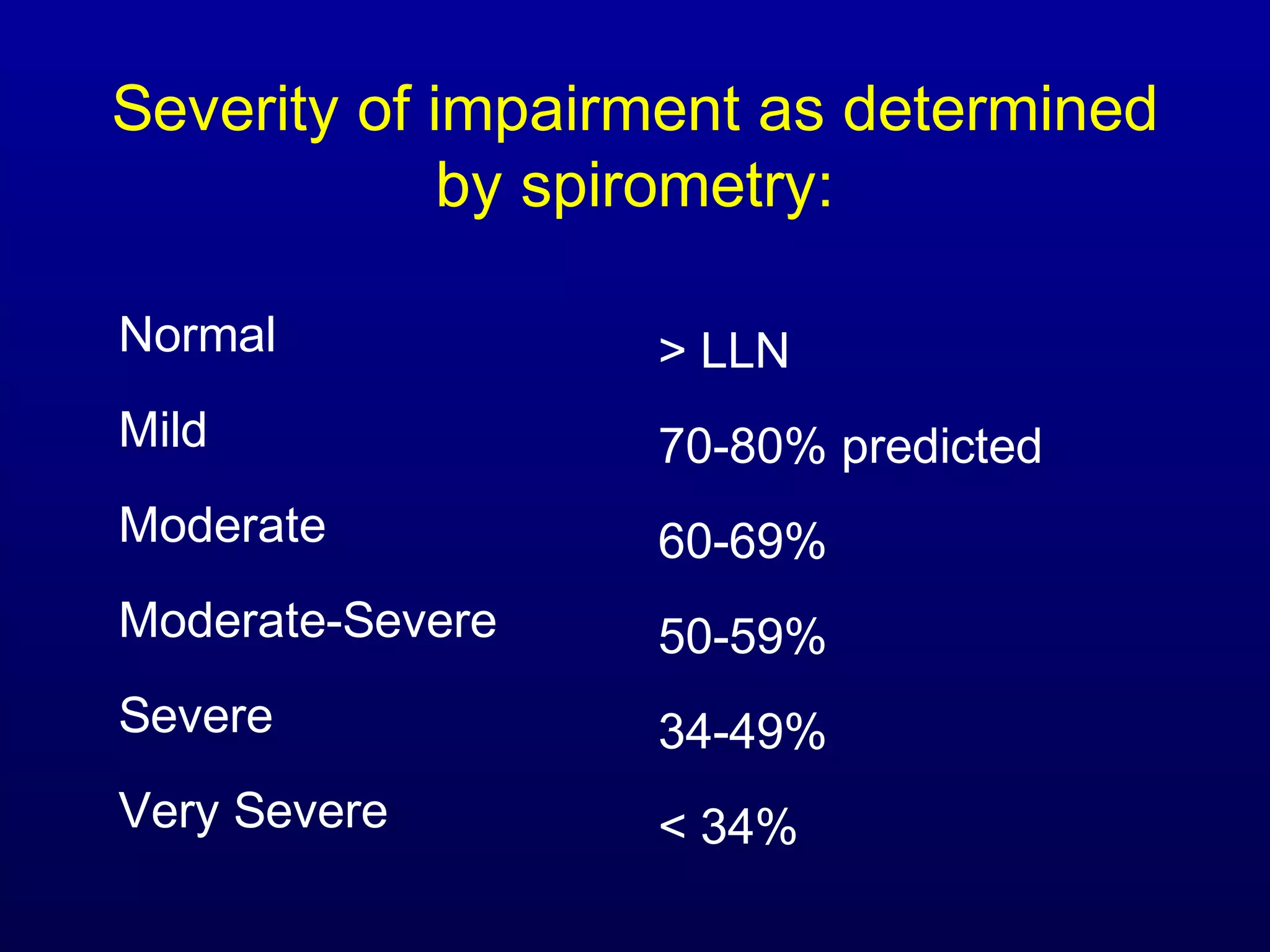
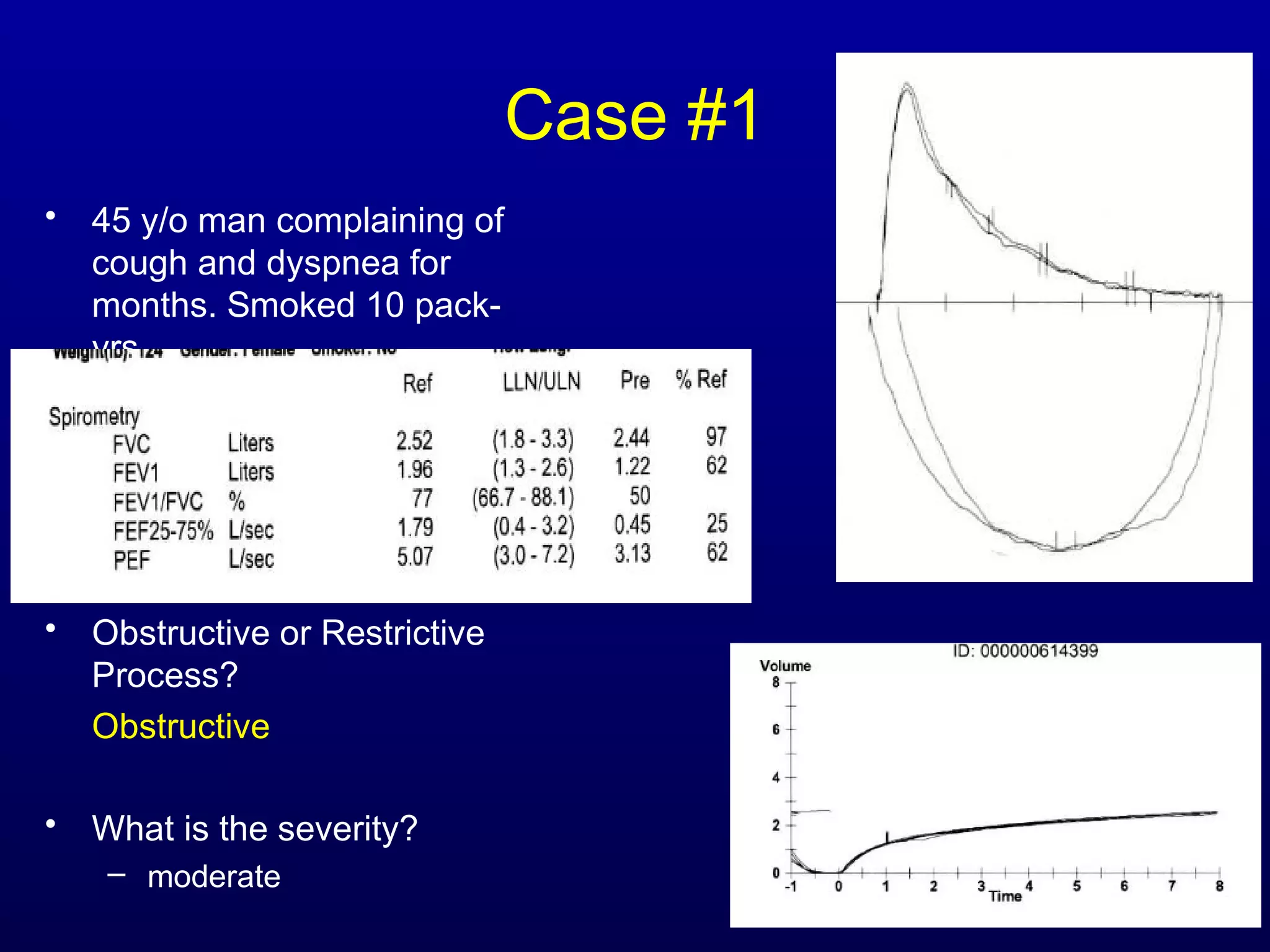
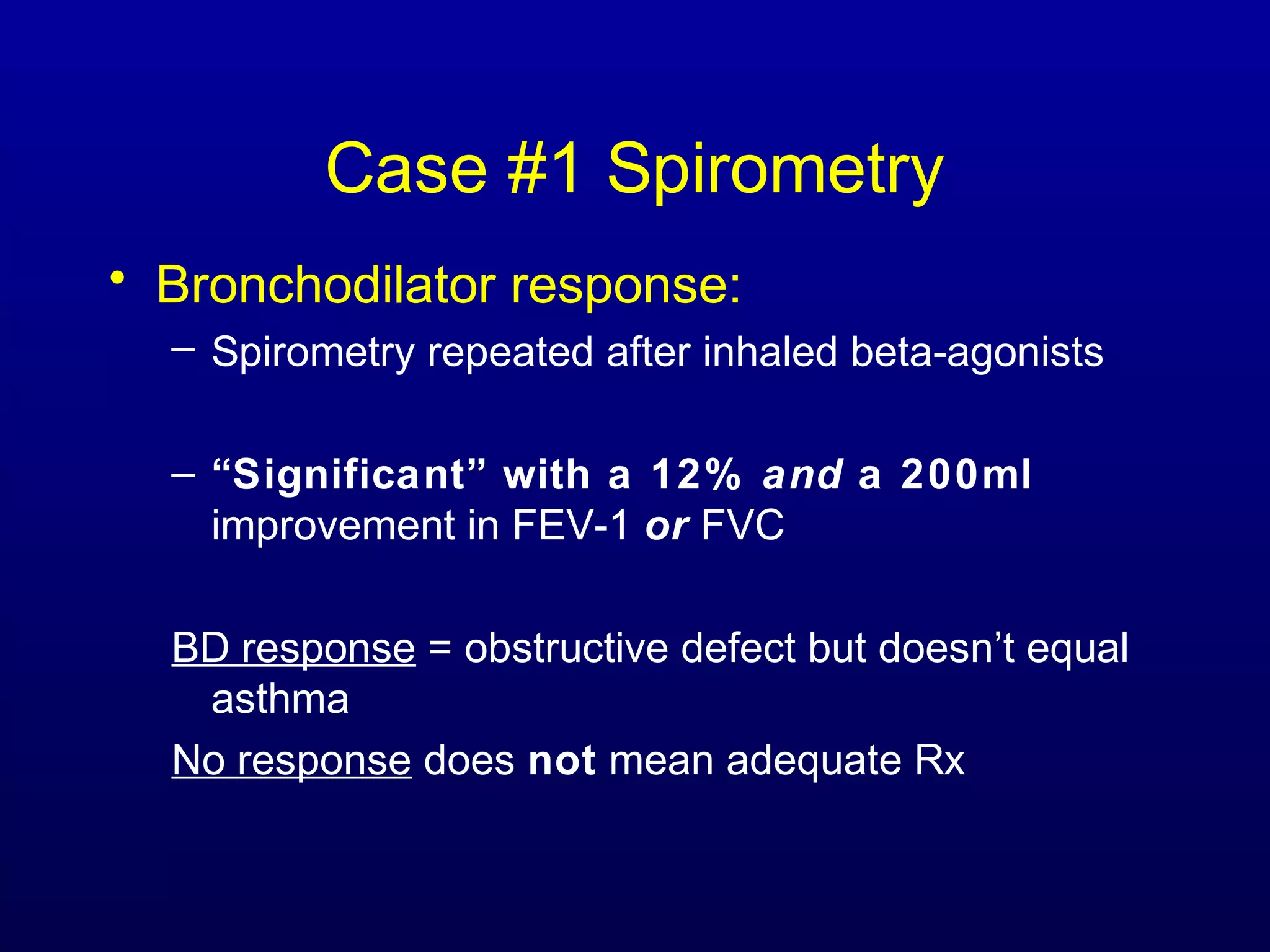
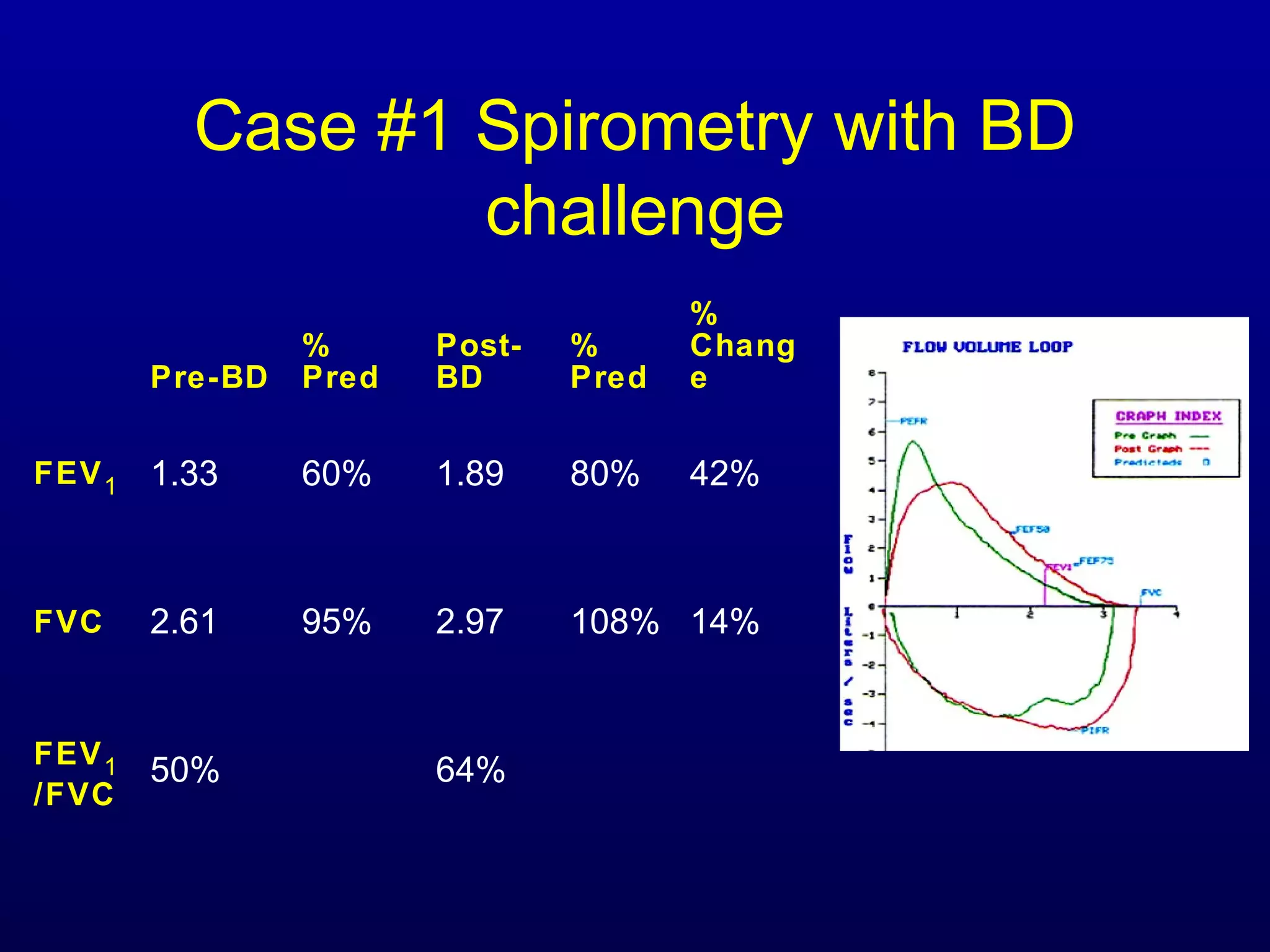
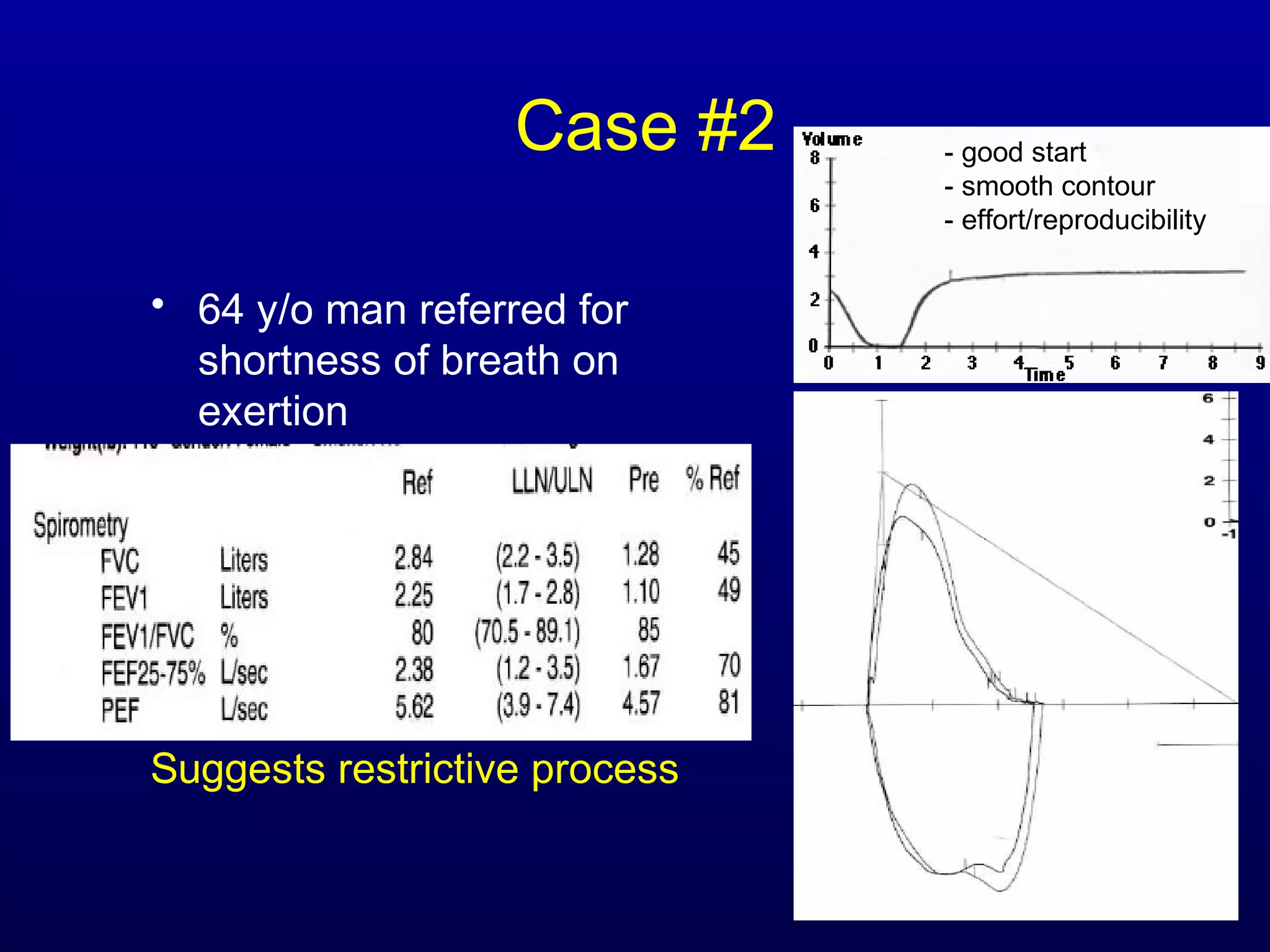
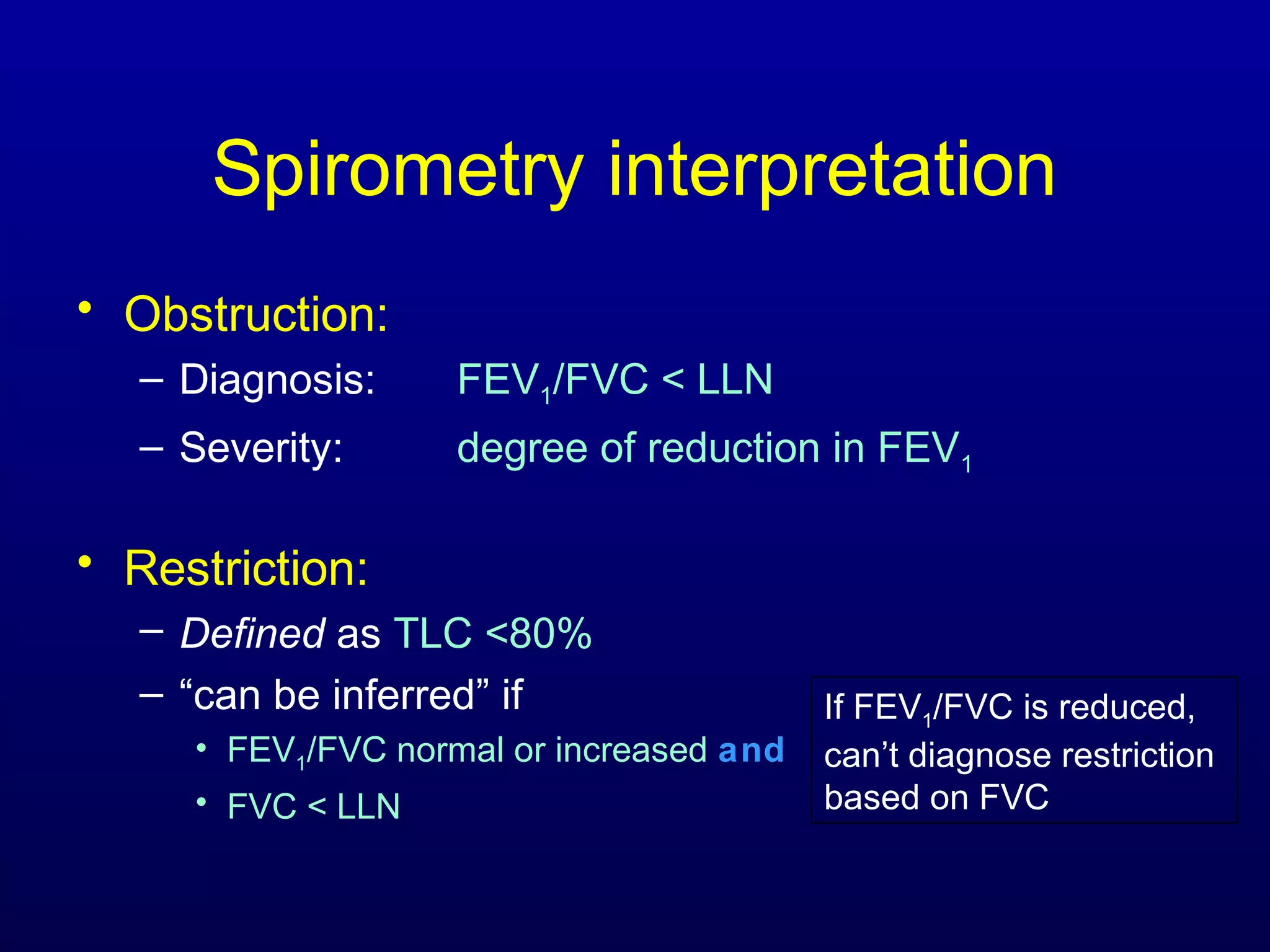
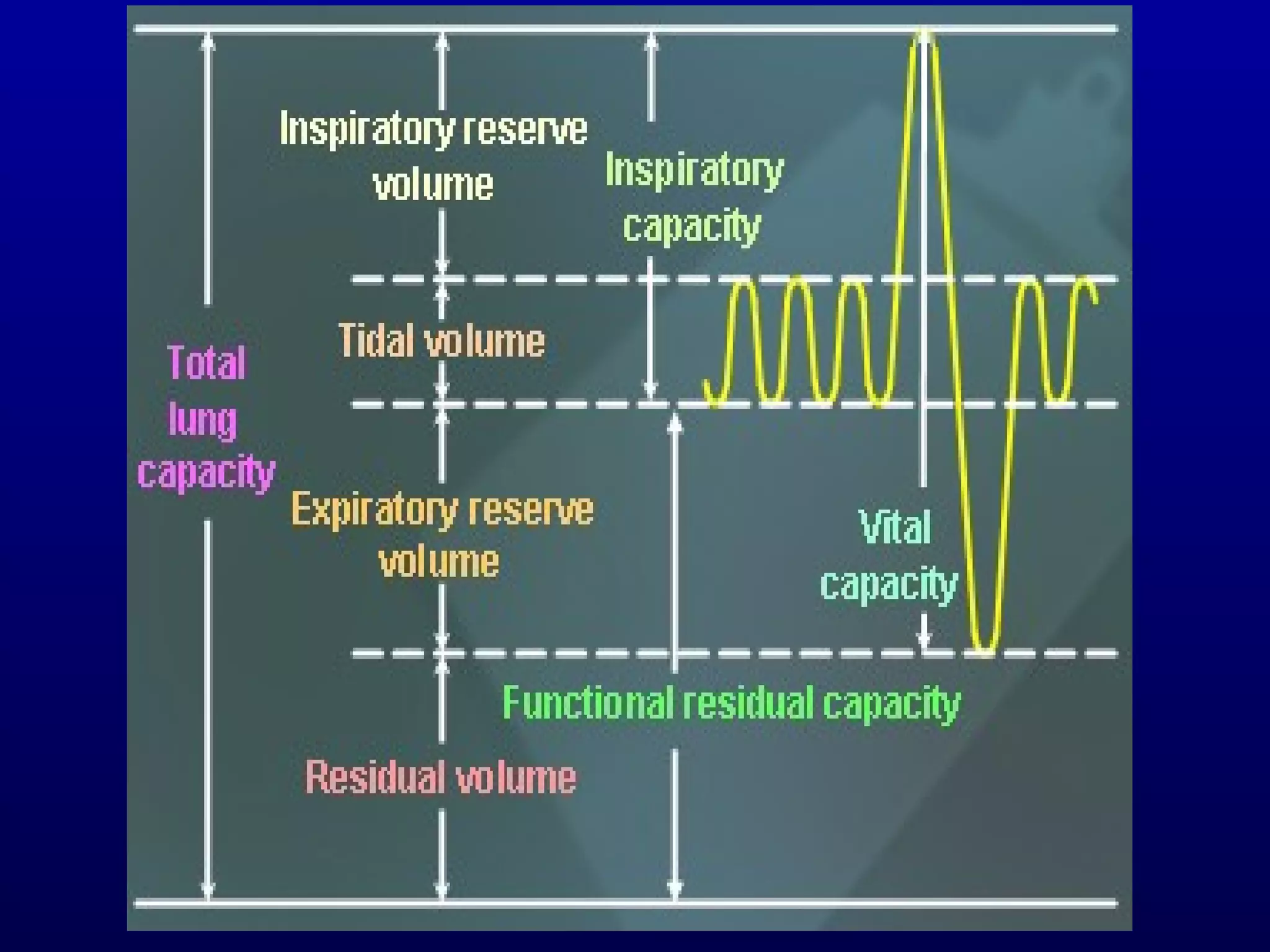
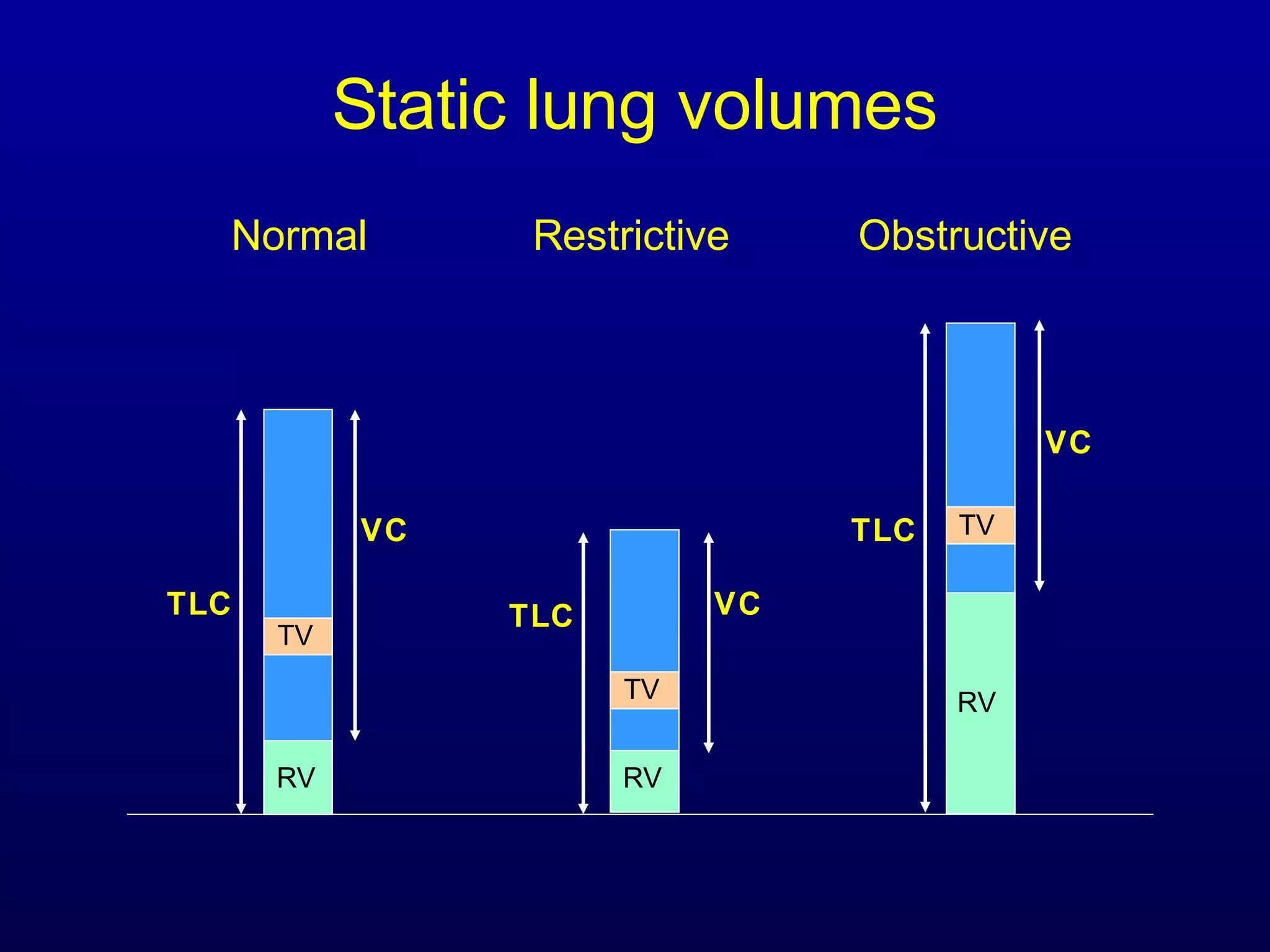
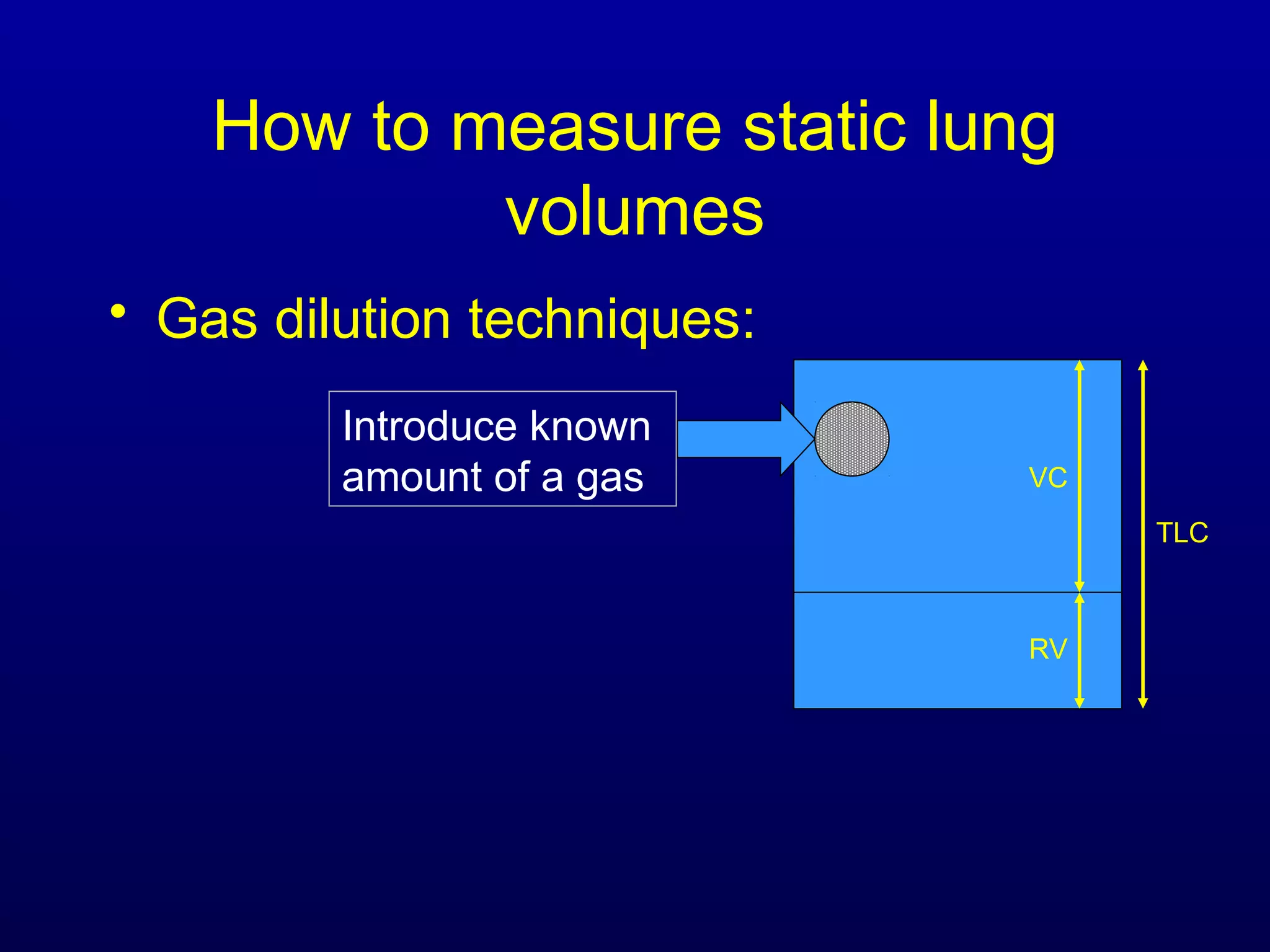
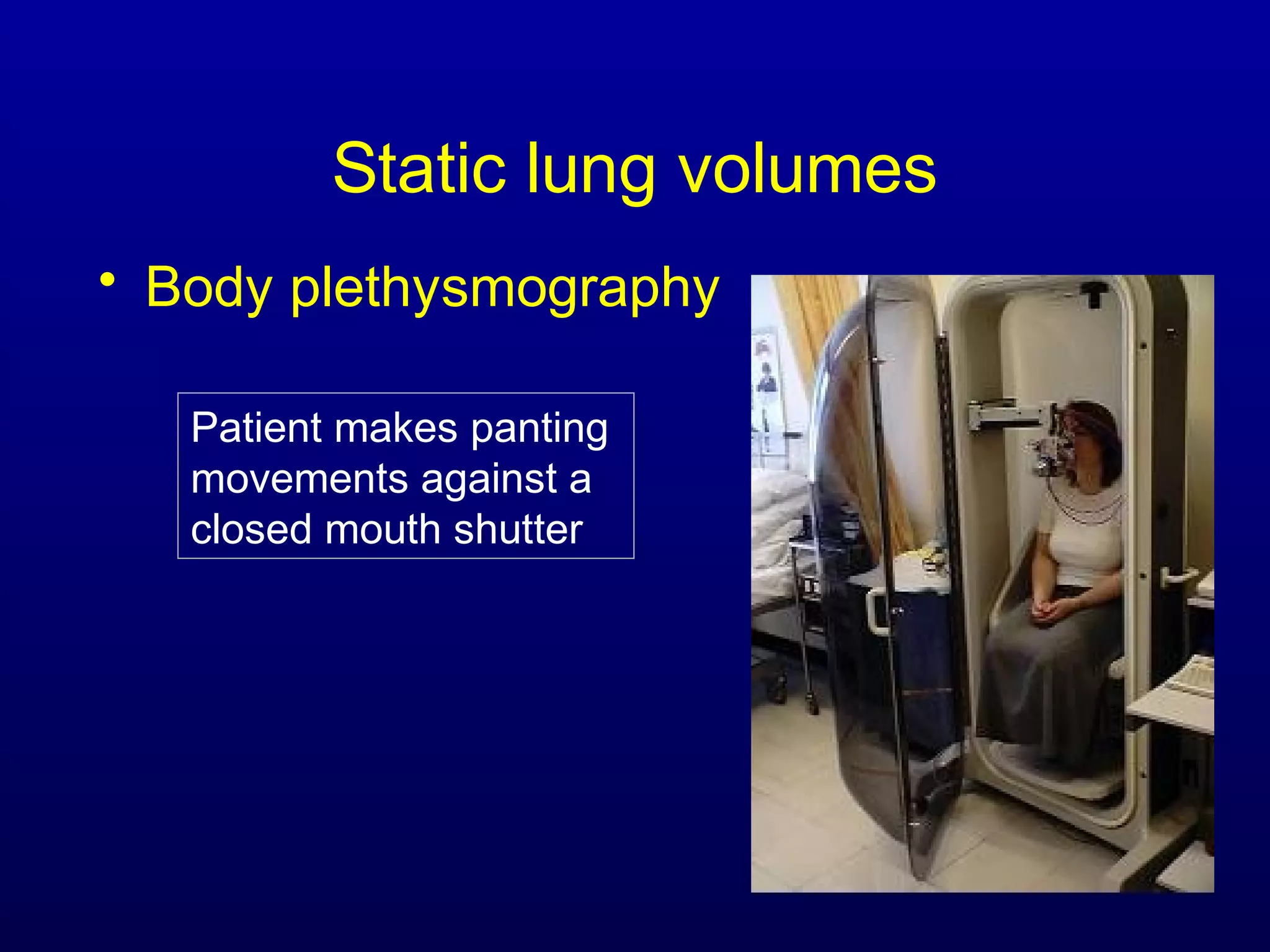
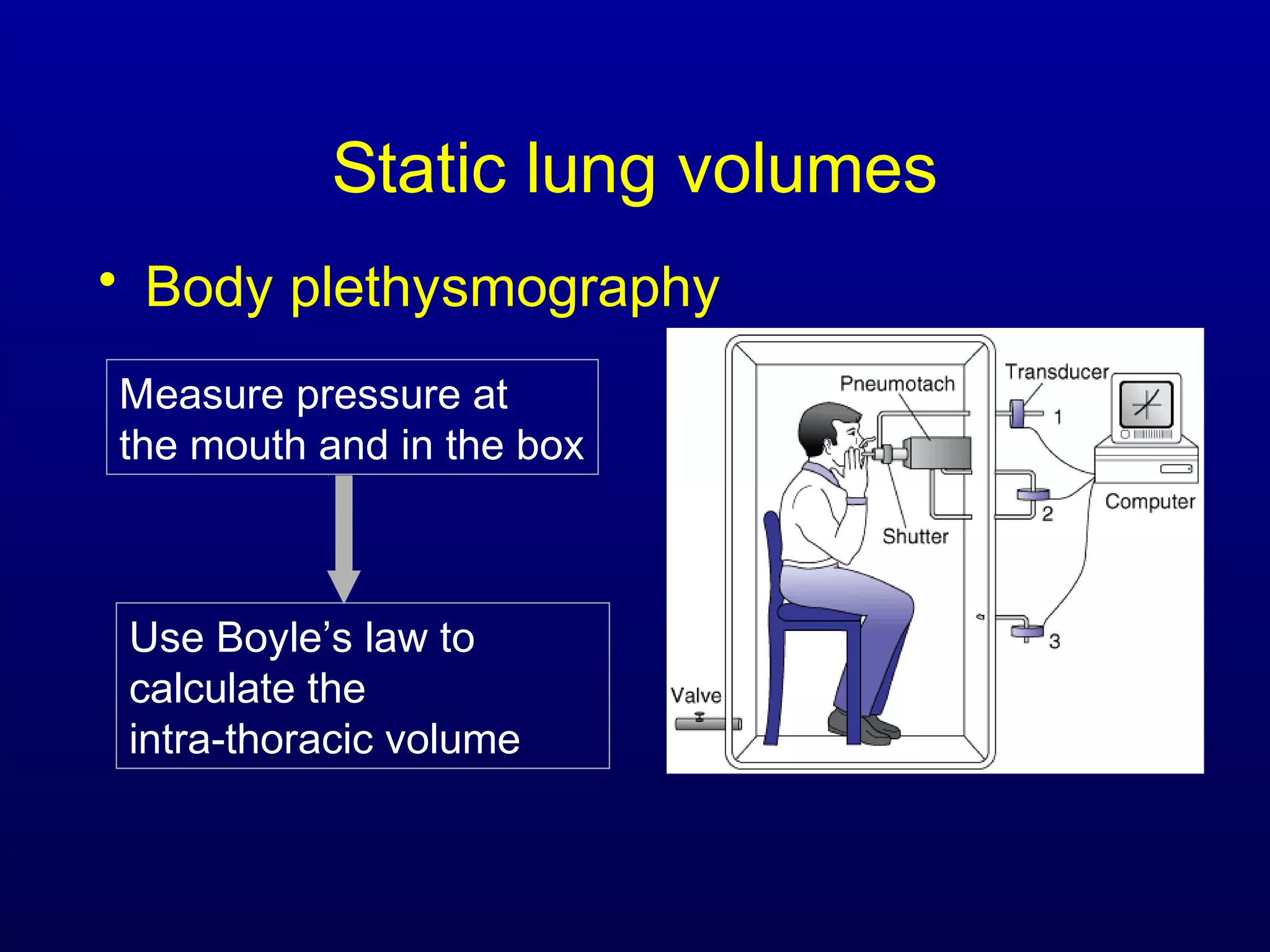
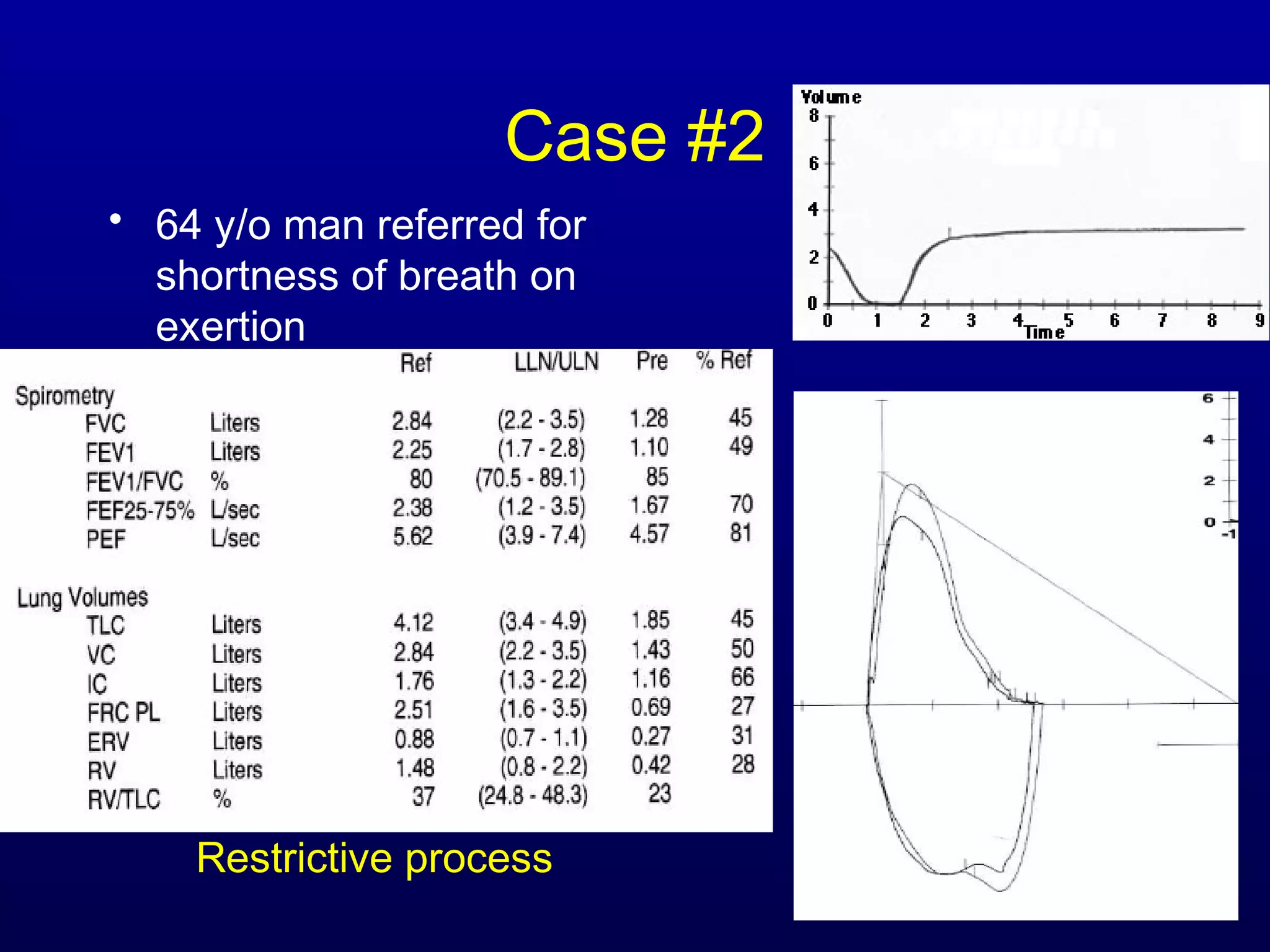
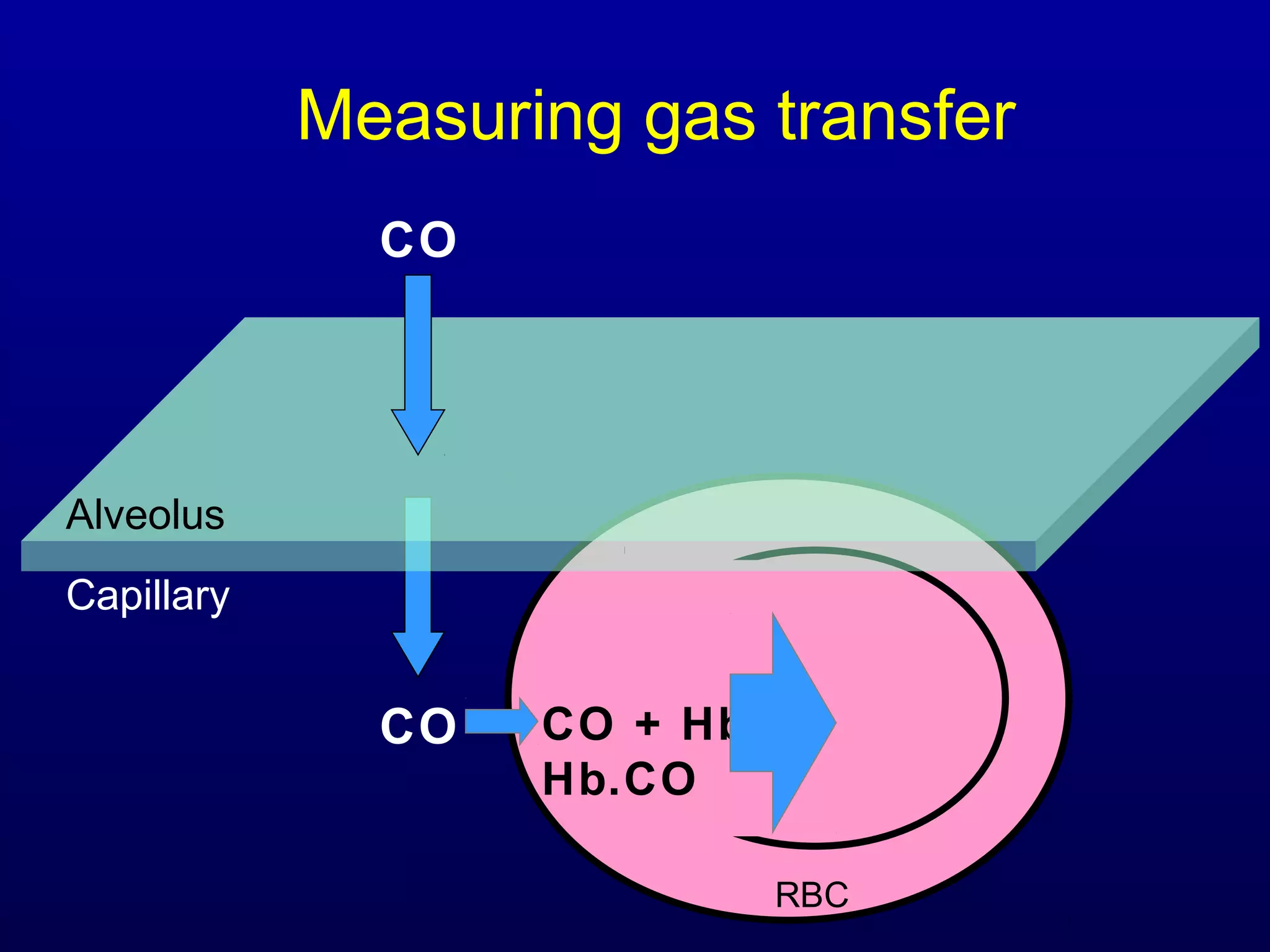
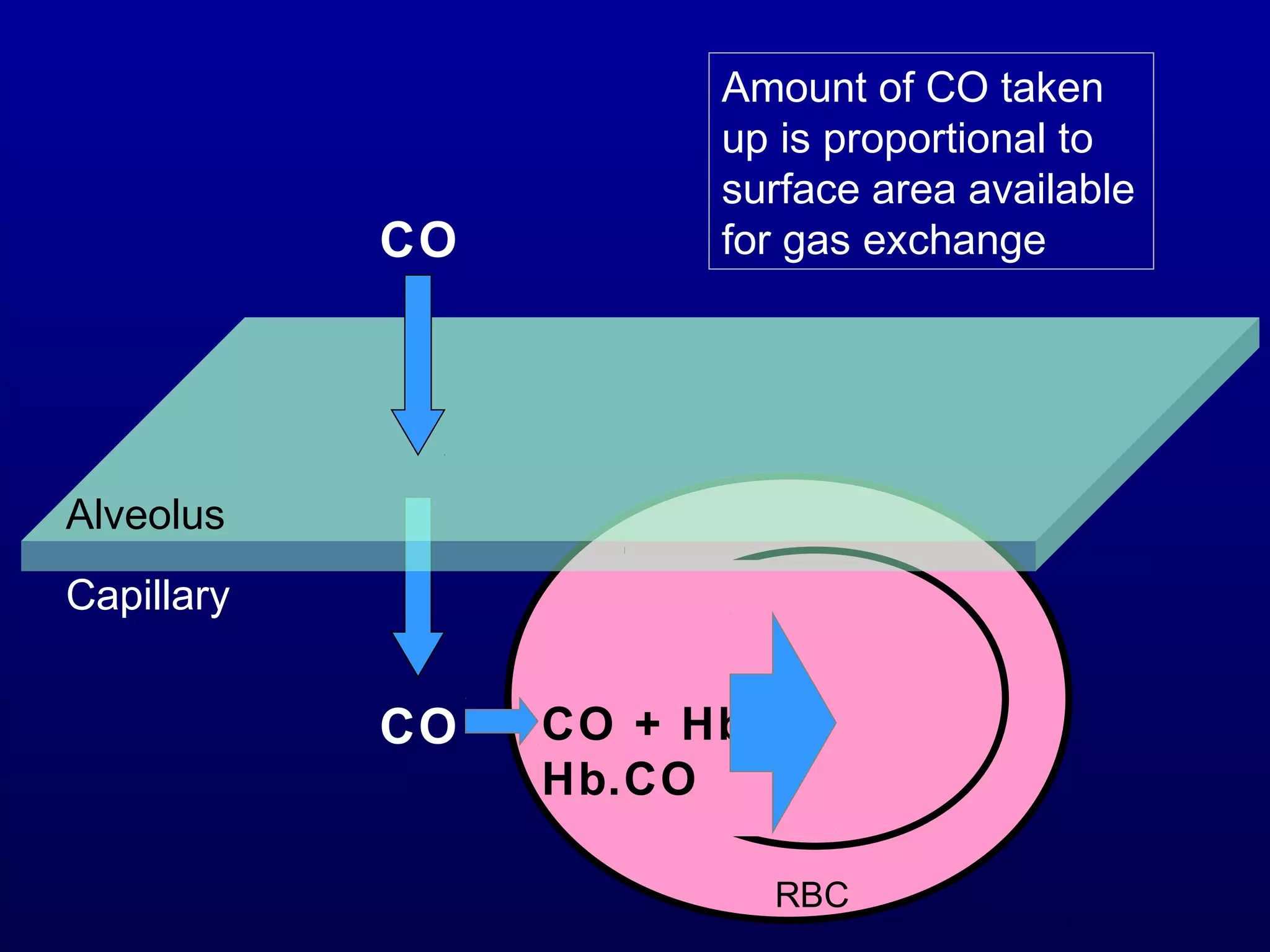
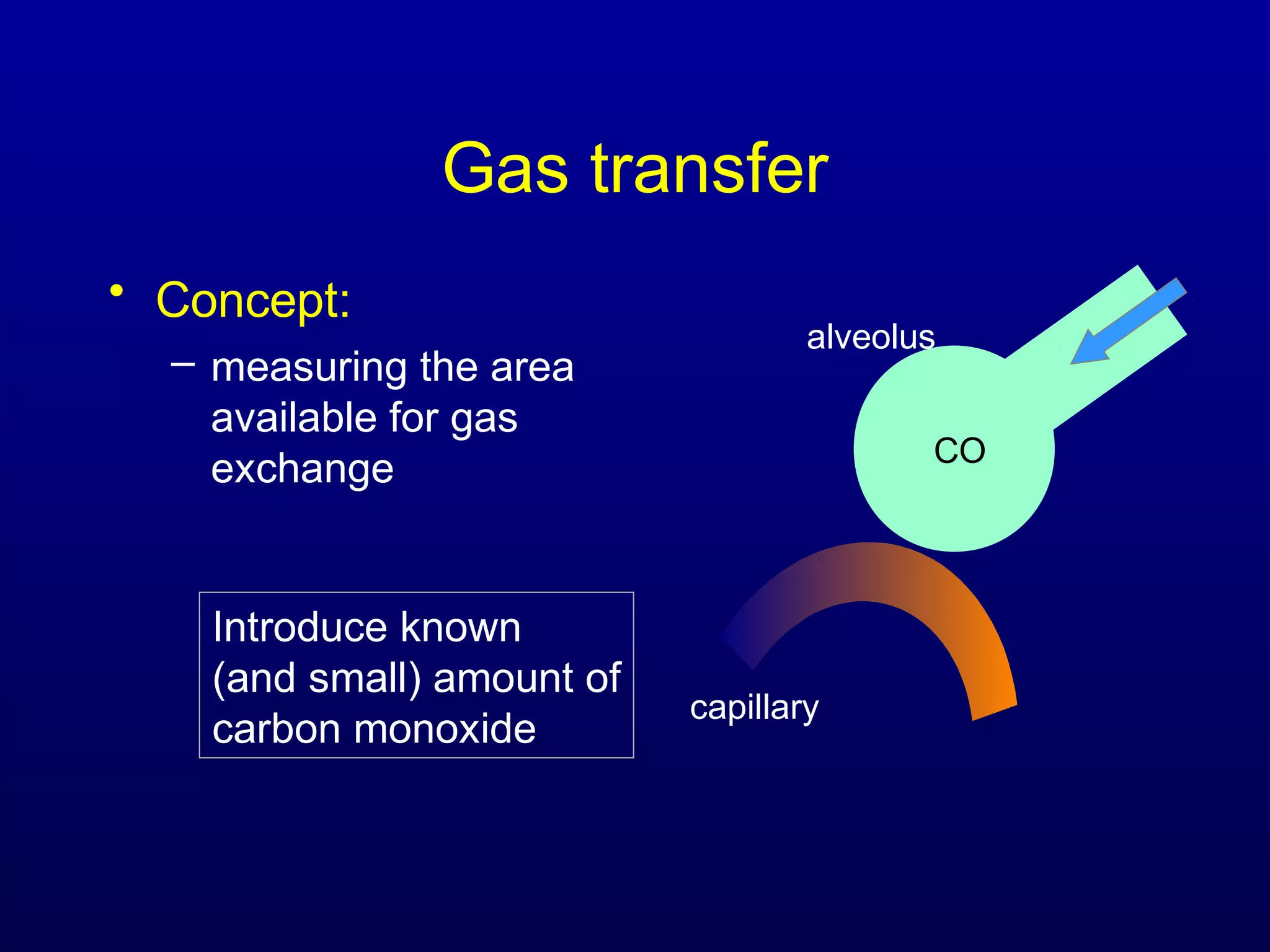
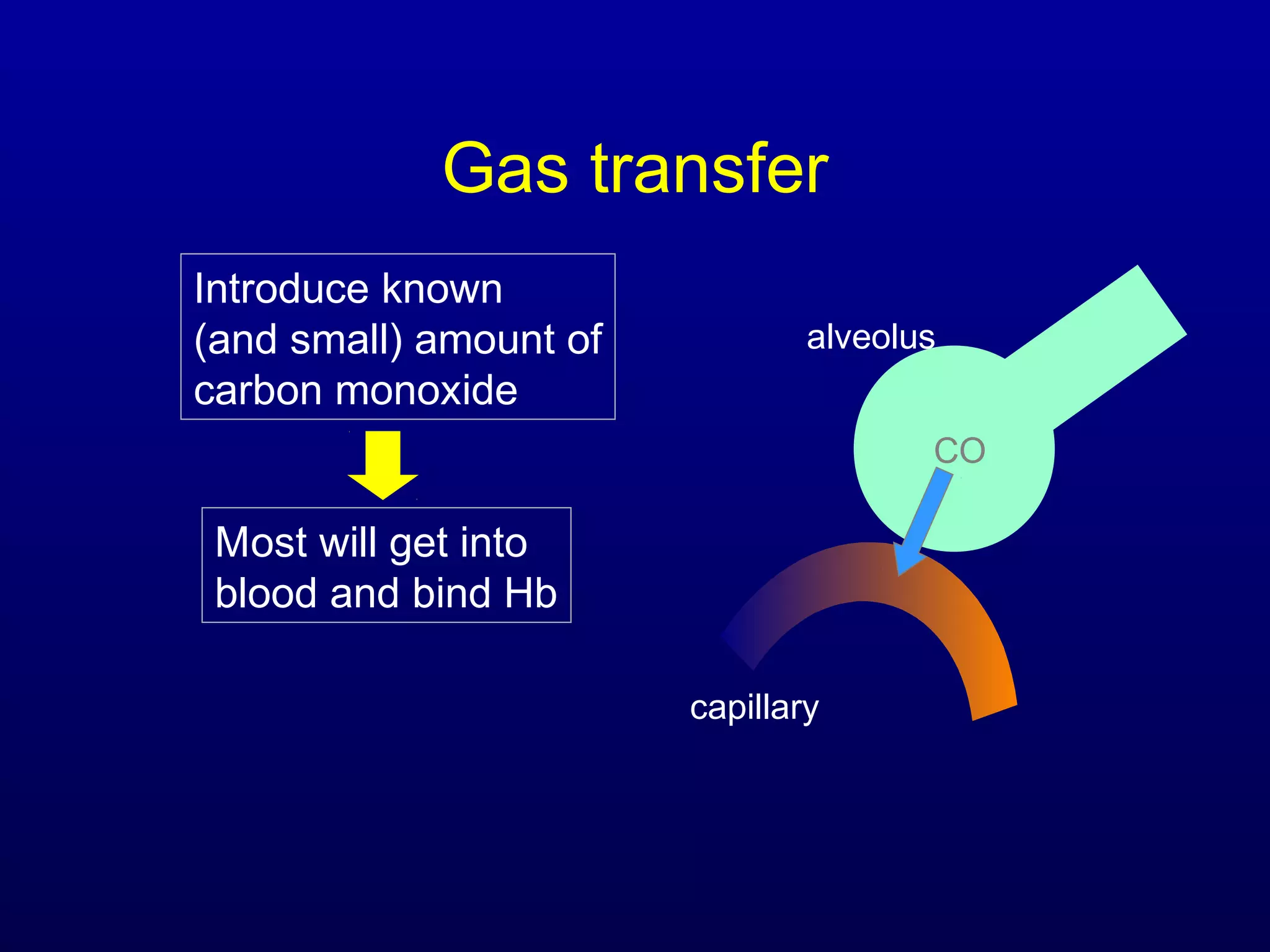
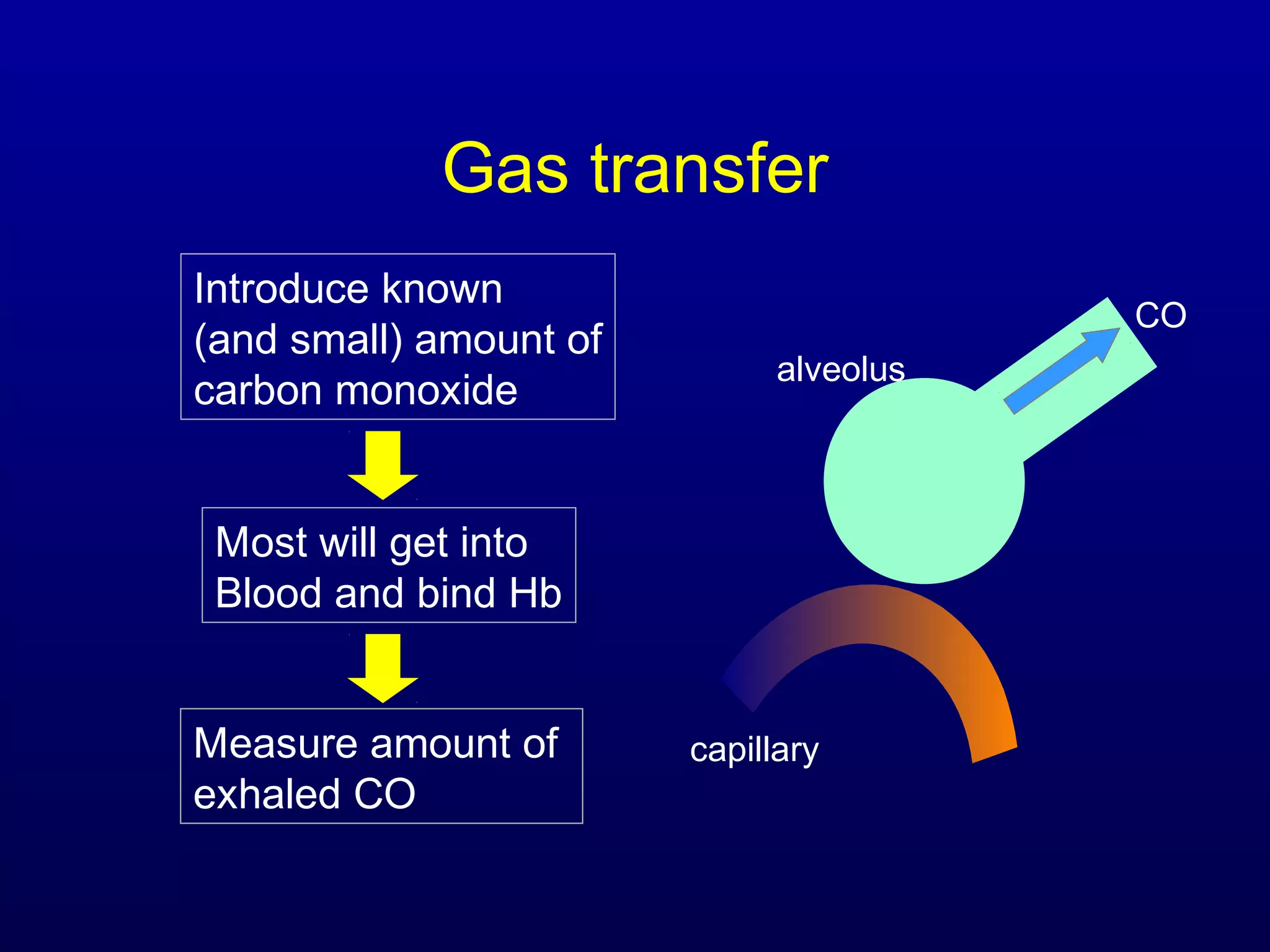
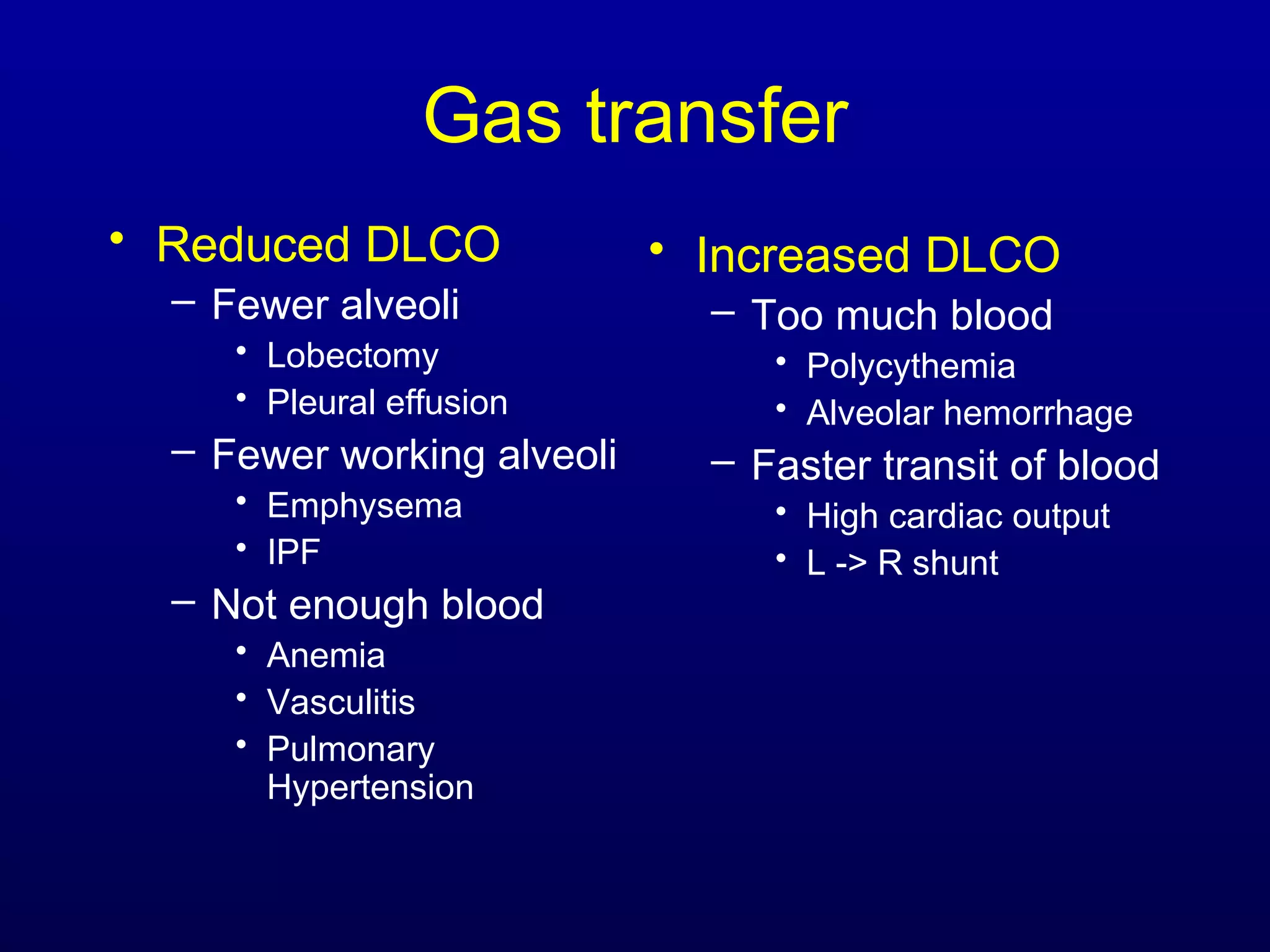
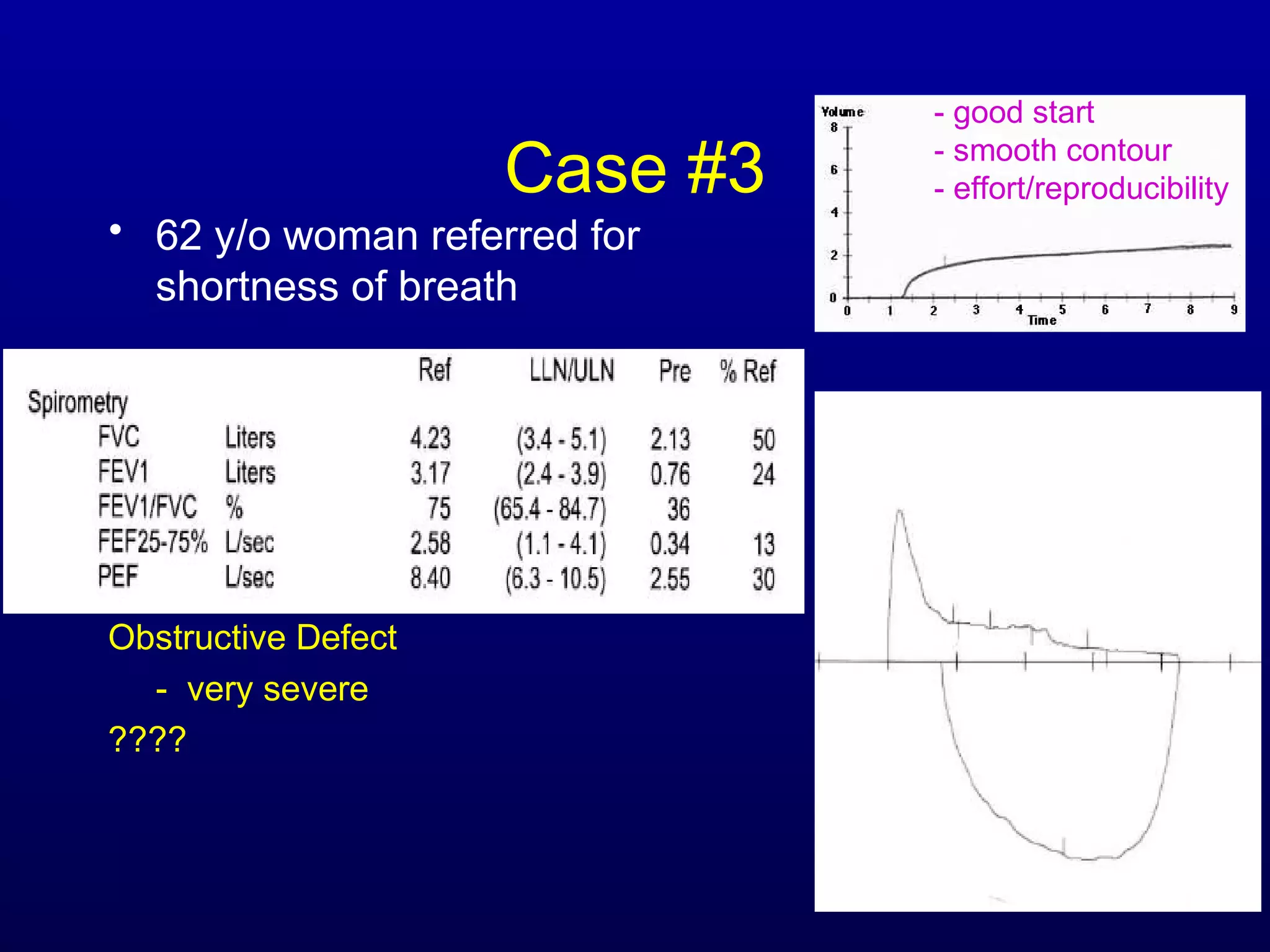
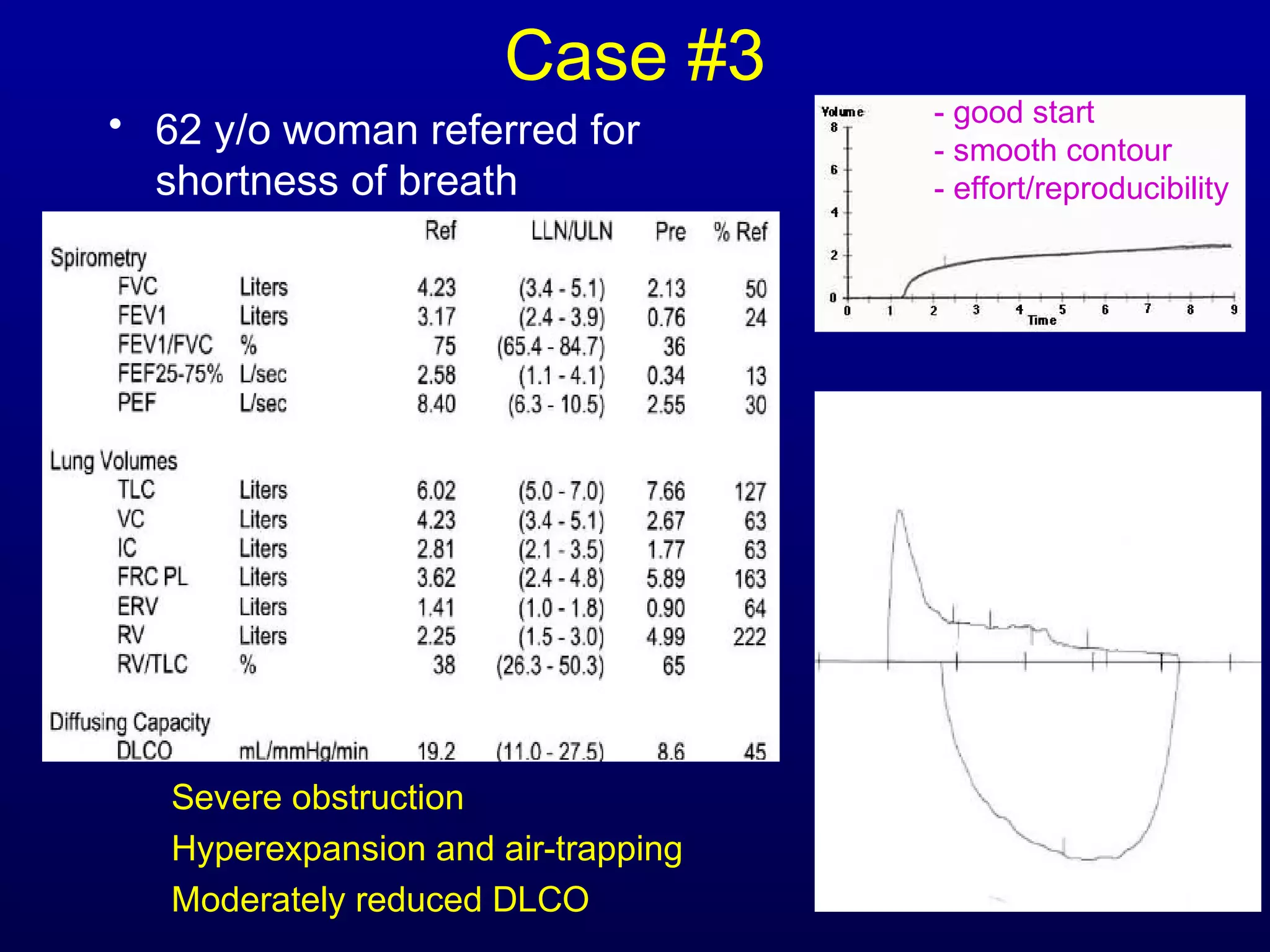
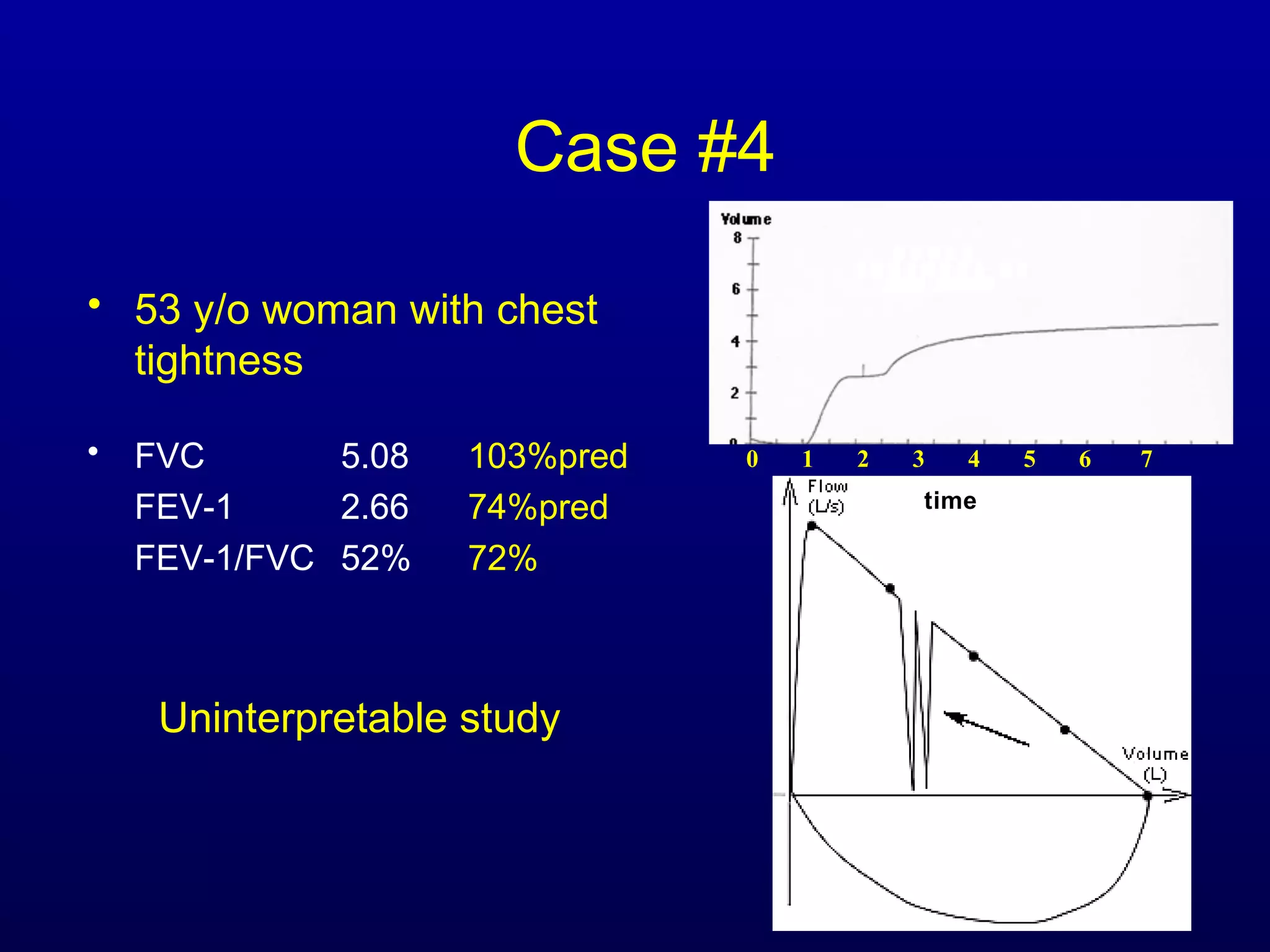
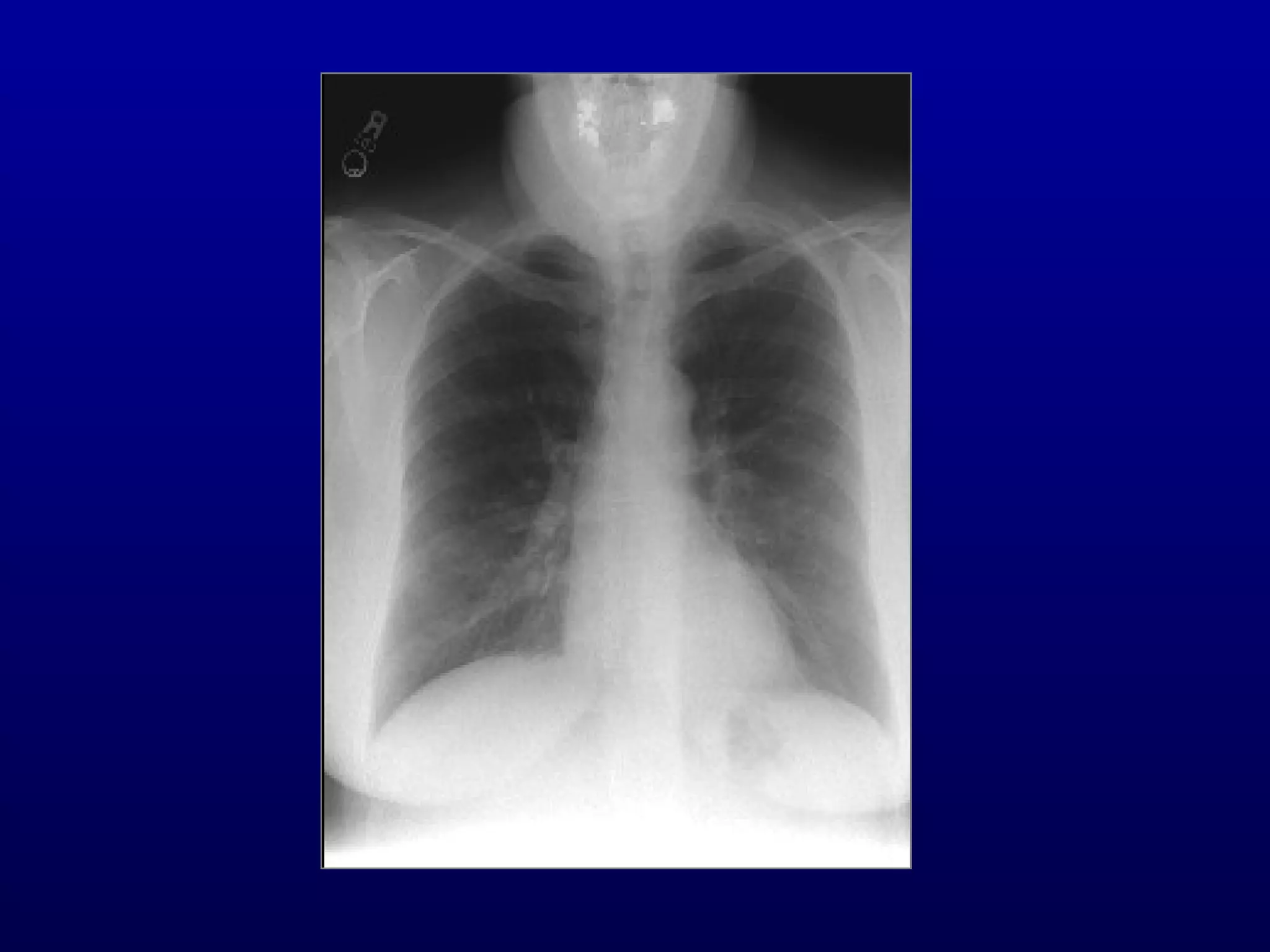
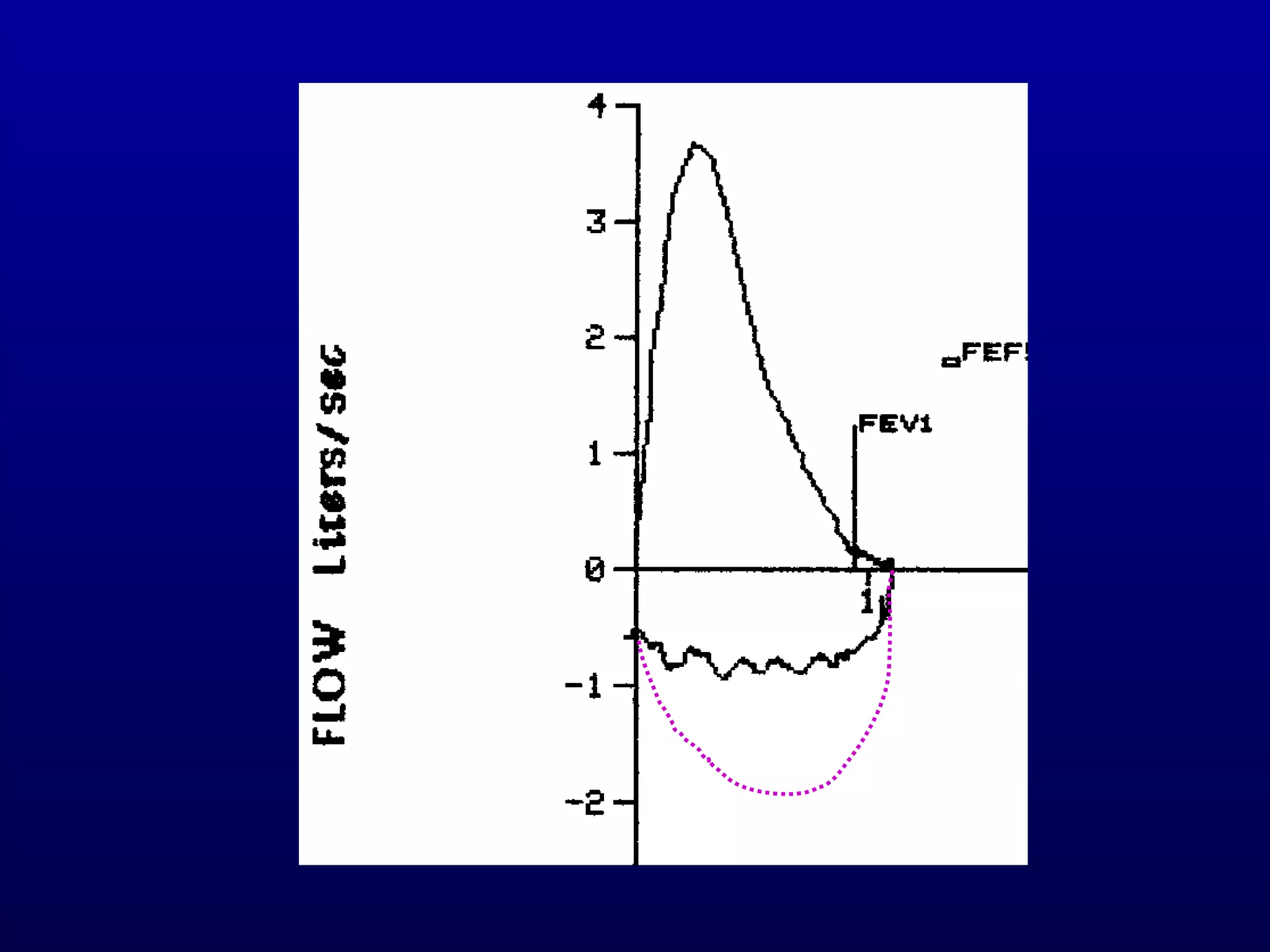
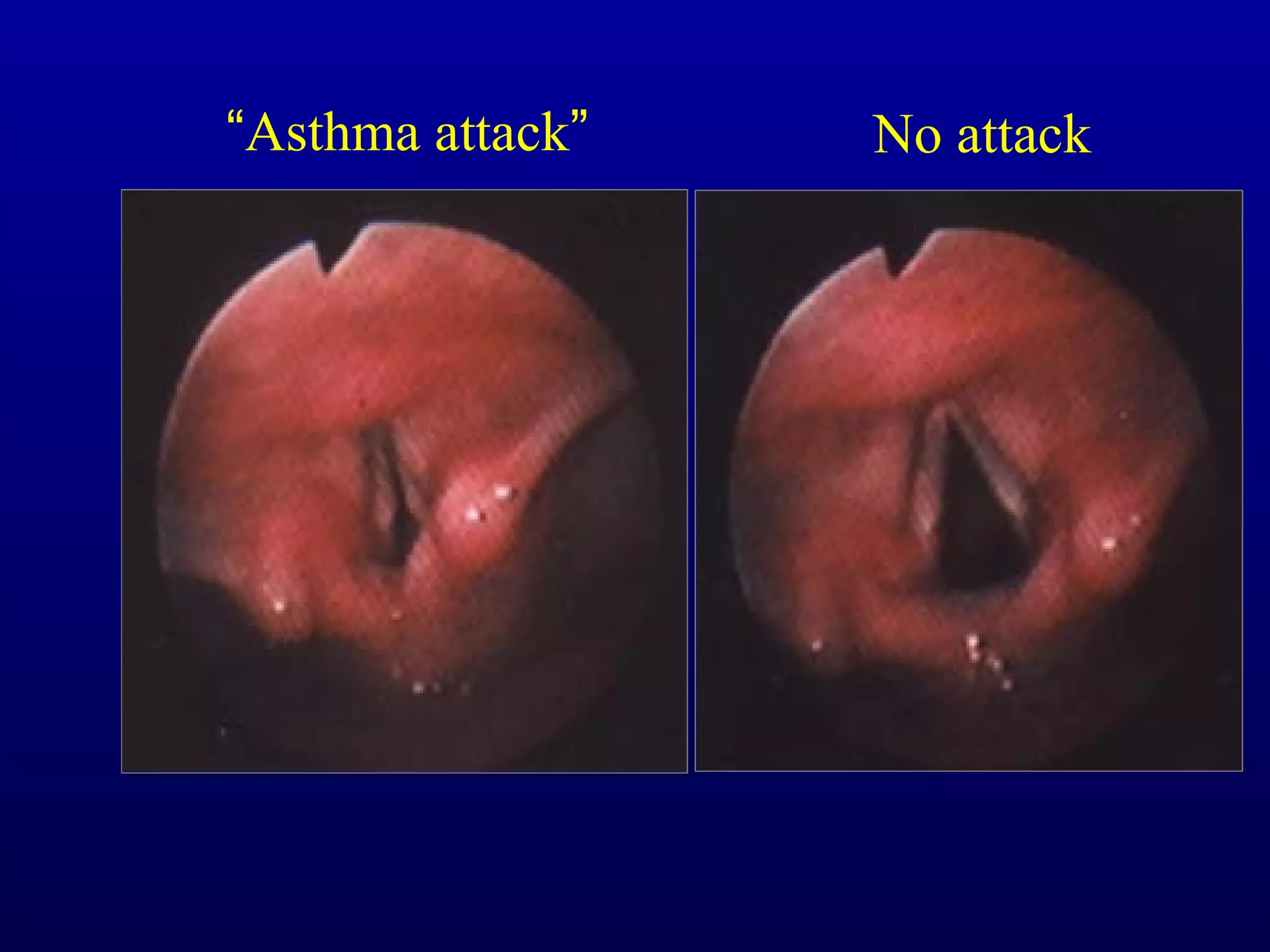
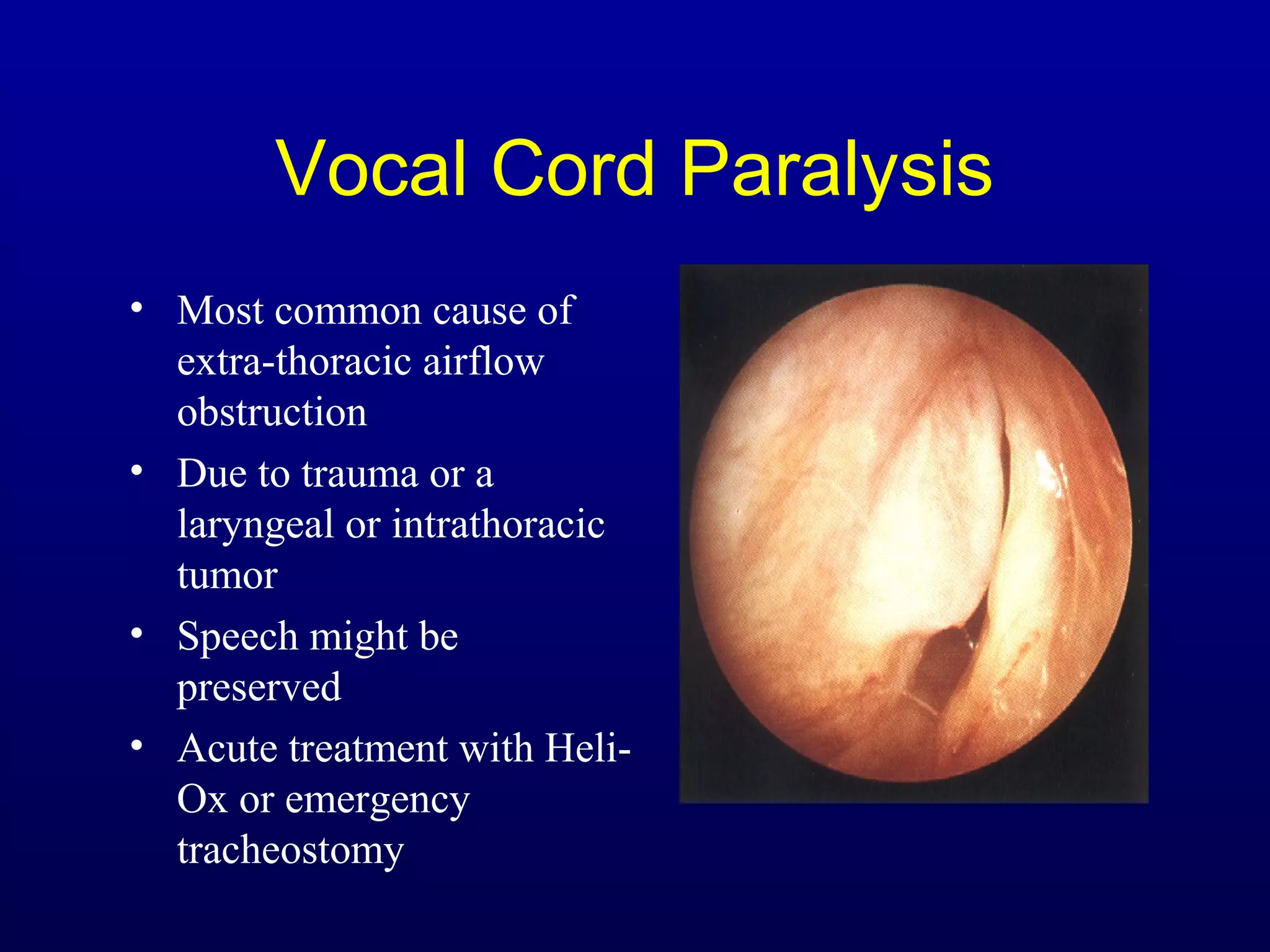
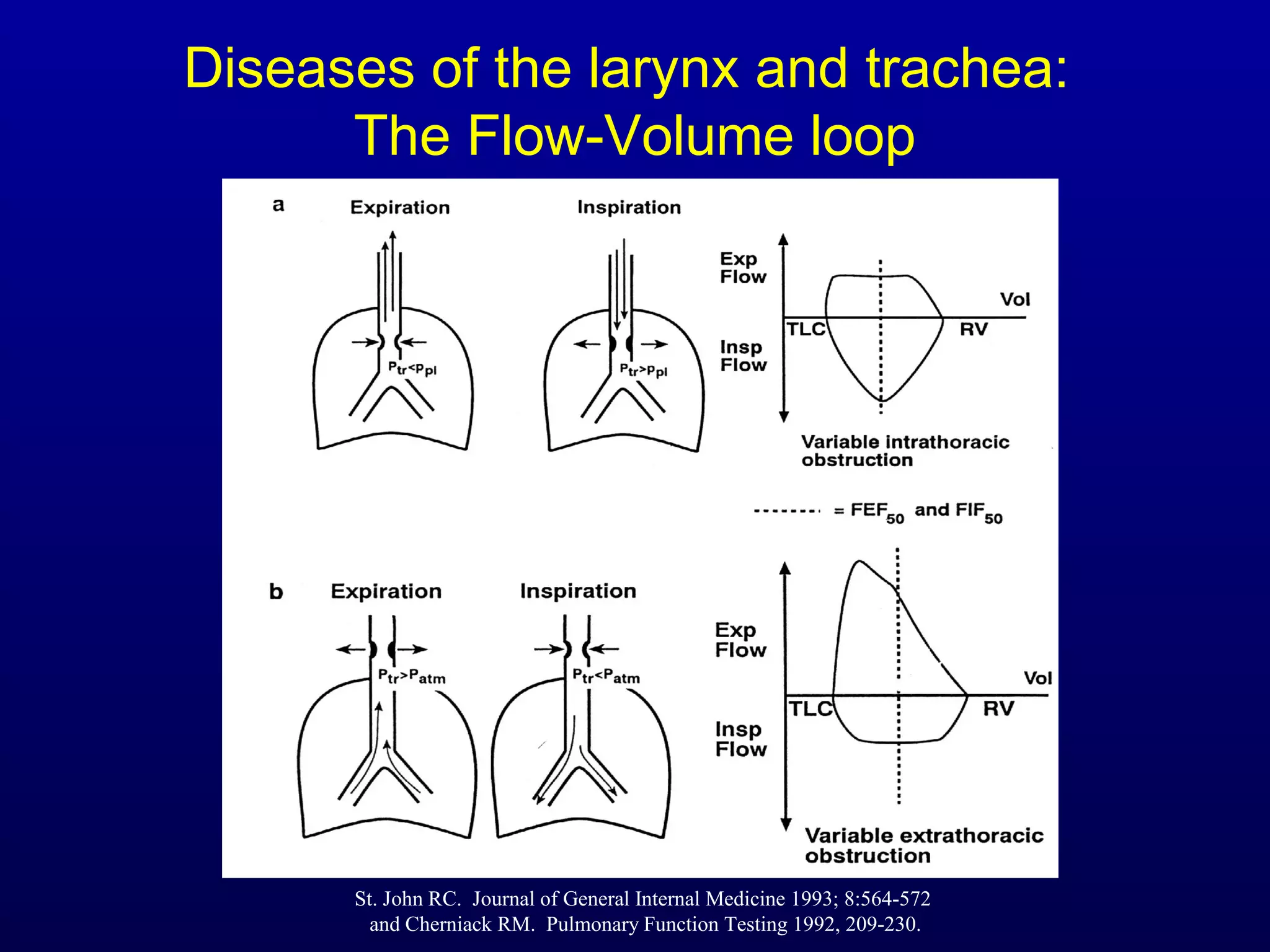
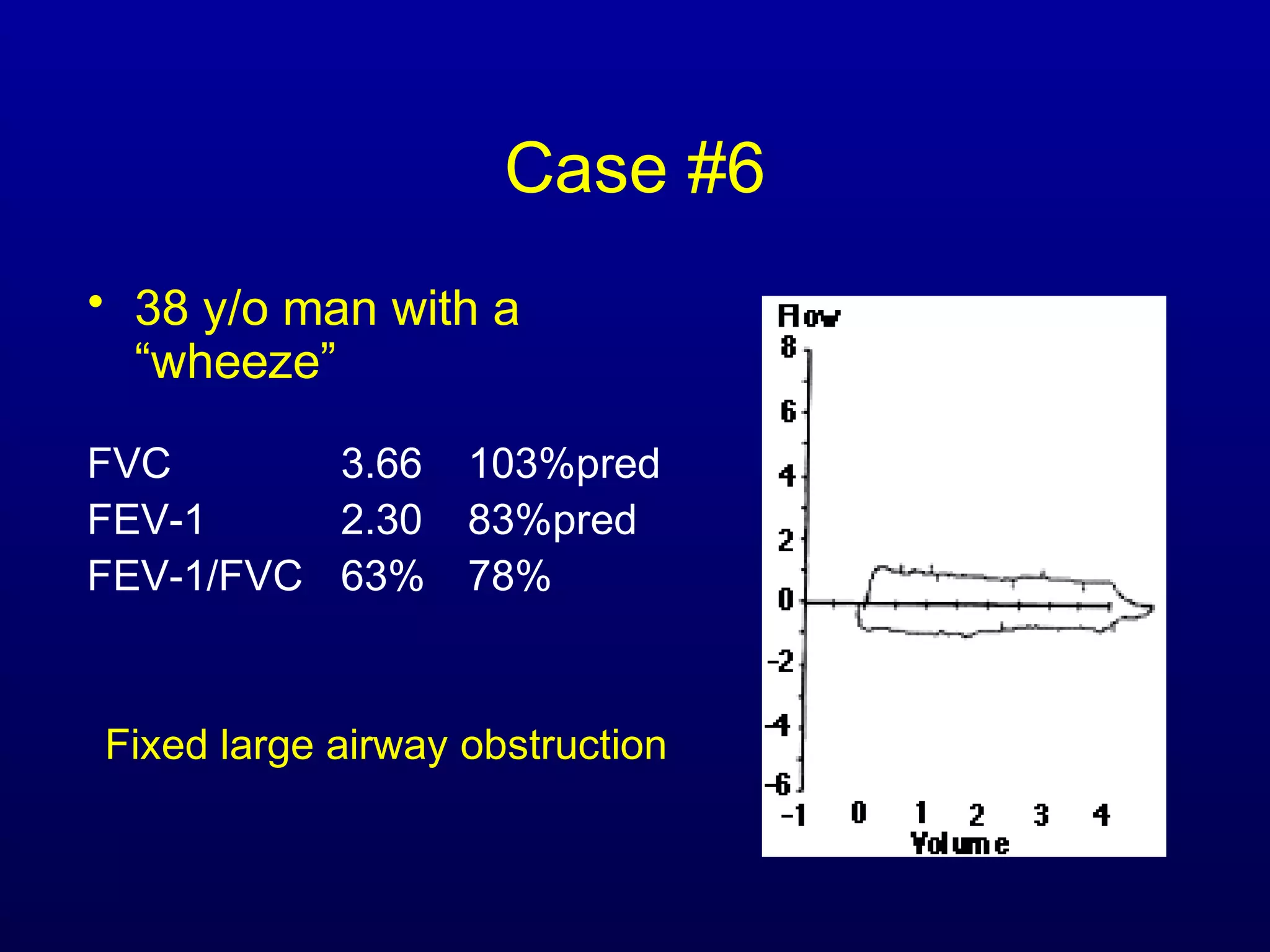
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) measure lung size and function through spirometry, static lung volumes, and gas transfer measurements to diagnose and assess diseases like COPD, asthma, and interstitial lung disease as well as evaluate treatment response and prognosis. PFTs involve forced exhalation and inhalation maneuvers to measure flows, volumes, and the surface area available for gas exchange. Abnormal PFT results can indicate obstructive or restrictive lung diseases and the severity is classified based on percentages of predicted values.