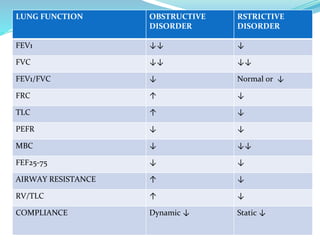
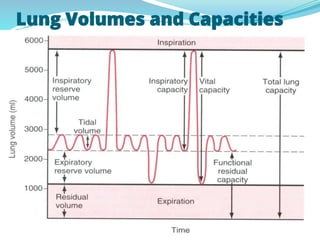
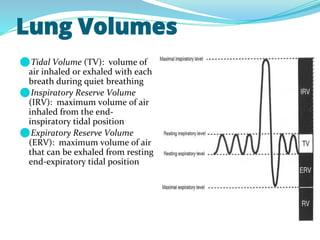
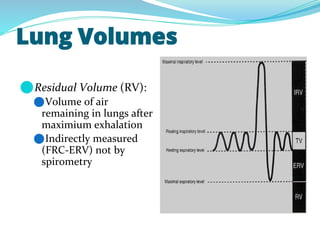
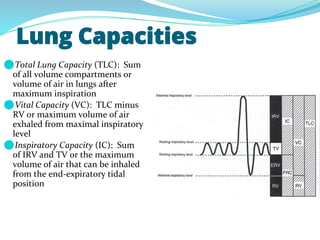
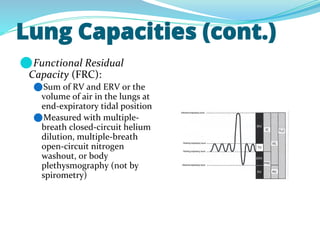
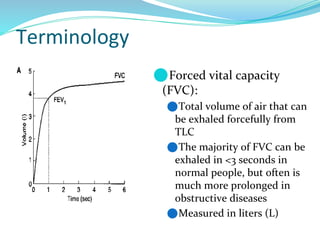
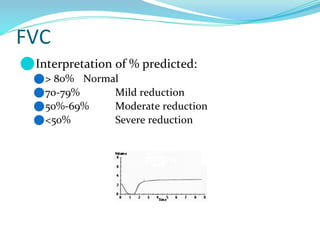
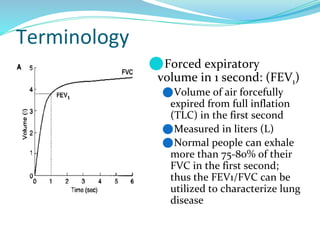
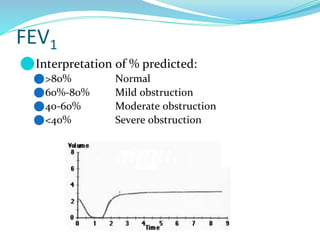
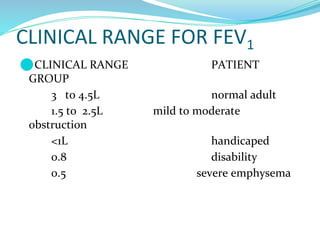
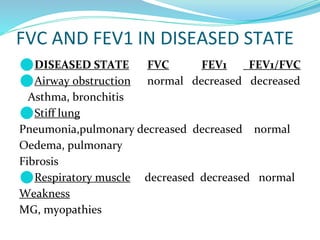
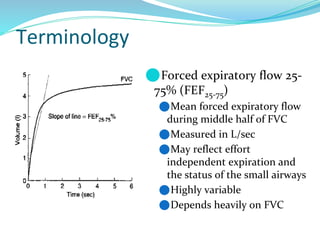
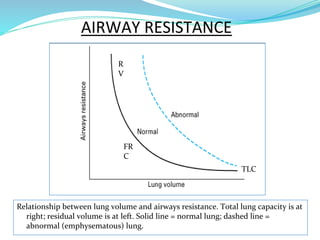
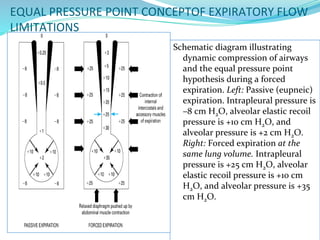
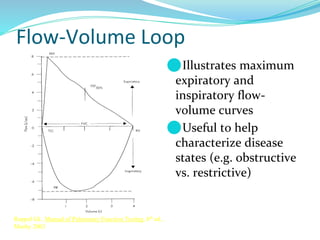
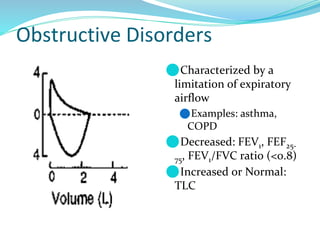
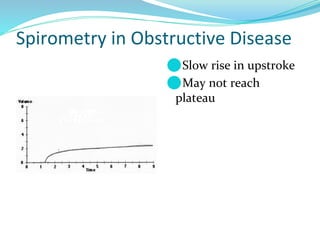
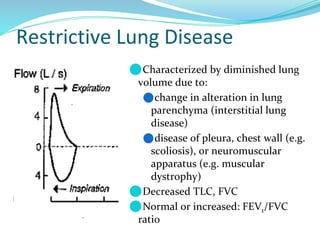
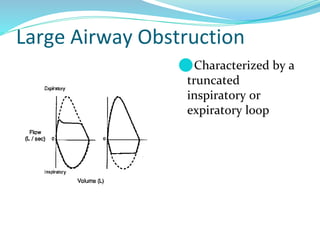
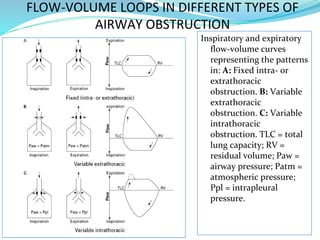
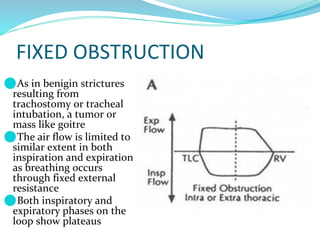
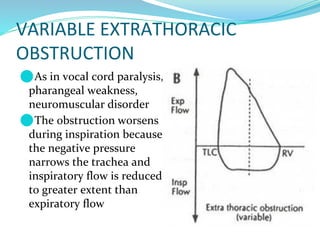
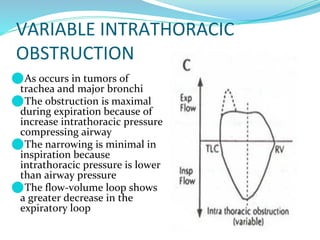
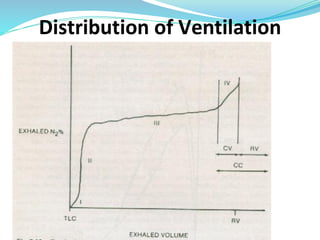
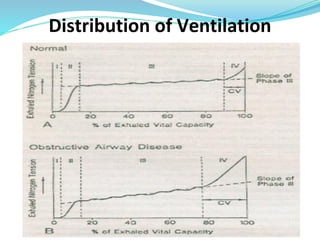
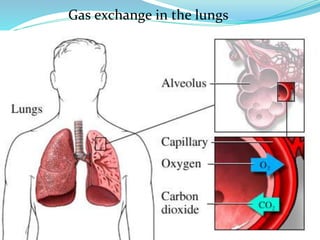
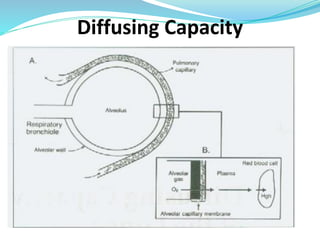
PFTs measure lung function through objective methods like spirometry, lung volumes, diffusing capacity, and exercise tests. They are useful for diagnosing pulmonary diseases, monitoring disease progression and treatment effectiveness, and assessing surgical risk. Spirometry specifically measures volumes of air inhaled and exhaled over time through tests like FVC, FEV1, and FEF25-75. Flow-volume loops can help characterize obstructive, restrictive, and mixed lung diseases. Bronchodilator tests assess reversibility of airway obstruction.










































![Bicarbonate
⚫A calculated value from:
[H+] = 24 * (PaCO2/[HCO3
-])
⚫Values alter due to acidosis/alkalosis
⚫Base excess is calculated directly using PaCO2, pH,
and bicarbonate values
⚫Rule: a decrease in bicarb. by 10 mmoles decreases
the pH by 0.15, likewise, an increase in bicarb. By 10
mmoles increases pH by 0.15
⚫A bicarb. of 13 would result in a pH of 7.25
⚫Total body bicarb. deficit = (base deficit * wt in Kg *
0.4), in mEq/L, usually replace ½ of deficit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonarypftfunctests-231206064723-c393feb7/85/pulmonaryPFTfunc-Tests-pdf-71-320.jpg)