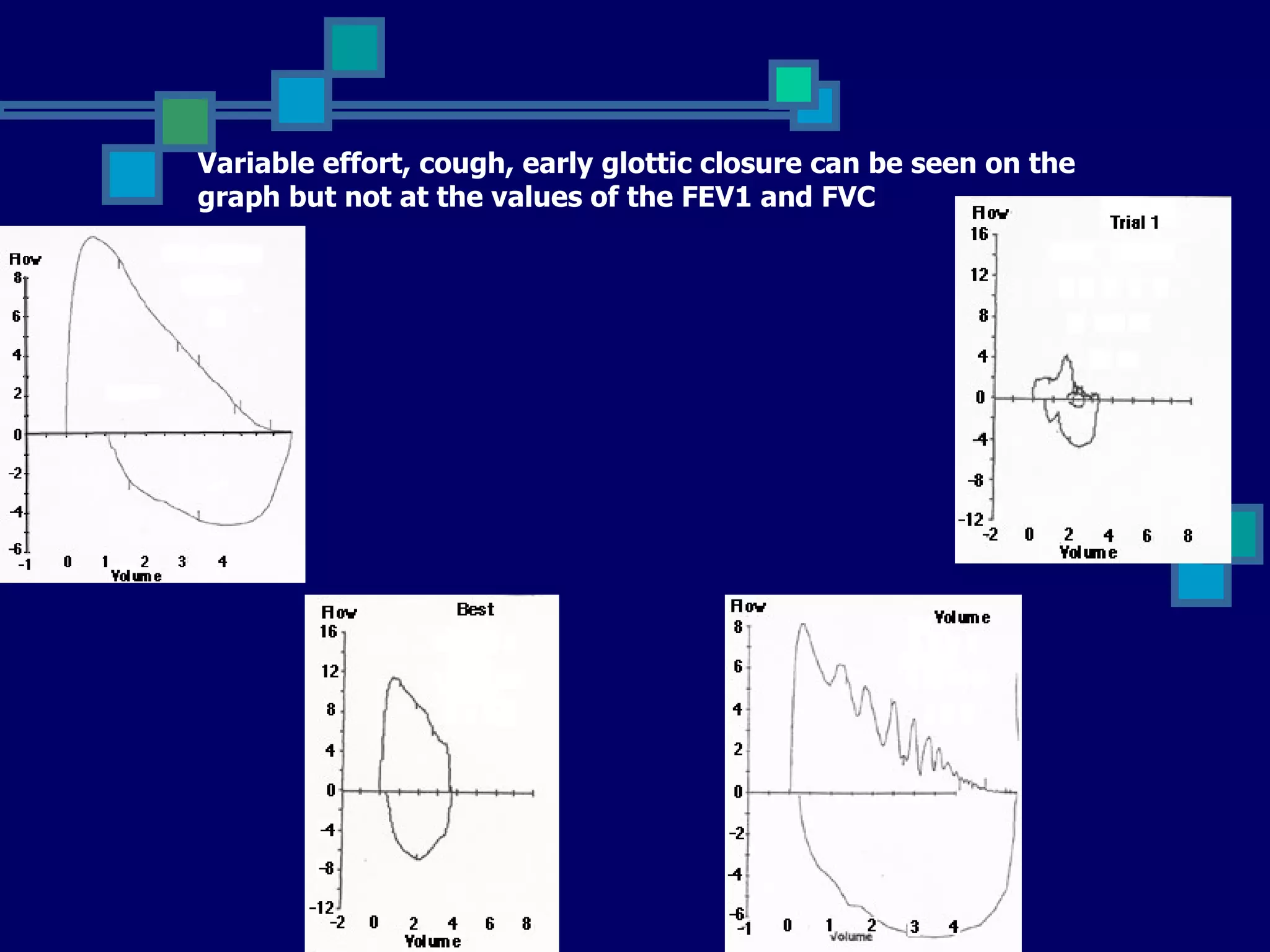
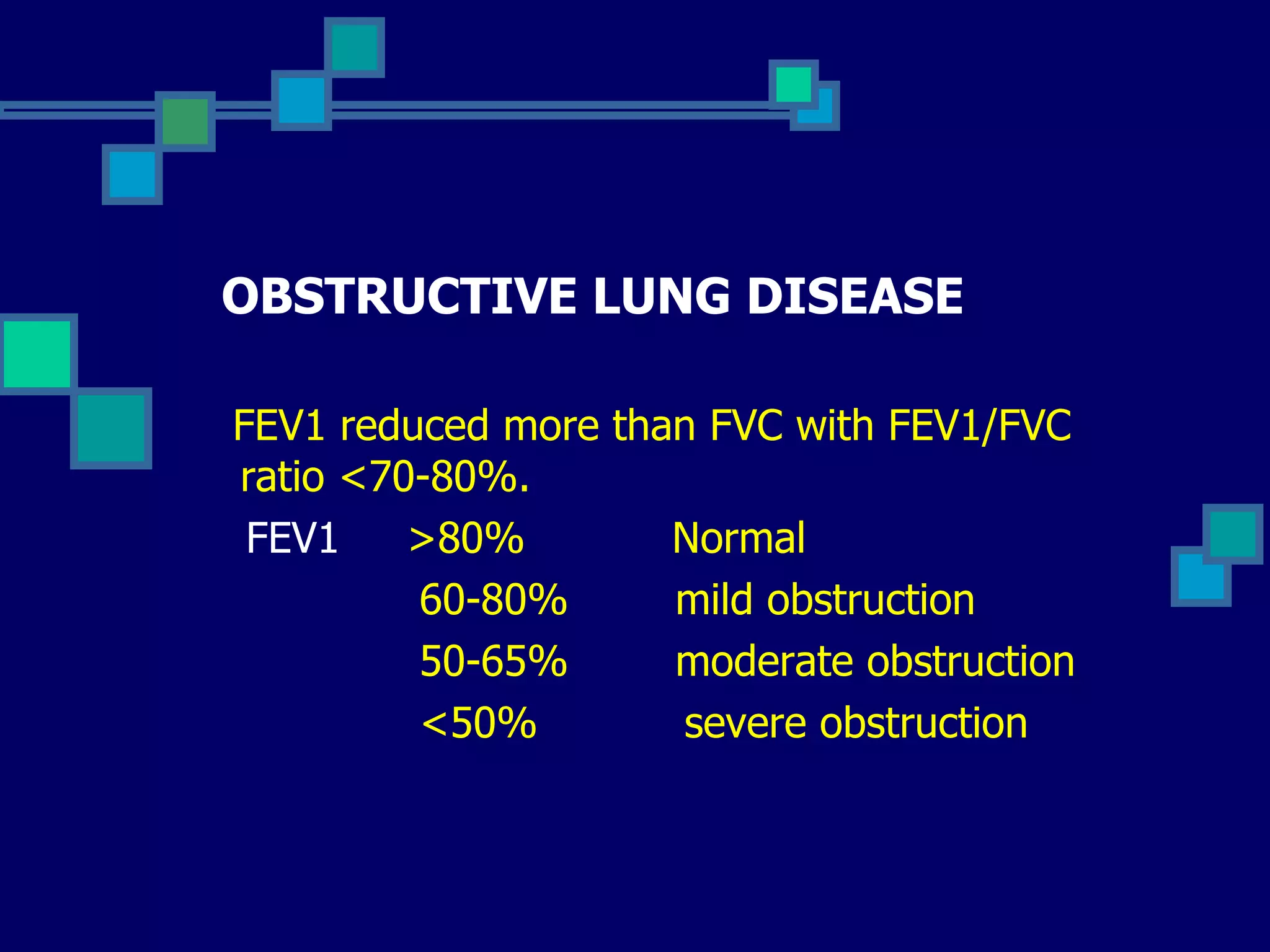
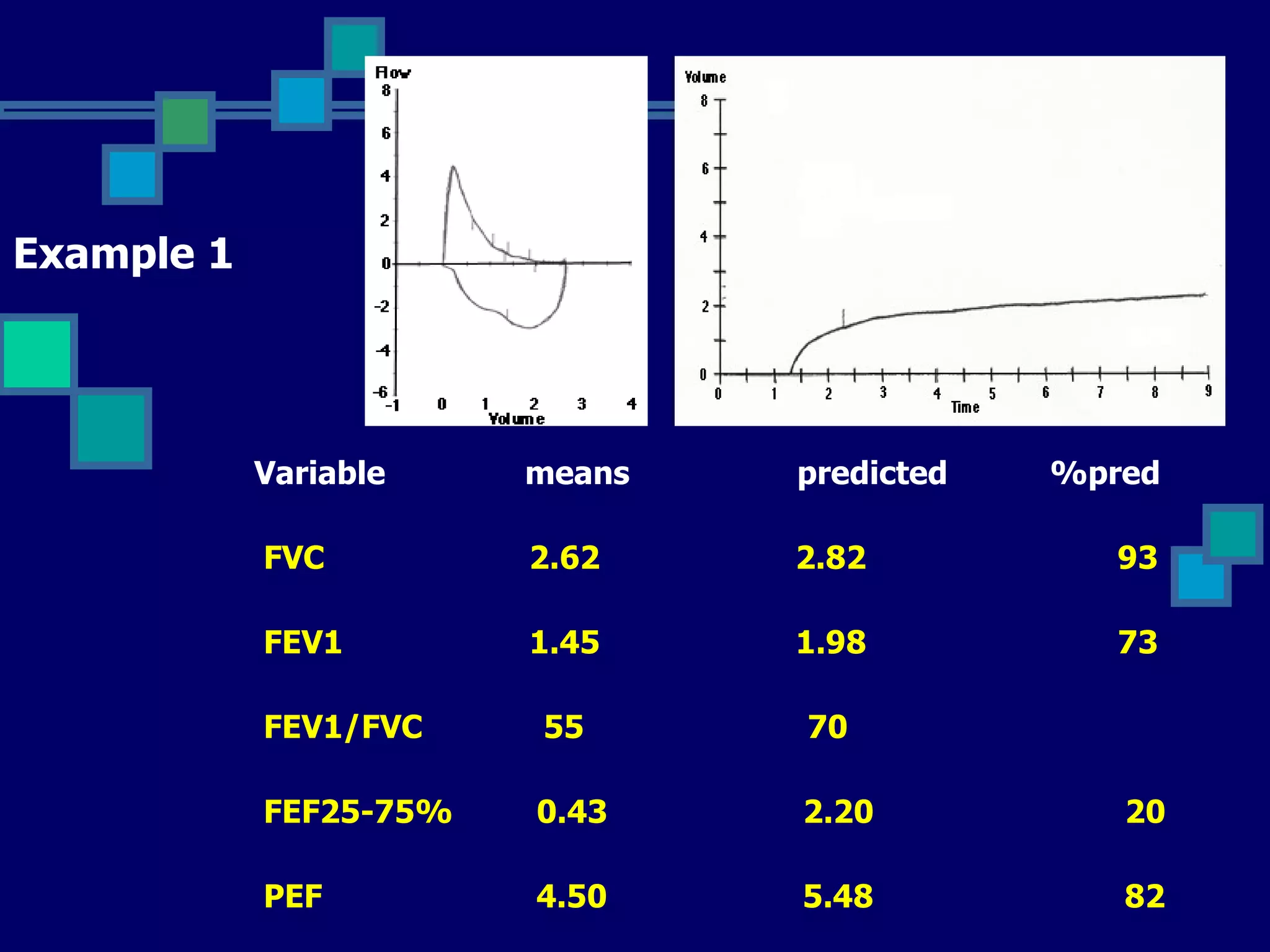
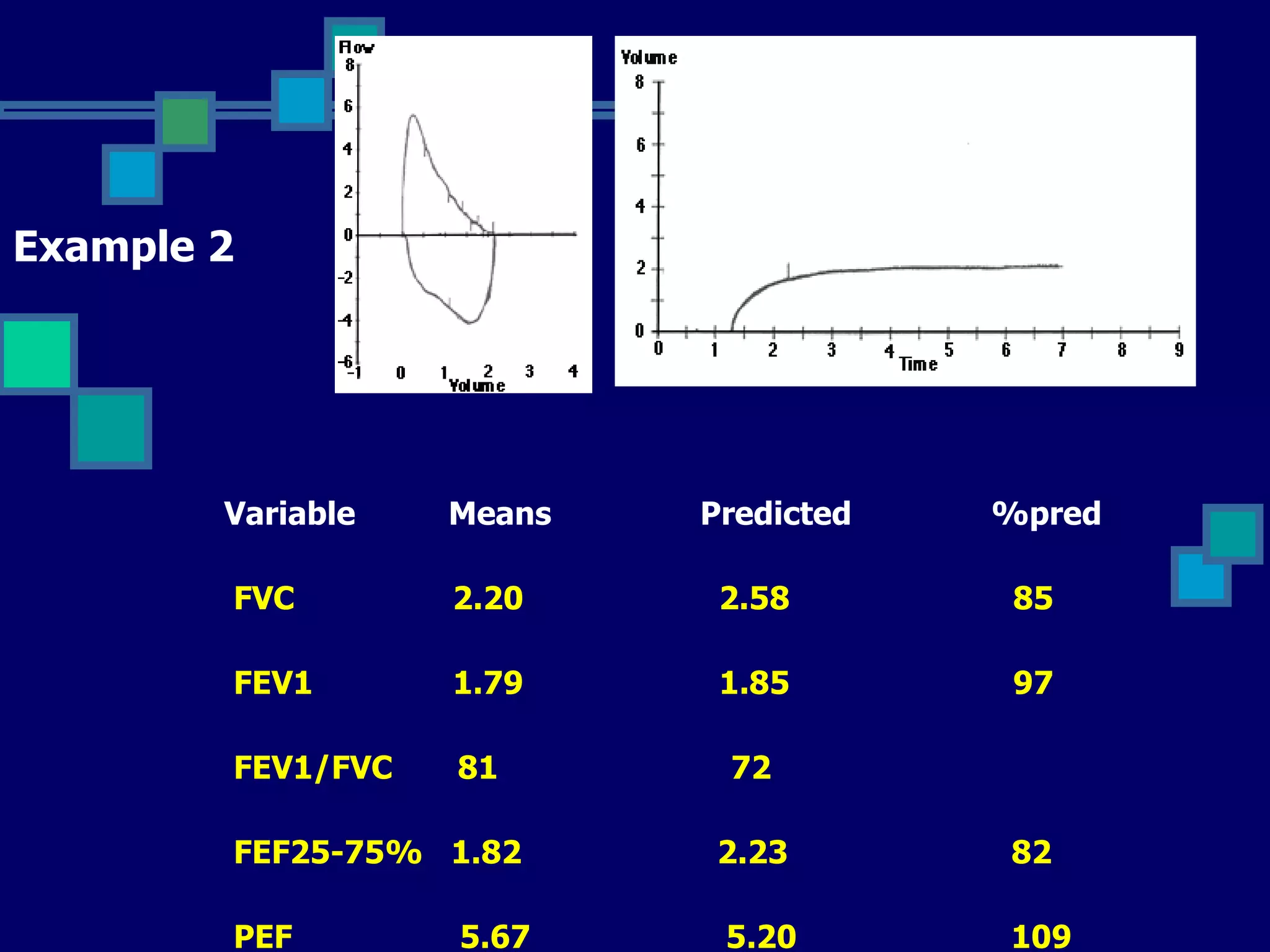
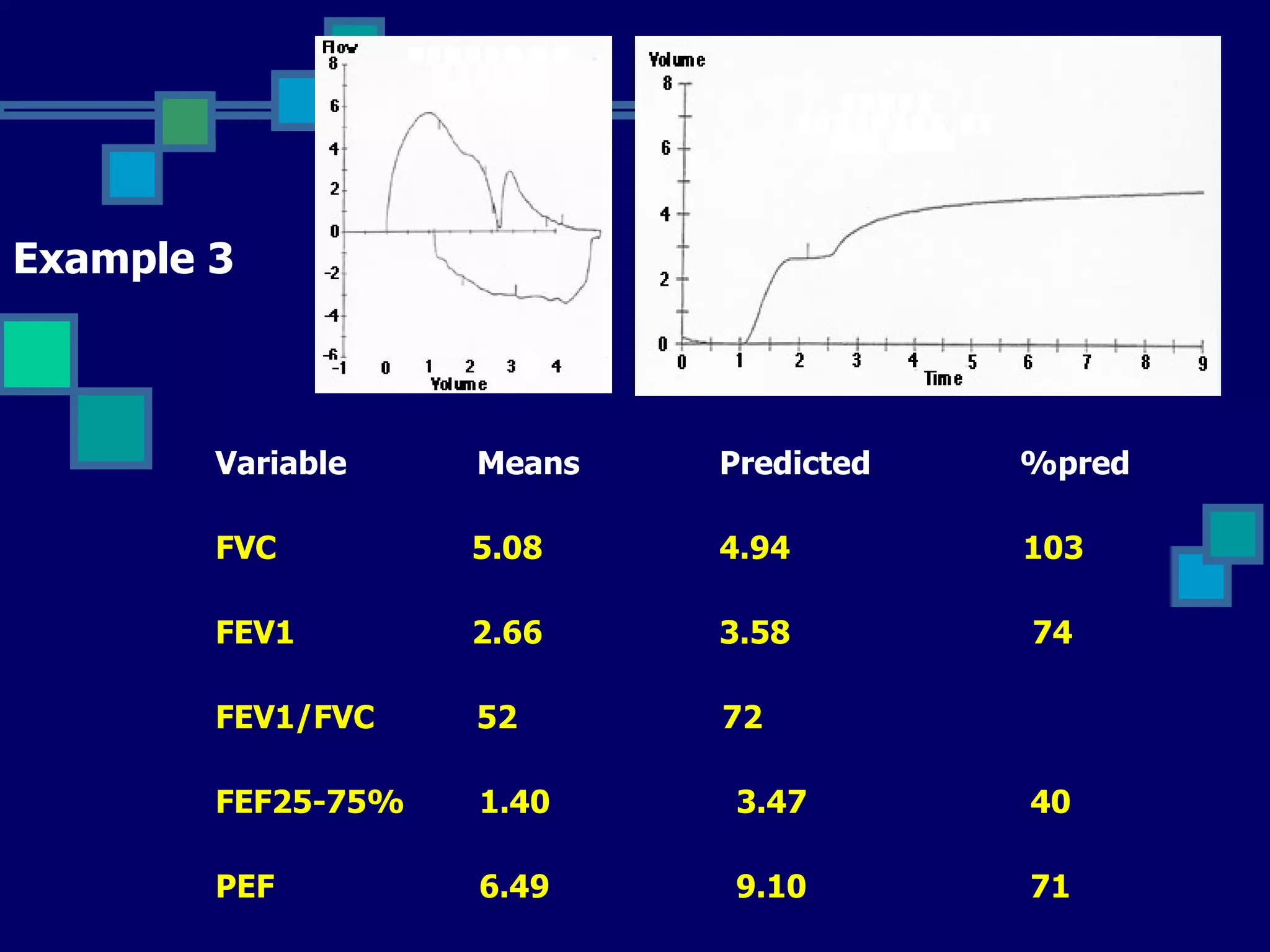
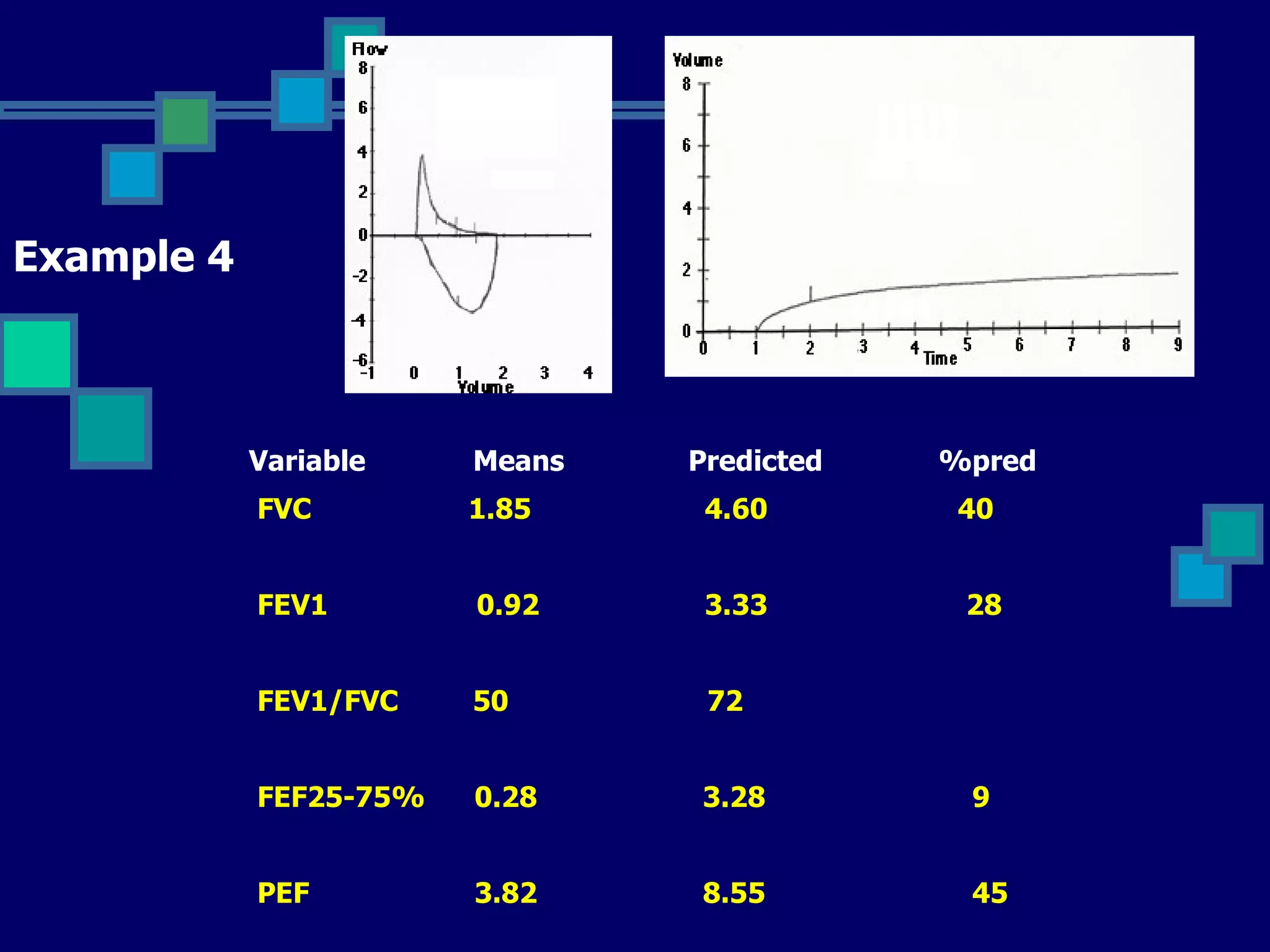
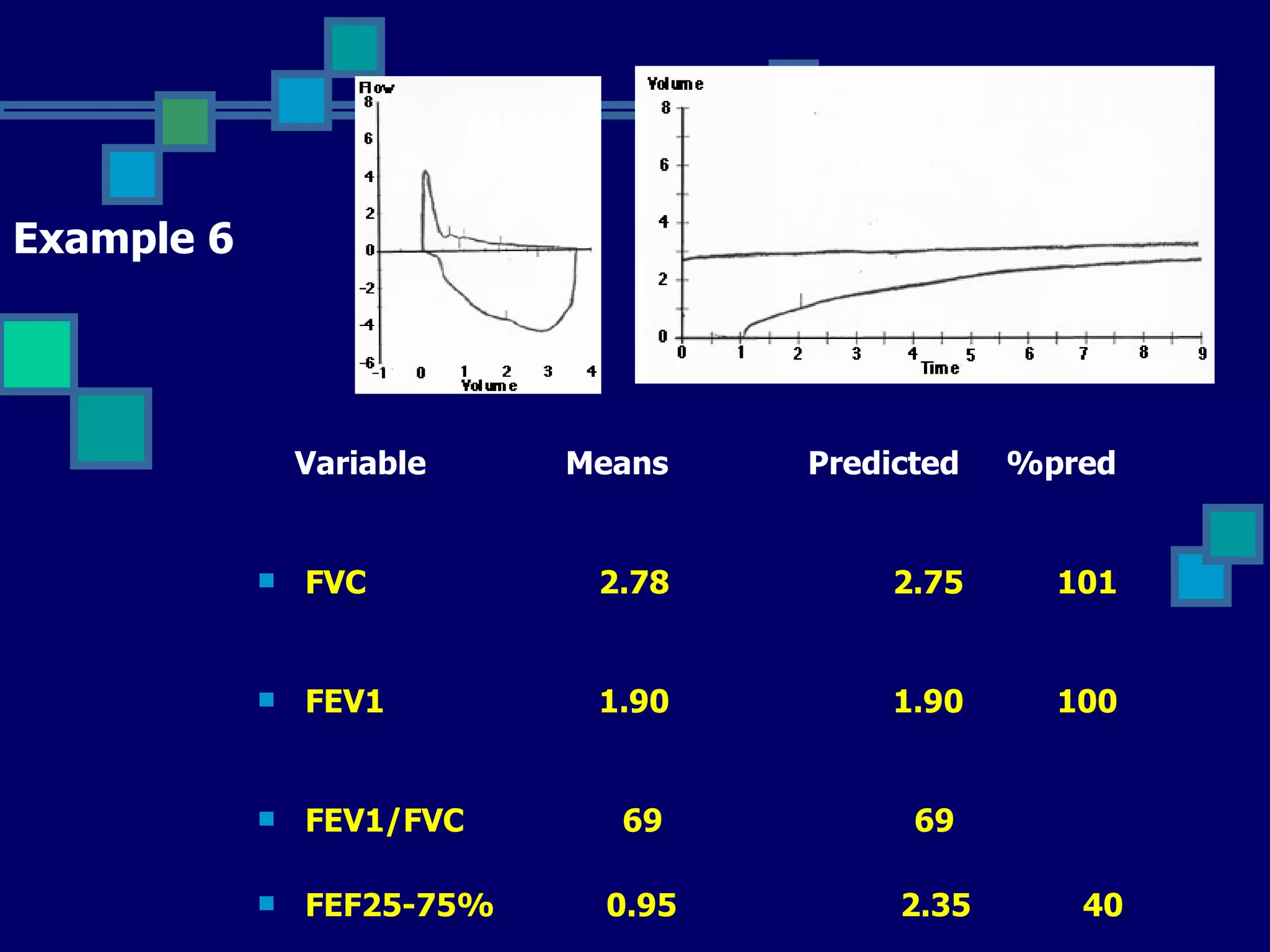
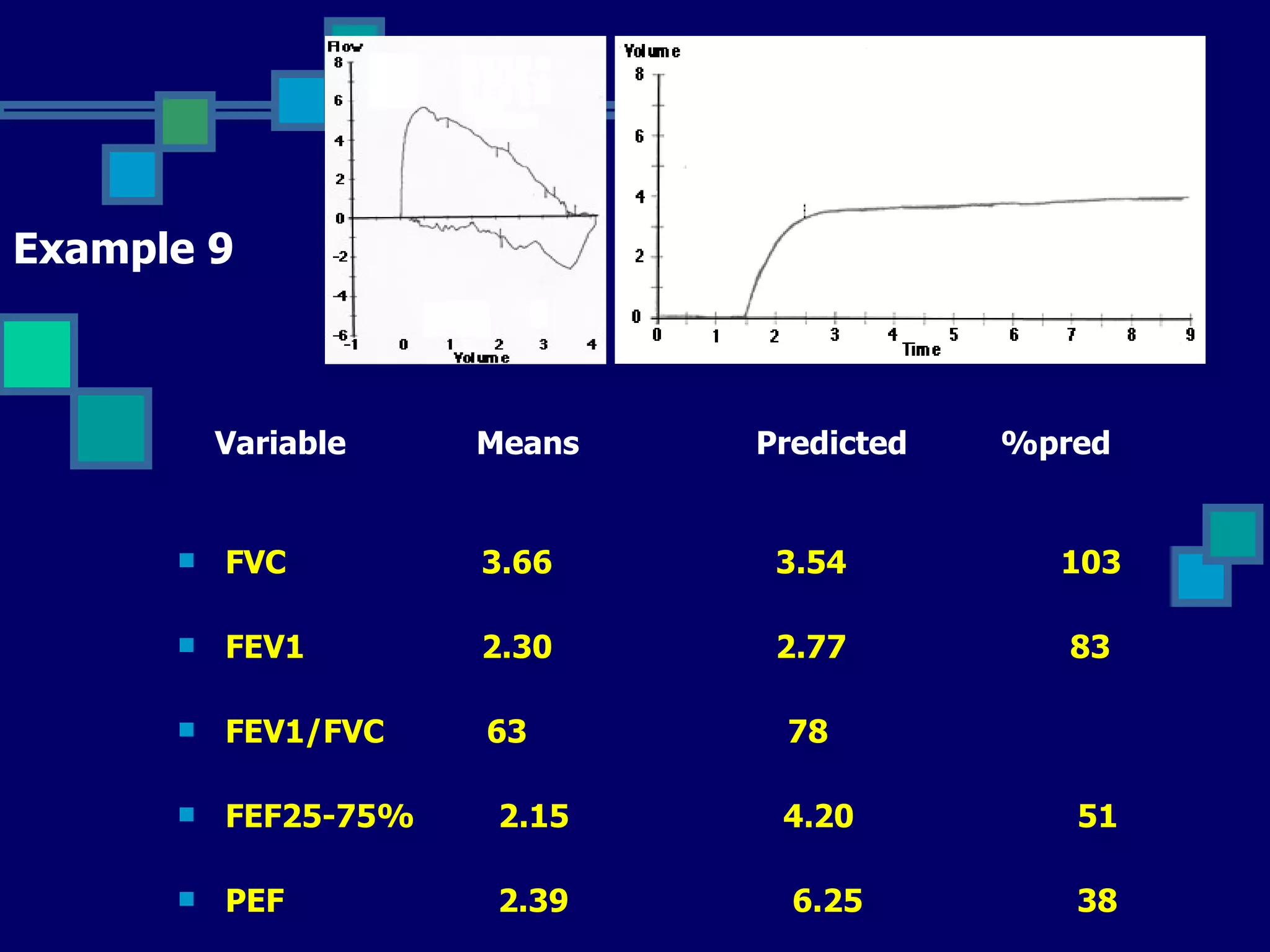
Pulmonary function tests are used to evaluate respiratory status, quantify pulmonary disability, and manage patients with known pulmonary disease. Acceptable tests require adequate equipment, lack of artifacts, satisfactory start and exhalation, and reproducibility between tests. Obstructive lung disease is identified by reduced FEV1/FVC ratio below normal limits, while restrictive lung disease shows reduced FEV1 and FVC proportionately with normal FEV1/FVC ratio. Upper airway obstruction can be extra-thoracic or intra-thoracic.
![INTERPRETATION OF PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS A.A. Eldawlatly [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpretation-of-pft4335/75/Interpretation-OF-PFT-1-2048.jpg)