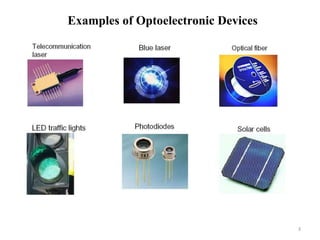
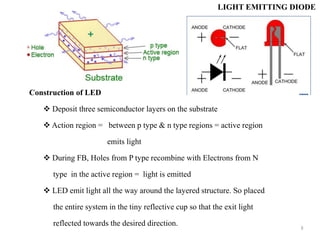
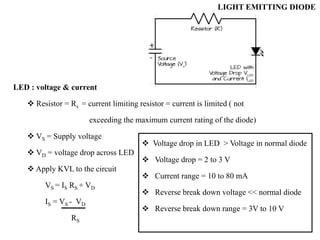
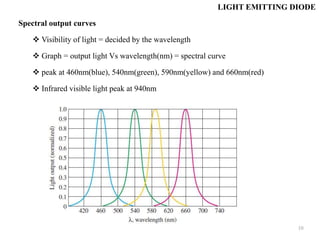
Optoelectronics combines electronics and optics to study and apply electronic devices that interact with light. Major optoelectronic devices include light-emitting diodes (LEDs), laser diodes, photodiodes, and solar cells. A light emitting diode (LED) is an optical diode that emits light when forward biased. LEDs use semiconductors like gallium arsenide to emit light of different colors depending on the material's band gap. They have advantages like small size, long life, and availability in many colors.