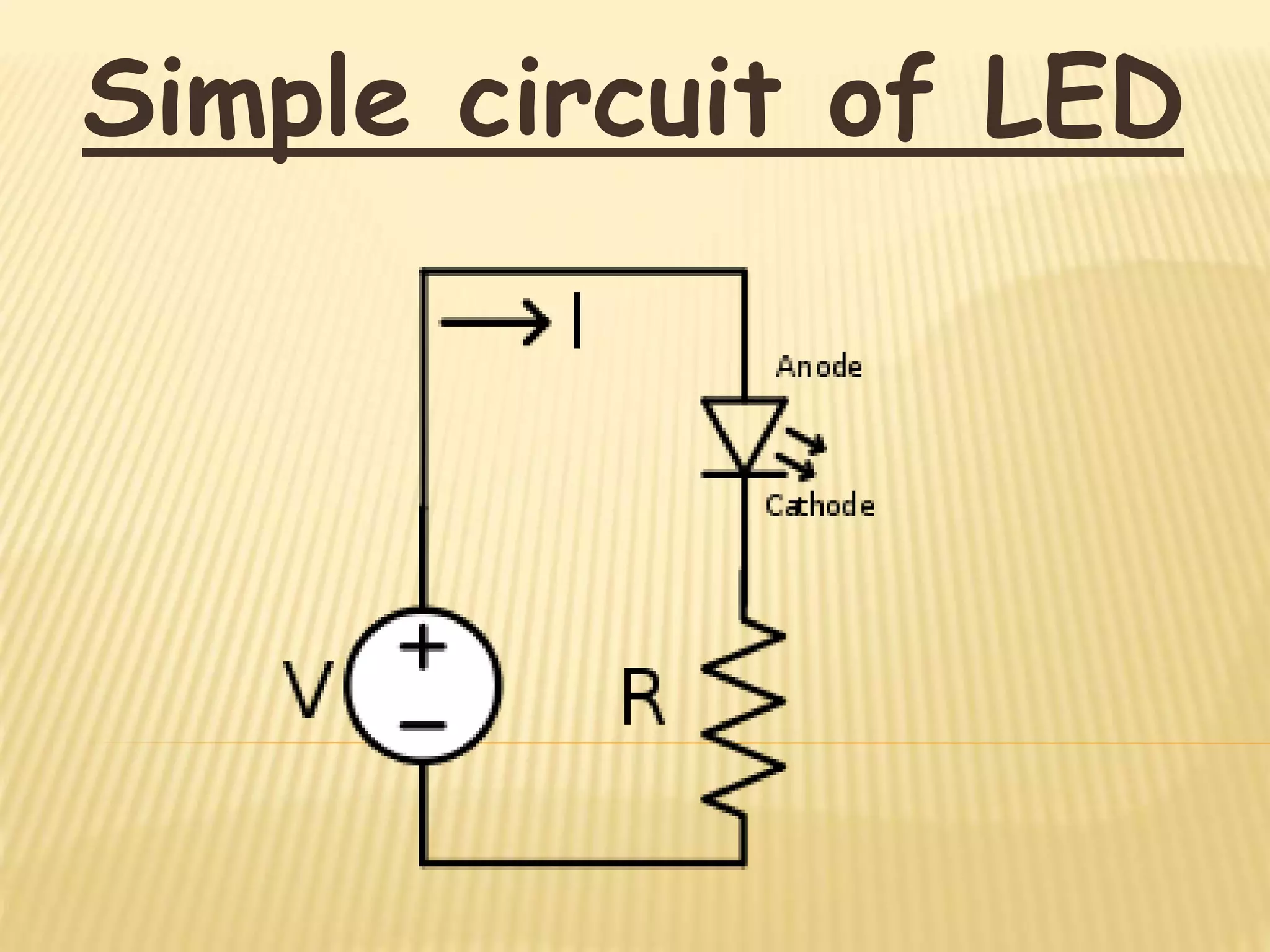
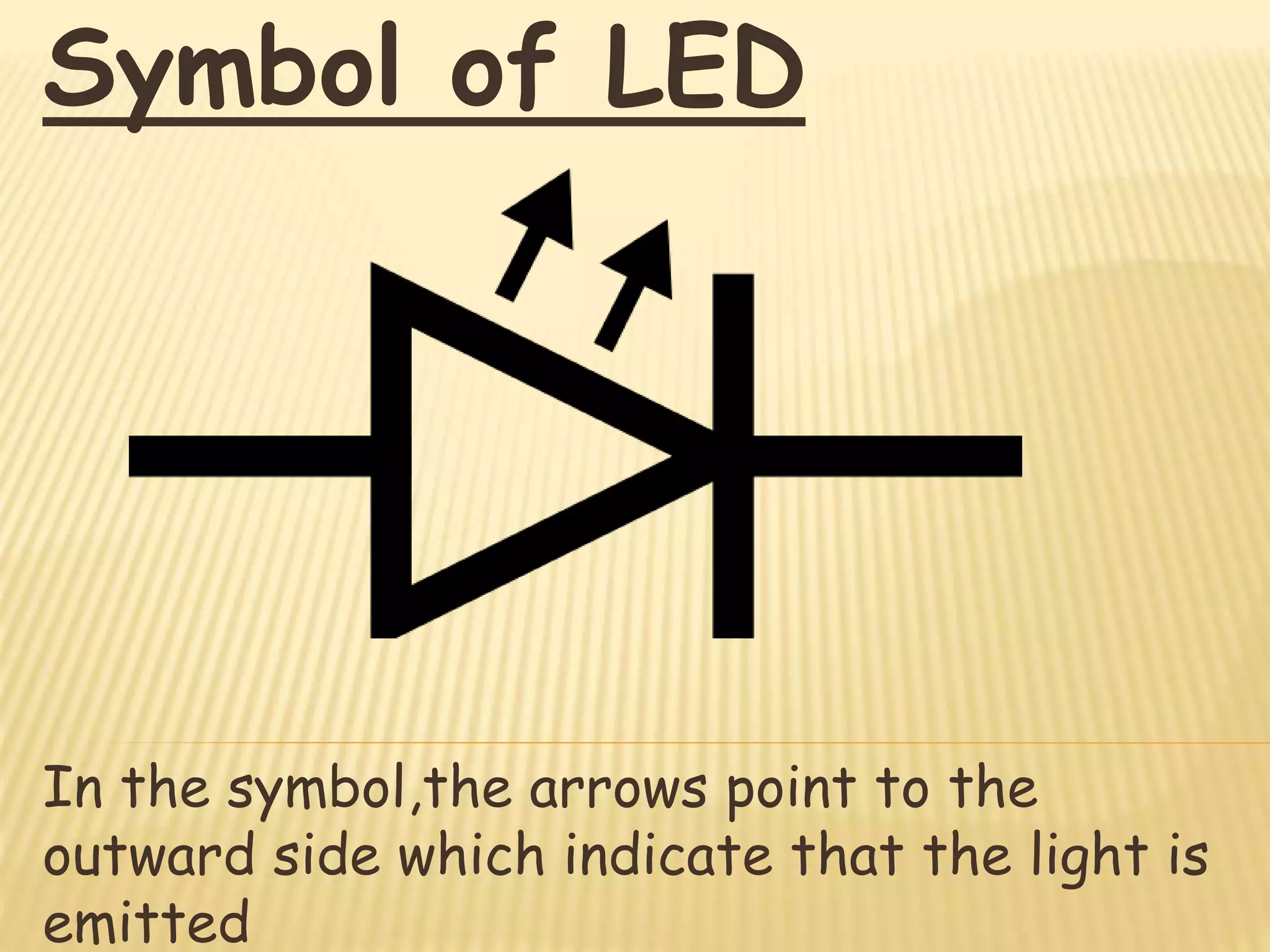
The document discusses the working of a light emitting diode (LED). It explains that in a forward biased PN junction, electrons from the N-region combine with holes in the P-region, releasing energy in the form of light. The color of light emitted depends on the semiconductor material used. Common materials produce red, green or infrared light. LEDs have advantages like long life and fast switching, but higher power consumption than LCD displays. They are used as indicators, in opto-isolators, optical communication and numeric displays.