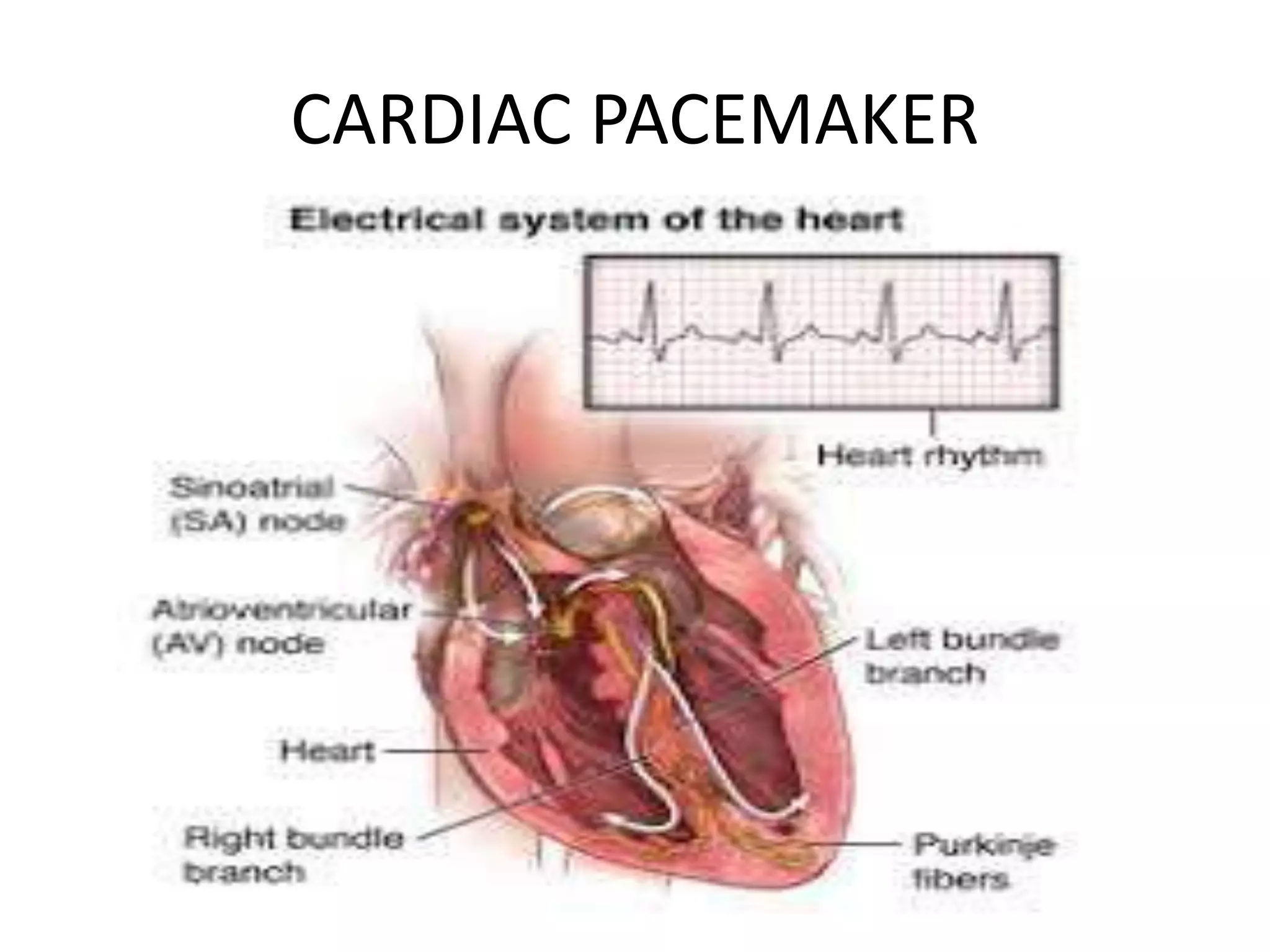
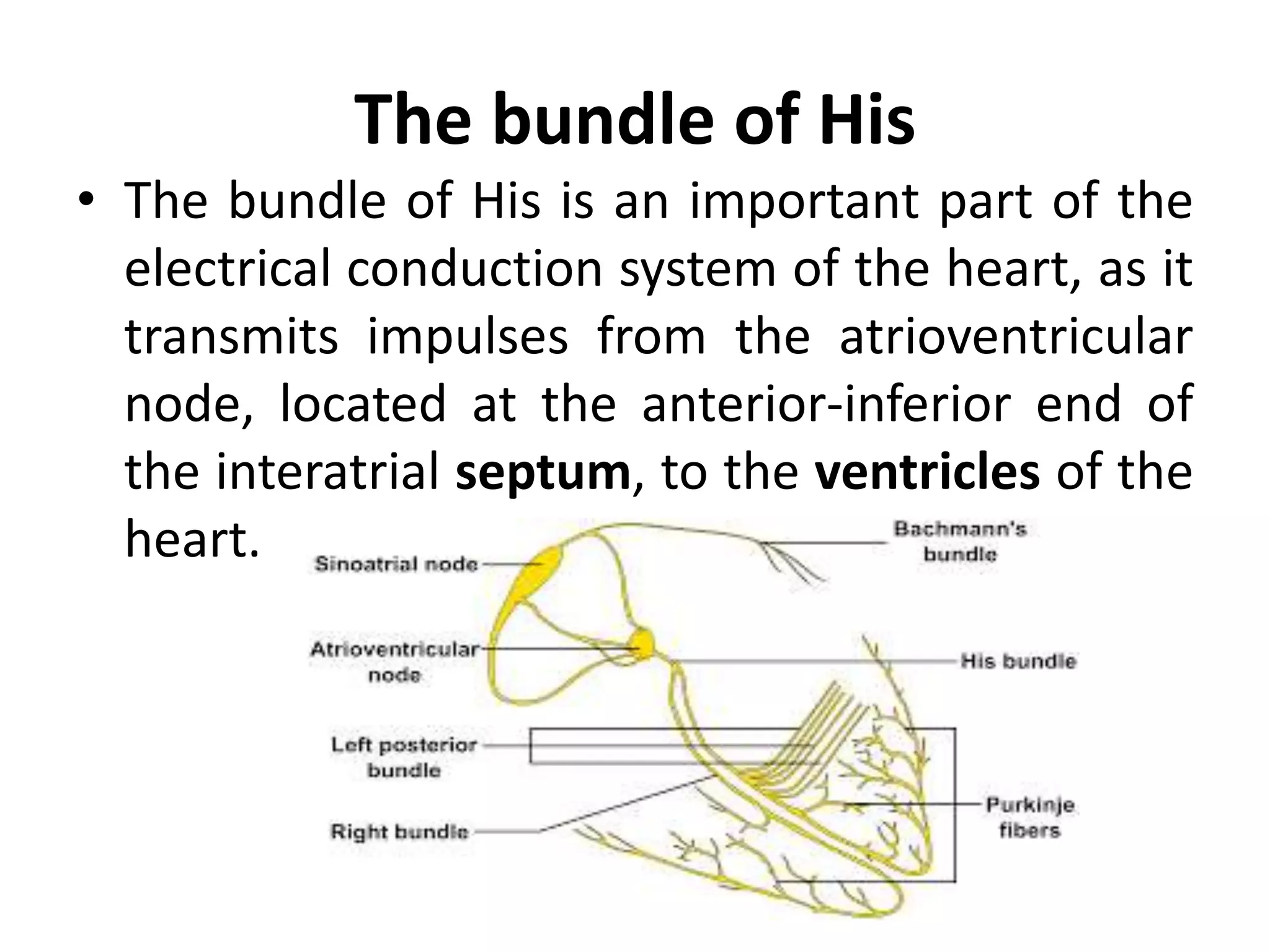
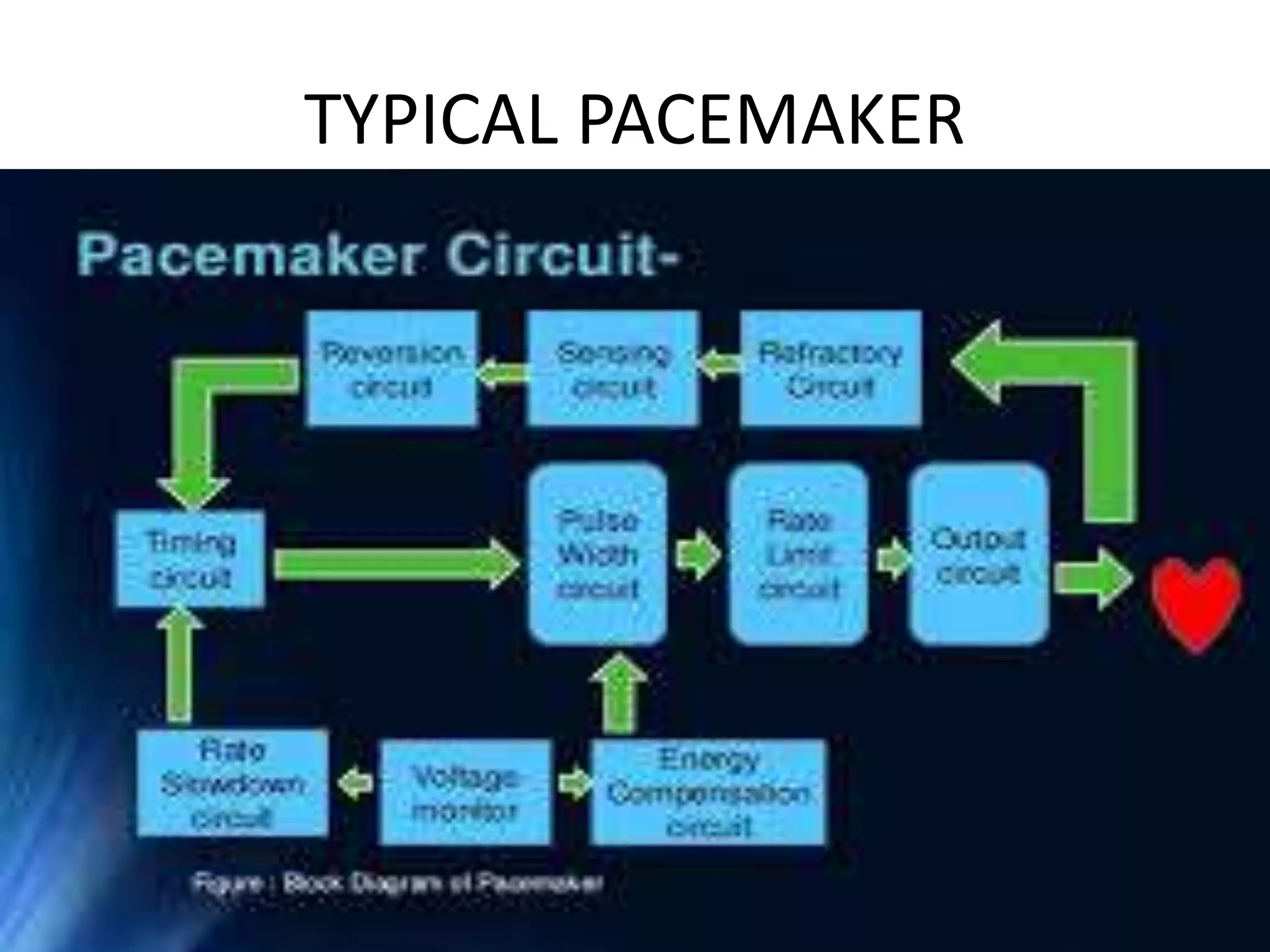
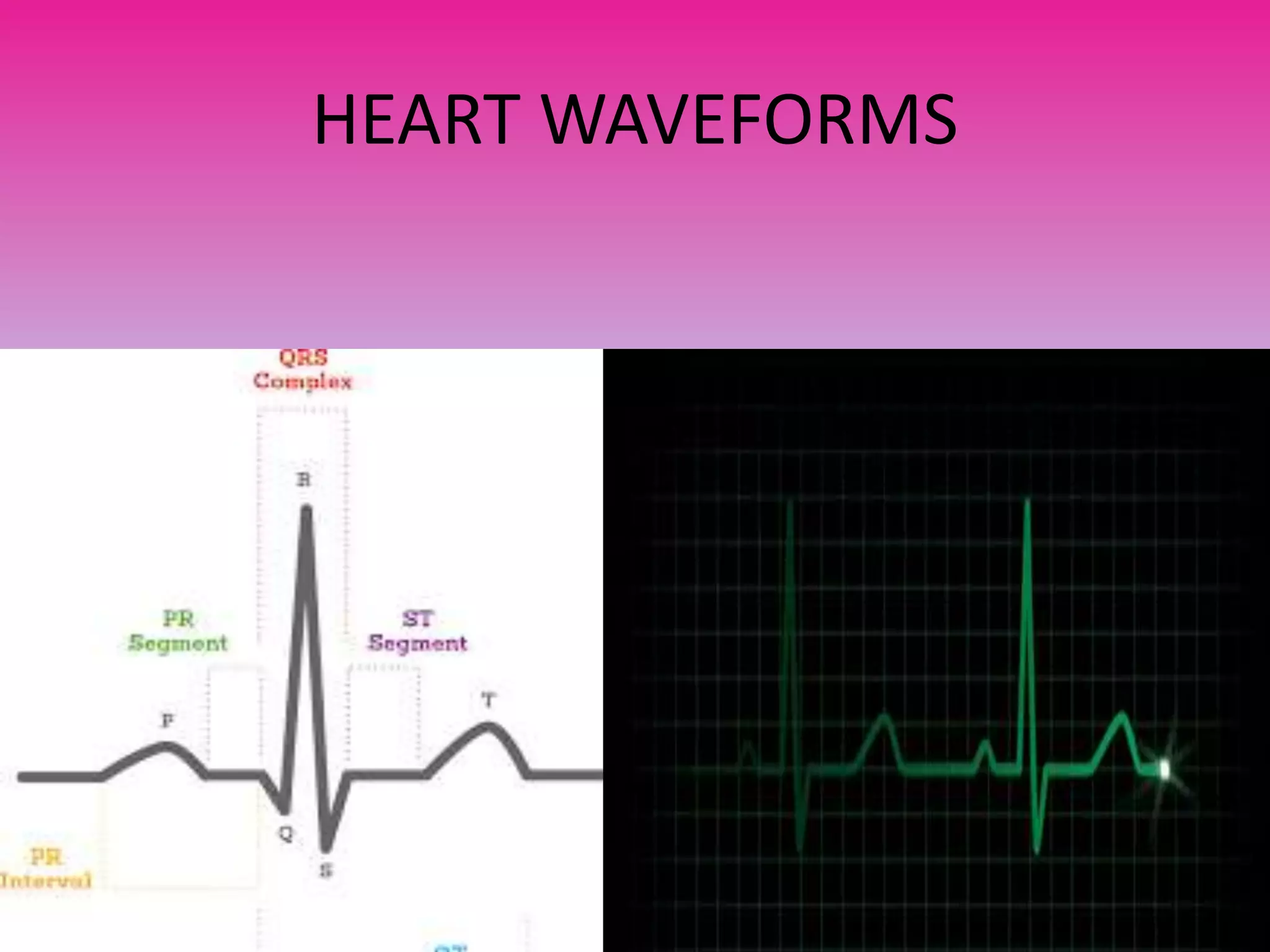
A pacemaker is a small device implanted in the chest or abdomen to regulate abnormal heart rhythms using electrical pulses. It is utilized in conditions like bradycardia and various types of heart blocks, including first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree AV blocks. Modern pacemakers can be synchronous, responding to the heart's needs, or non-competitive, aimed at preventing certain fast heart rhythms.