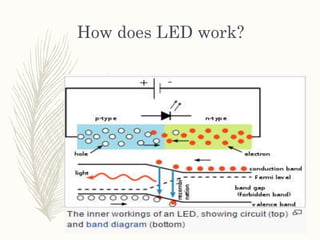
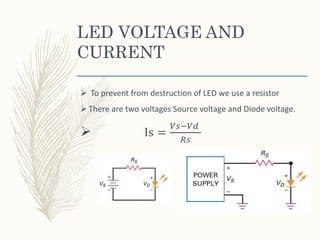
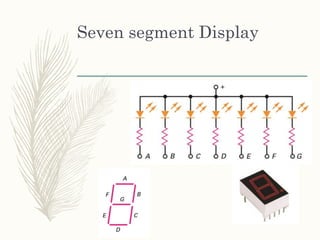
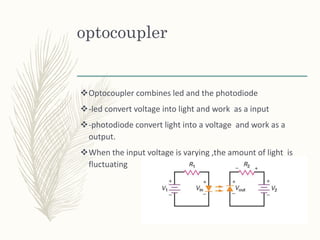
This document provides information on light emitting diodes (LEDs) including how they work, different types of LEDs, and their applications. It explains that LEDs are semiconductors that emit light when electrically biased in the forward direction. The light is produced by electron-hole recombination which releases photons. It also discusses LED voltage and current characteristics, color production, and how LEDs are used in various optical sensors, mobile devices, signs, automobiles, and indicators.