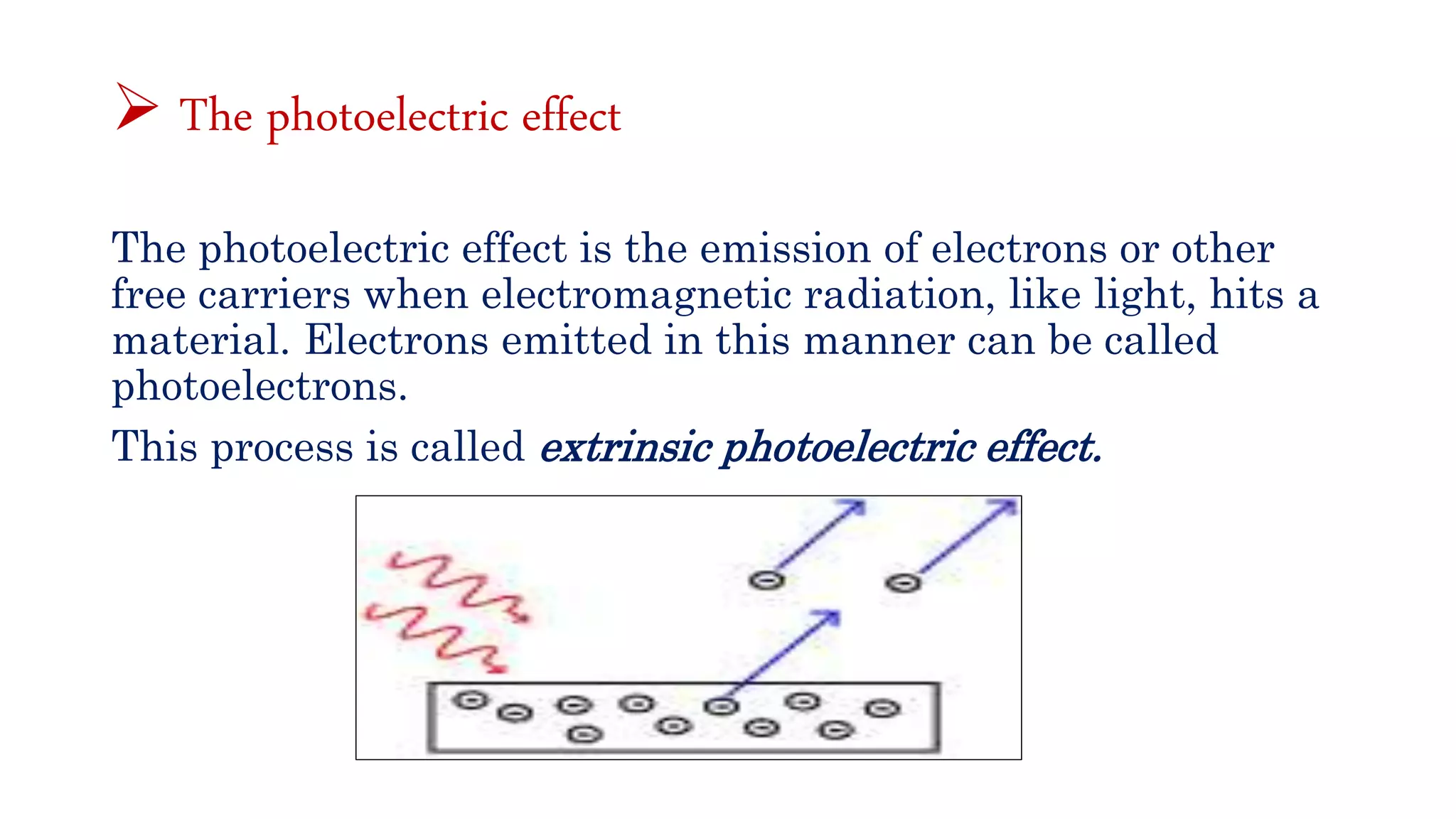
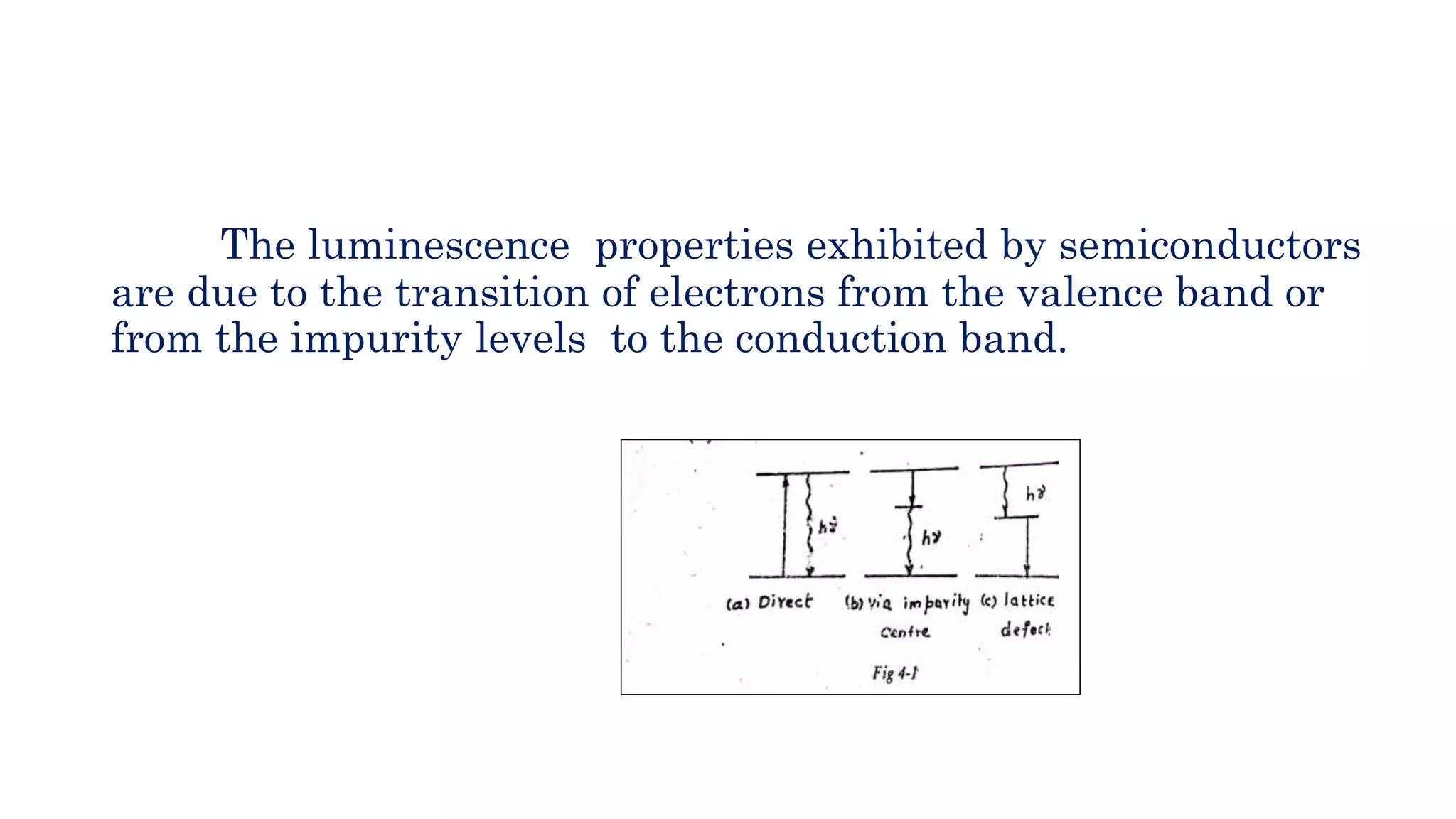
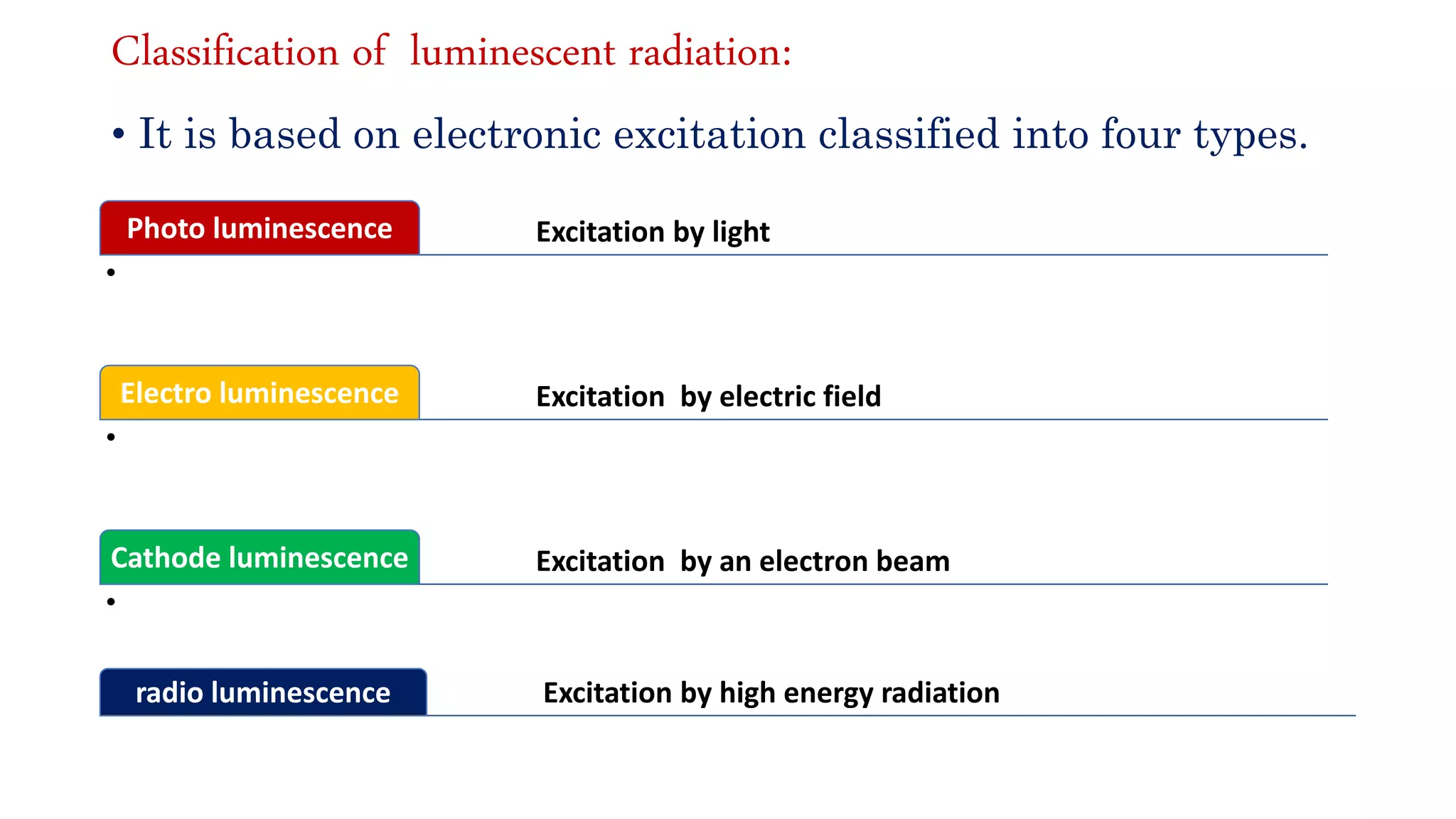
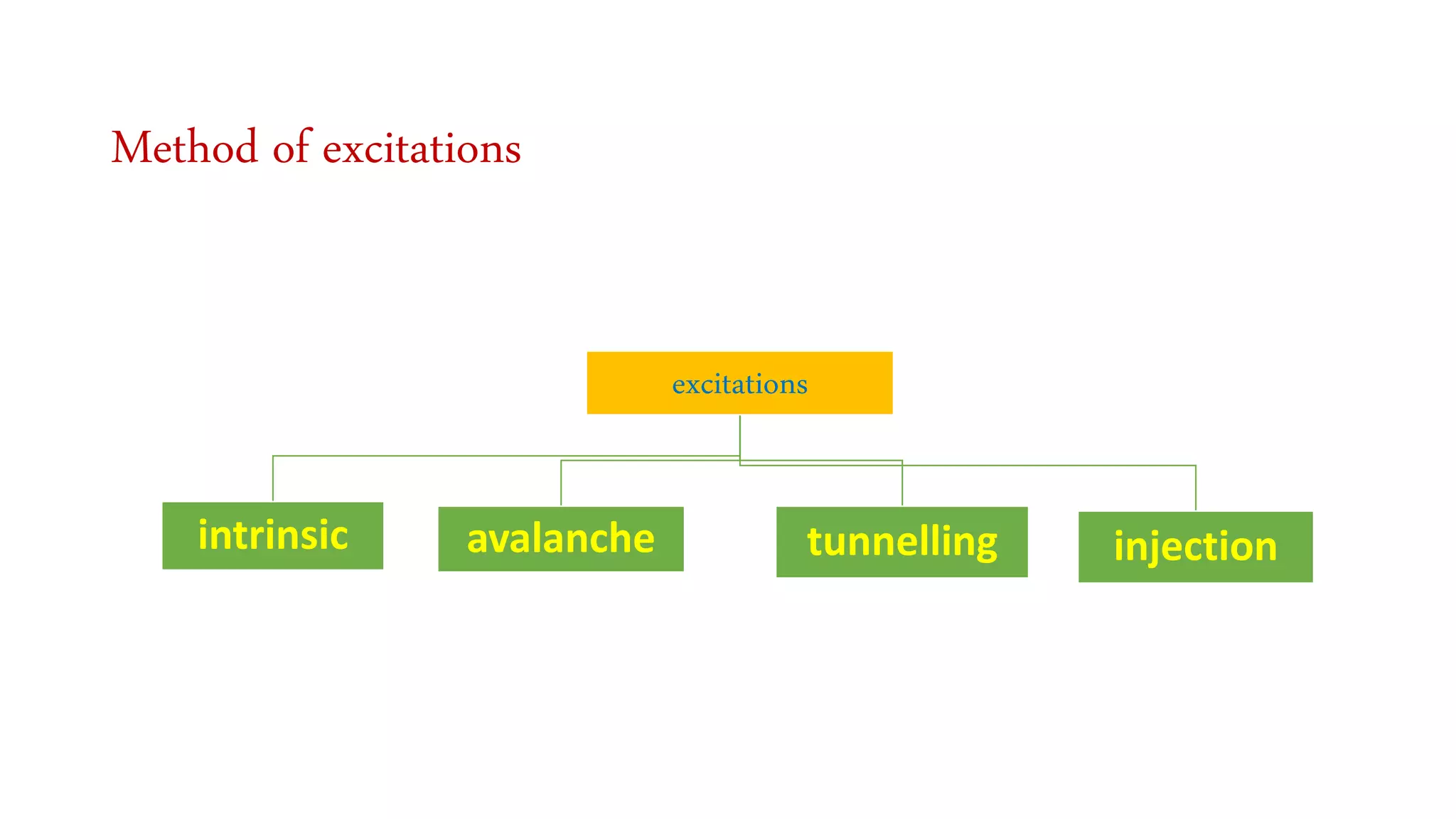
The document discusses optoelectronic devices, which convert electrical energy into light and vice versa using semiconductors. It explains the photoelectric effect, classifications of photonic devices, and luminescence types, including electroluminescence and radioactive luminescence. Additionally, it covers methods of excitation such as intrinsic, avalanche, tunneling, and injection processes for generating light in semiconductors.