- Maulik R. Shah is a consultant biomedical engineer, medical equipment planner, and hospital project consultant based in India. He has degrees in biomedical engineering and healthcare administration.
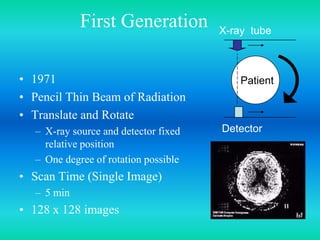
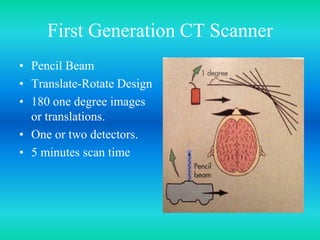
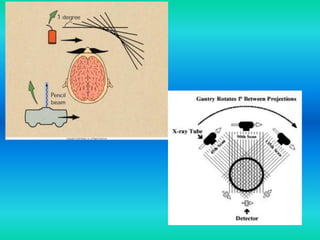
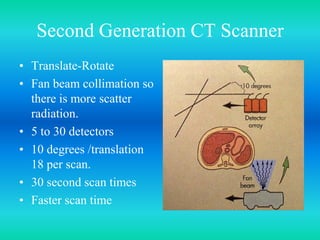
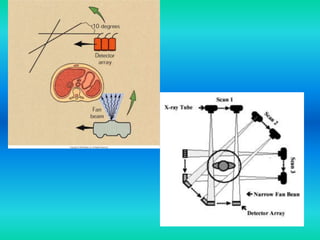
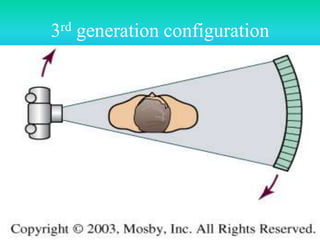
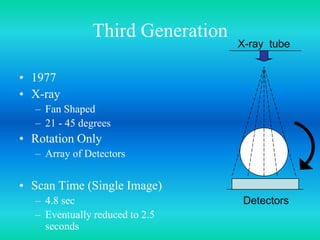
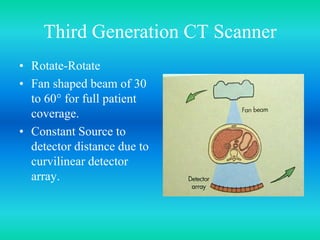
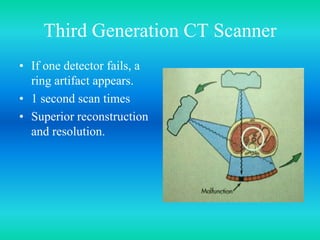
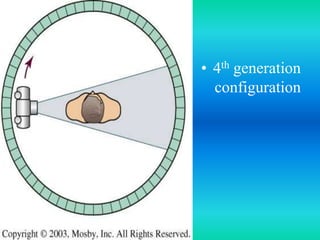
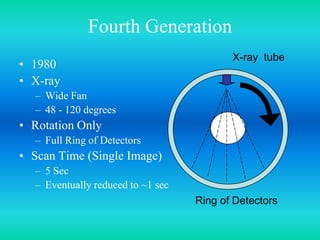
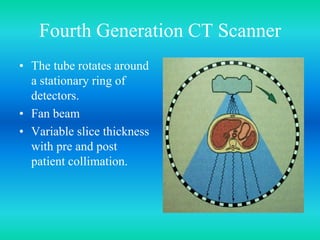
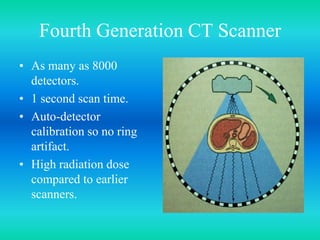
- The document discusses the five generations of computed tomography (CT) scanners since 1970 and how each generation improved scan time and image quality/resolution. First generation scanners took 5 minutes for a single slice while current scanners can acquire a full scan in under 1 second.