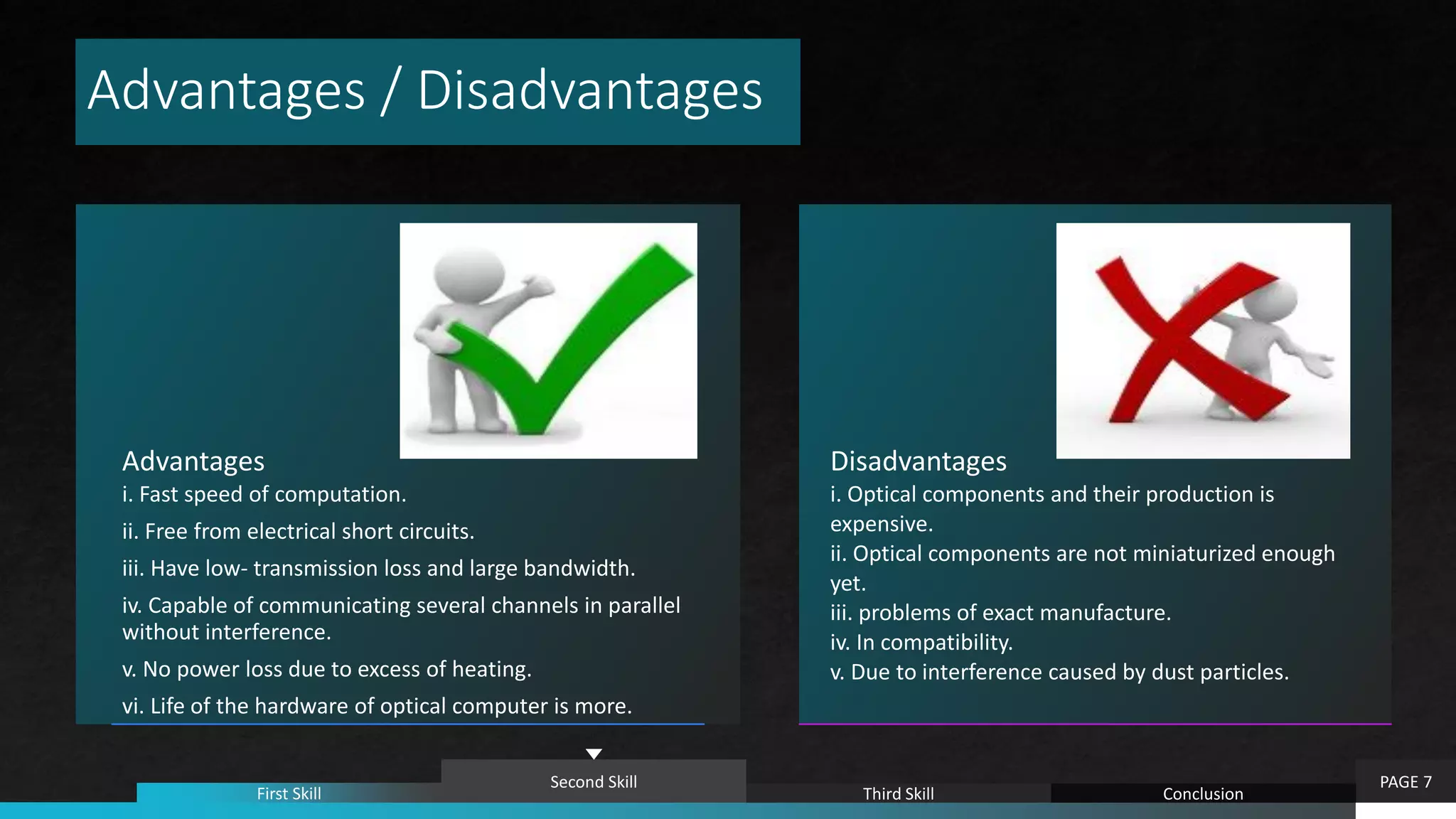
Photonic computing uses photons or light instead of electricity to perform computations. It has several advantages over traditional electronic computing including faster speeds, immunity to electromagnetic interference, low transmission losses, and massive parallelization capabilities. However, optical components are still more expensive to produce than electronic ones and have not been fully miniaturized. Future trends include developing new laser diodes, photodetectors, and nonlinear materials to enable even faster optical switches and truly optical computers.