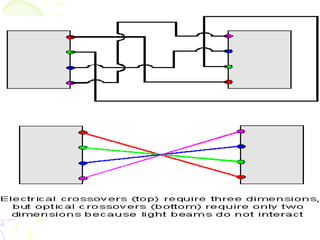
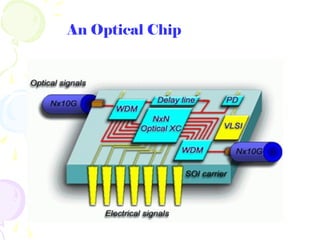
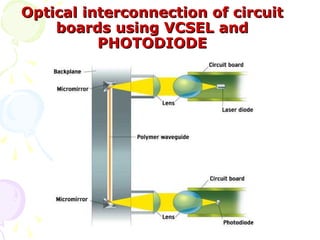
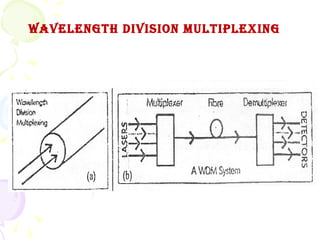
The document discusses optical computing technology as an alternative to traditional electronic computing. It notes that optical computing was researched in the 1980s but work tapered off due to materials limitations. Light is well-suited for computing due to its speed, ability to be manipulated, and suitability for parallelization. Optical computing could solve miniaturization problems and allow data to be processed in parallel. Key components discussed include vertical cavity surface emitting lasers, smart pixel technology, wavelength division multiplexing, and spatial light modulators. The document outlines some advantages and challenges of optical computing.