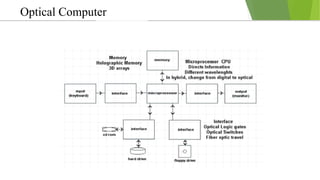
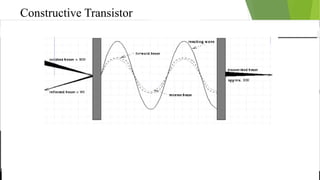
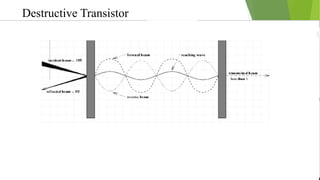
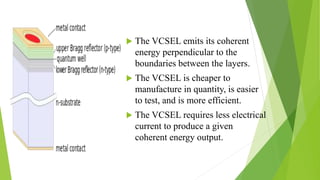
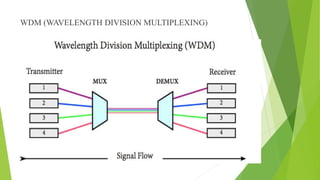
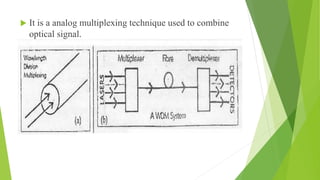
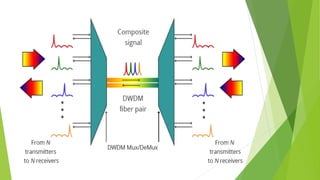
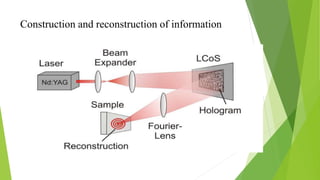
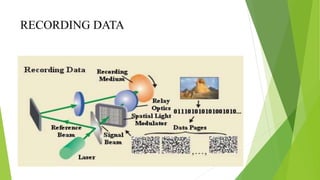
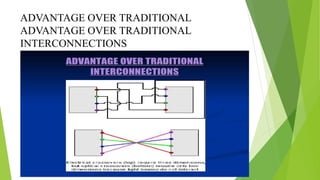
An optical computer uses light instead of electricity for computation. It has two types - hybrid, which uses both light and electricity, and pure optical, which uses only light. Optical computers are needed because transistors can no longer keep up with Moore's Law. They use components like lasers, fiber optics, and holographic memory to transmit and store information as light pulses. Optical computing provides benefits like vastly increased speed and bandwidth compared to traditional electronics. Potential applications include high-speed communications and database searches.