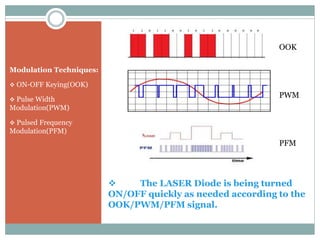
Laser communication systems use lasers to transmit data through free space instead of fiber optic links. The basic components are a transmitter with a laser diode, modulator and signal processing unit, a receiver with a telescope, photon sensor and signal processing unit, and the laser beam that travels through the medium. Common modulation techniques are ON-OFF keying, pulse width modulation and pulsed frequency modulation. Laser communication offers advantages over fiber optics and microwaves by having lower installation and maintenance costs, the ability to transmit through free space including satellite links, higher bandwidth, more secure and narrow beams compared to microwaves. While atmospheric effects can impact the laser link, techniques like tuning and multiple transmitters can reduce these impacts. Current applications