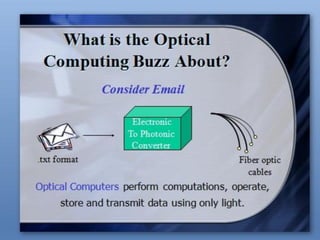
1) The presentation discusses optical computing, which uses photons in light beams rather than electric currents to perform computations. It has advantages like speed, easy manipulation of light, and suitability for parallelization.
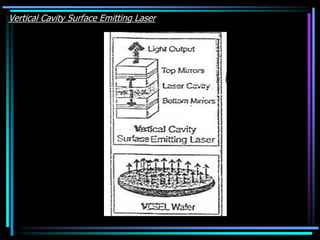
2) Optical computing is developing in two directions - hybrid systems that use optics alongside existing computer architectures, and new optical-only computers. Key components discussed include VCSEL lasers, smart pixel technology, and WDM for sending multiple wavelengths through a single fiber.
3) Potential benefits of optical computing include much higher speeds, smaller size, higher bandwidth, and less heat generation compared to electronic computers. However, challenges remain around high power needs, interference effects, and cost of optical