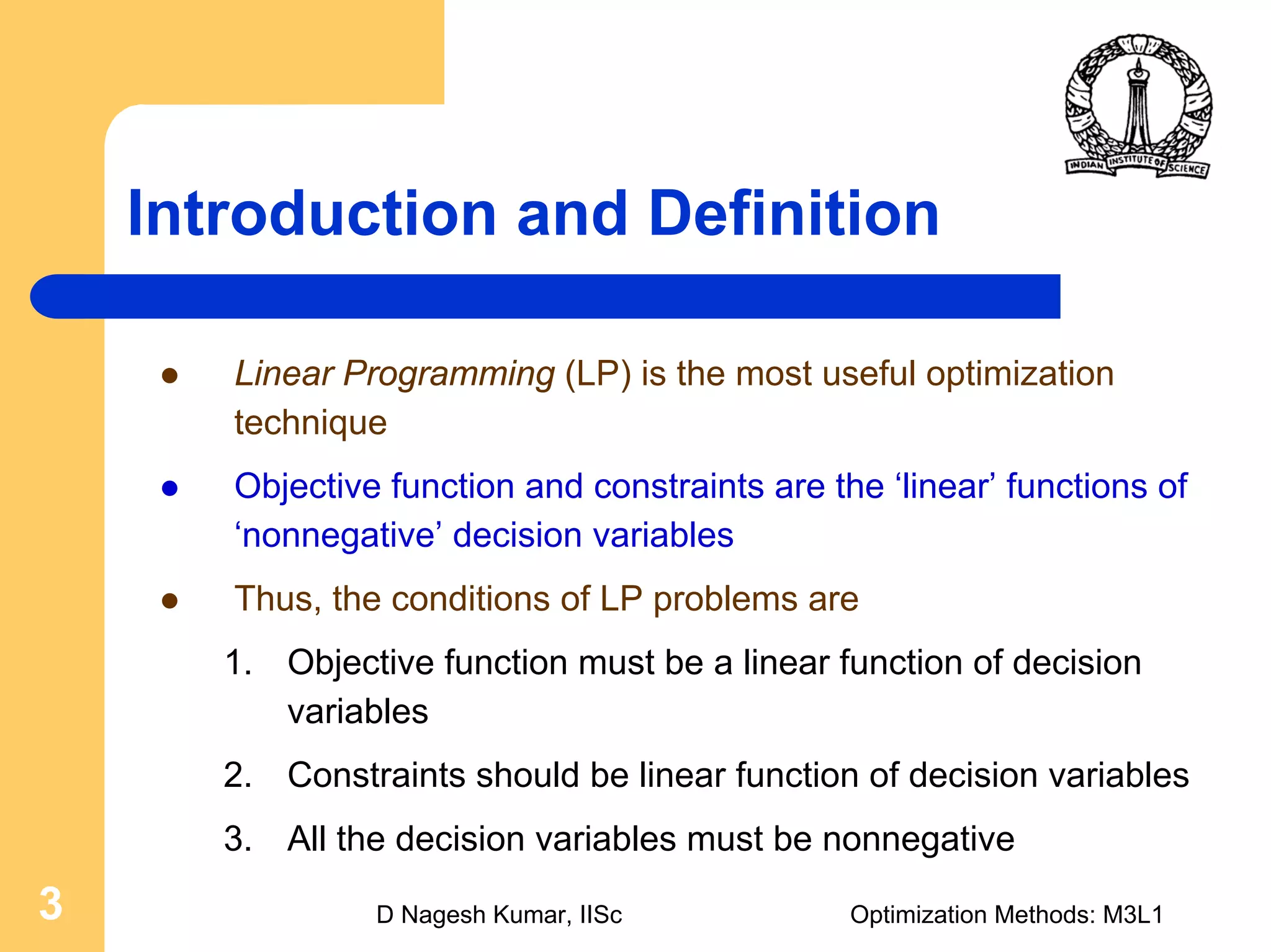
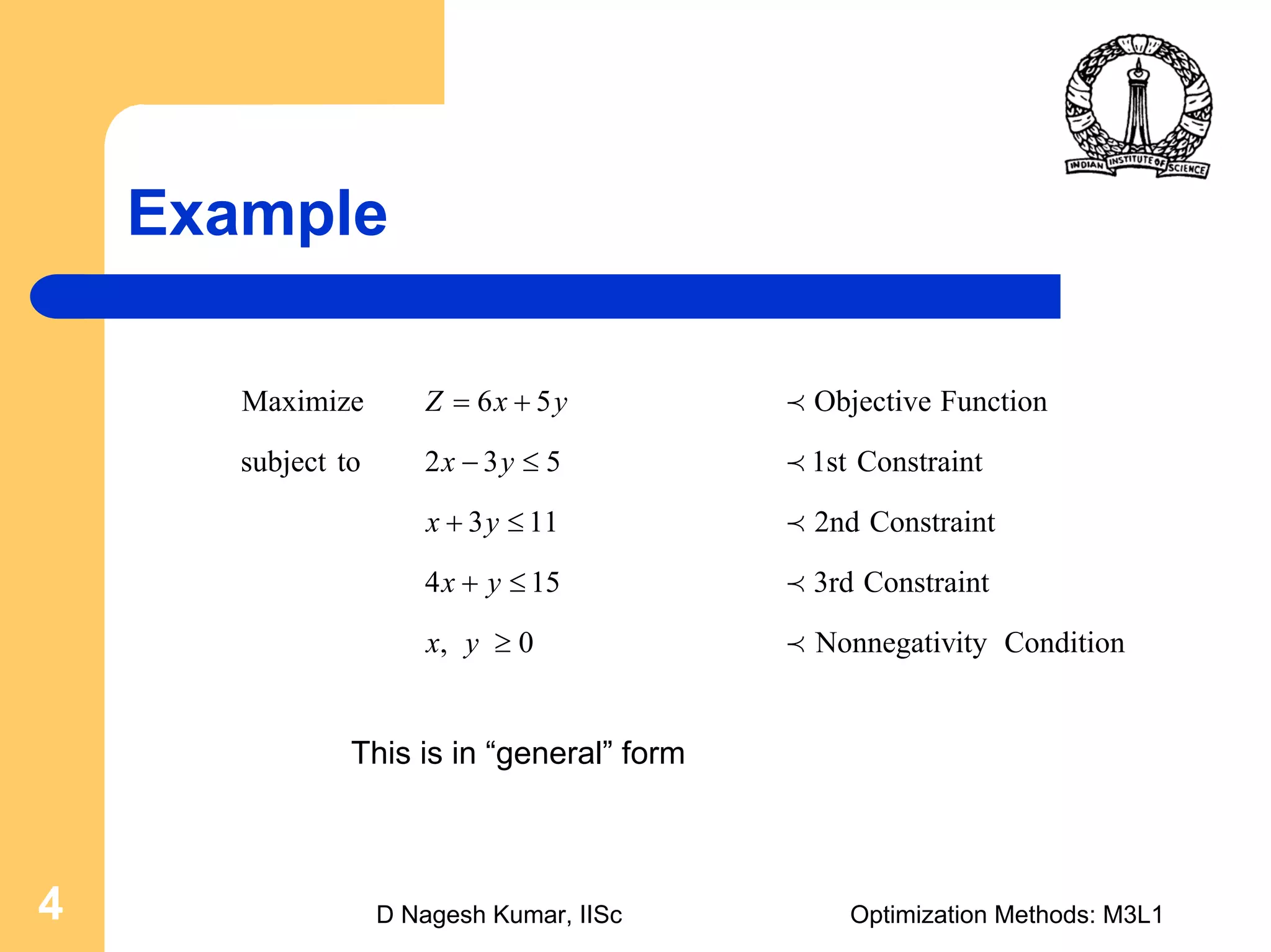
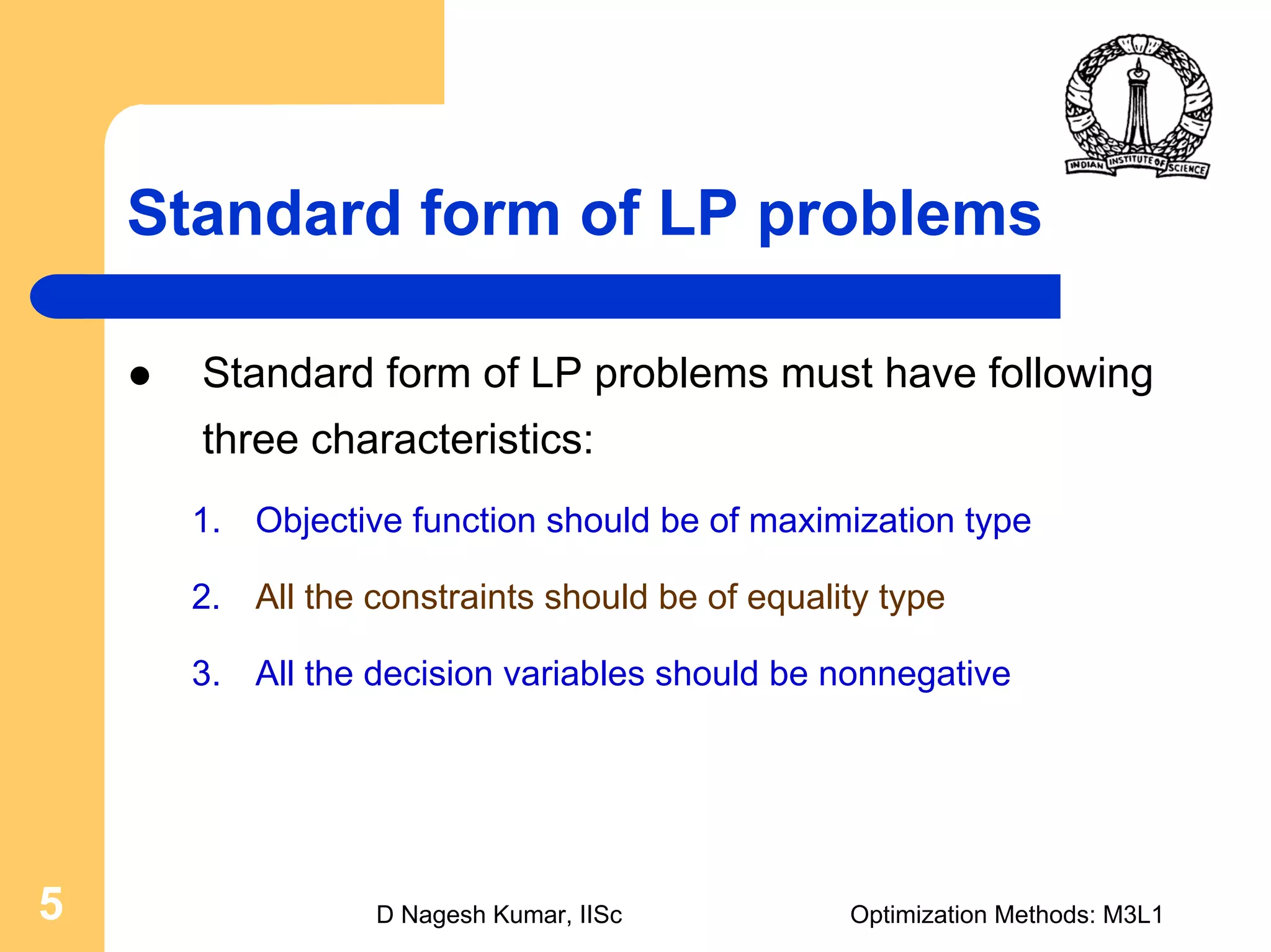
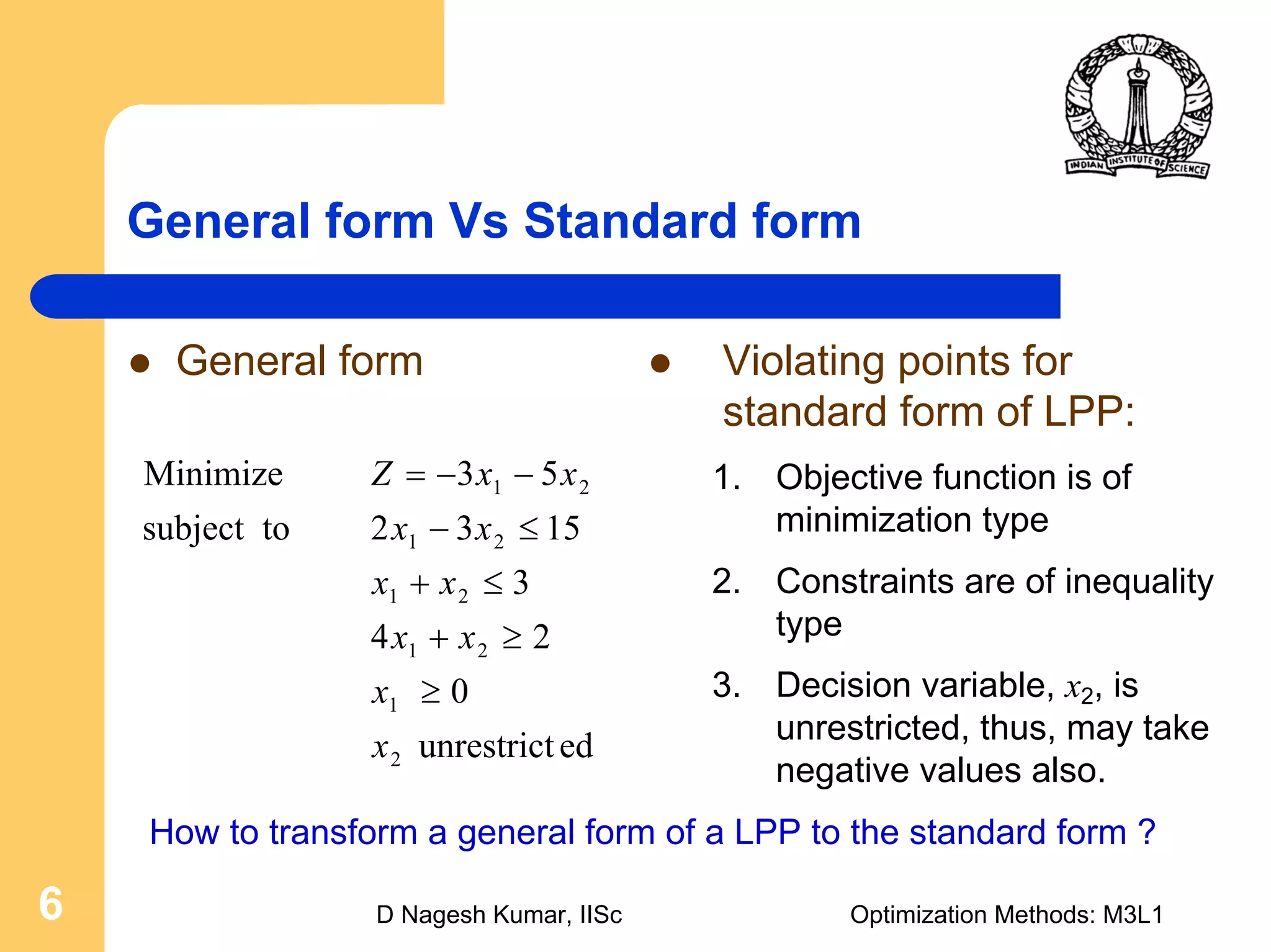
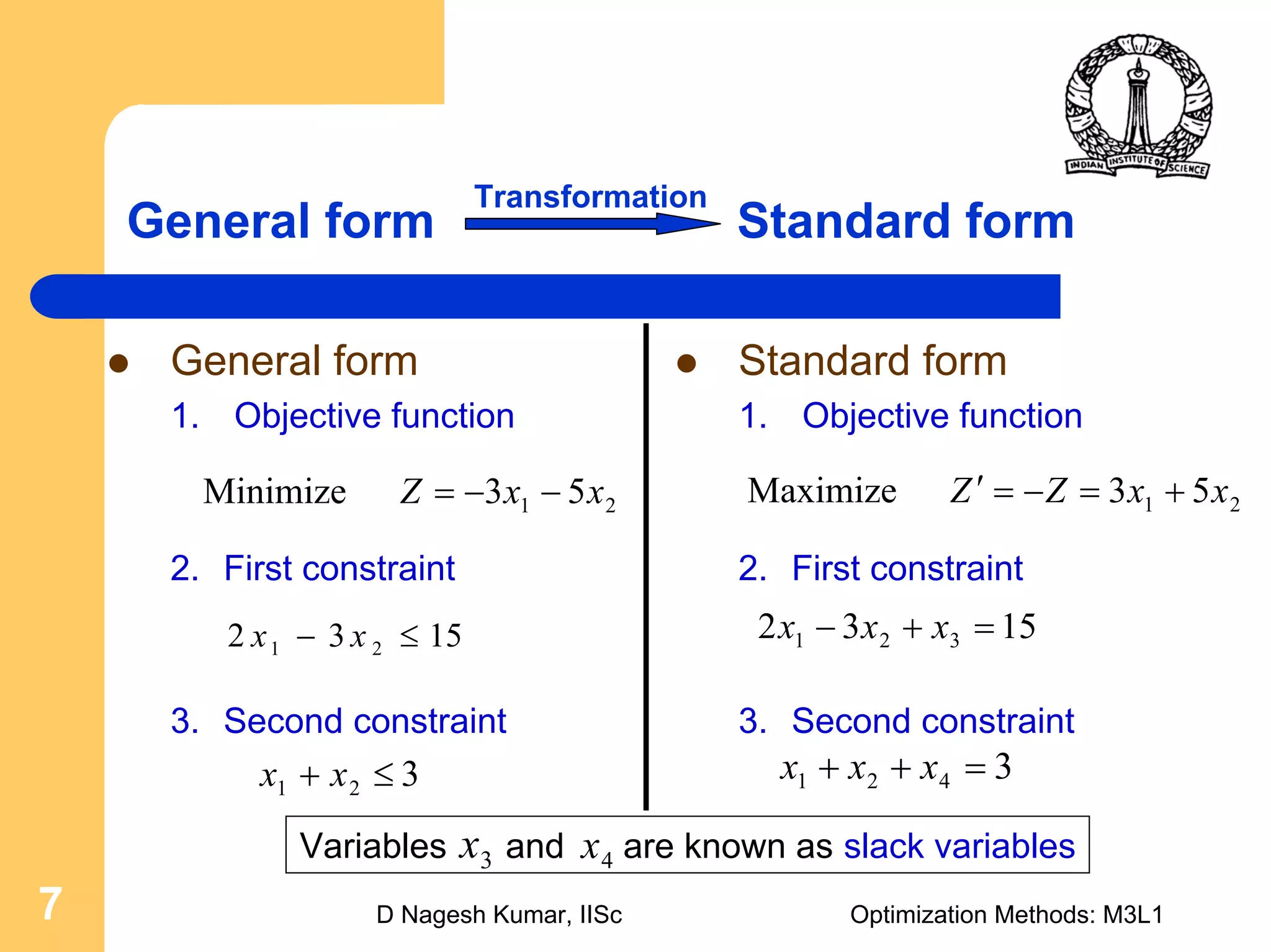
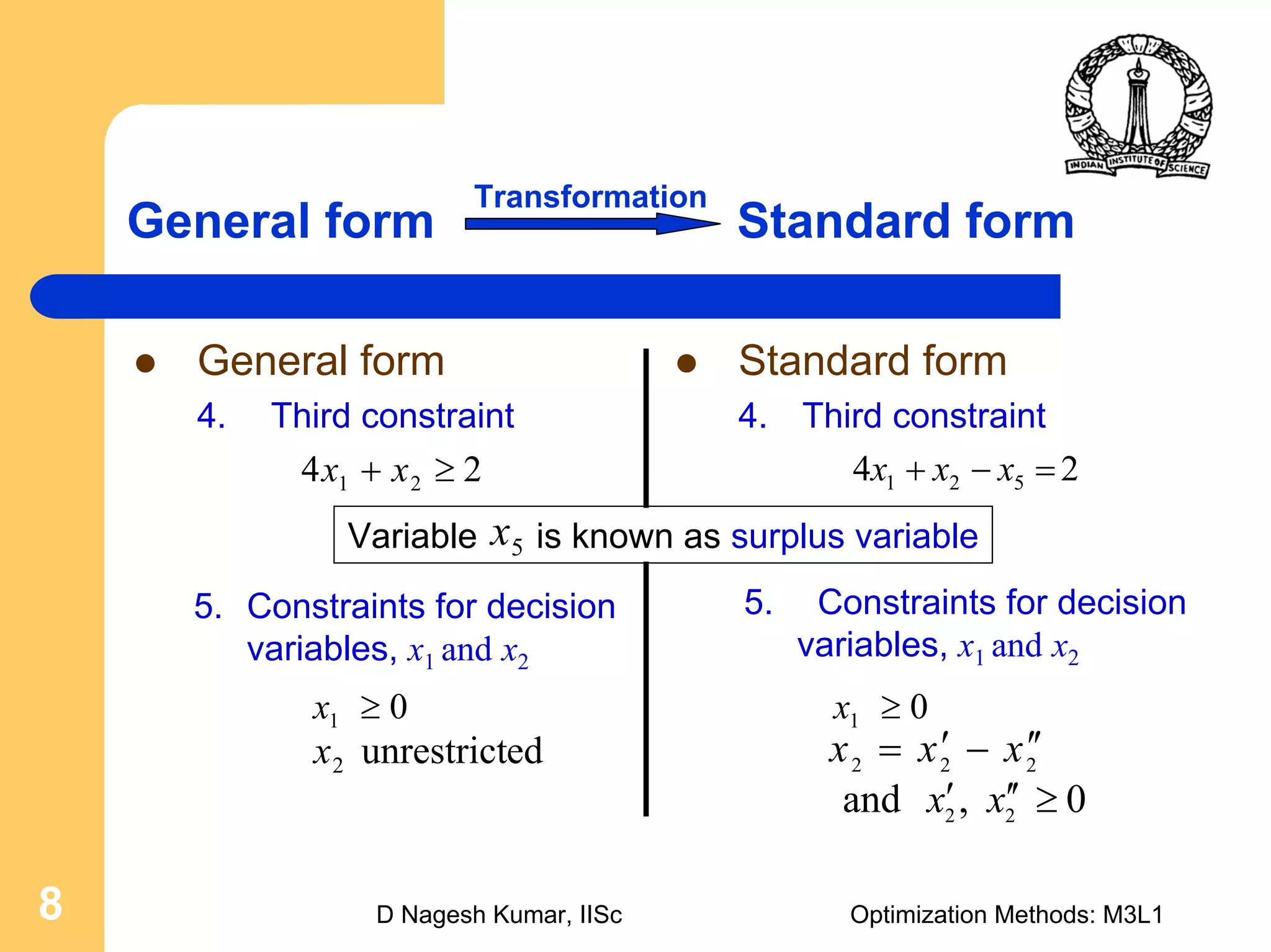
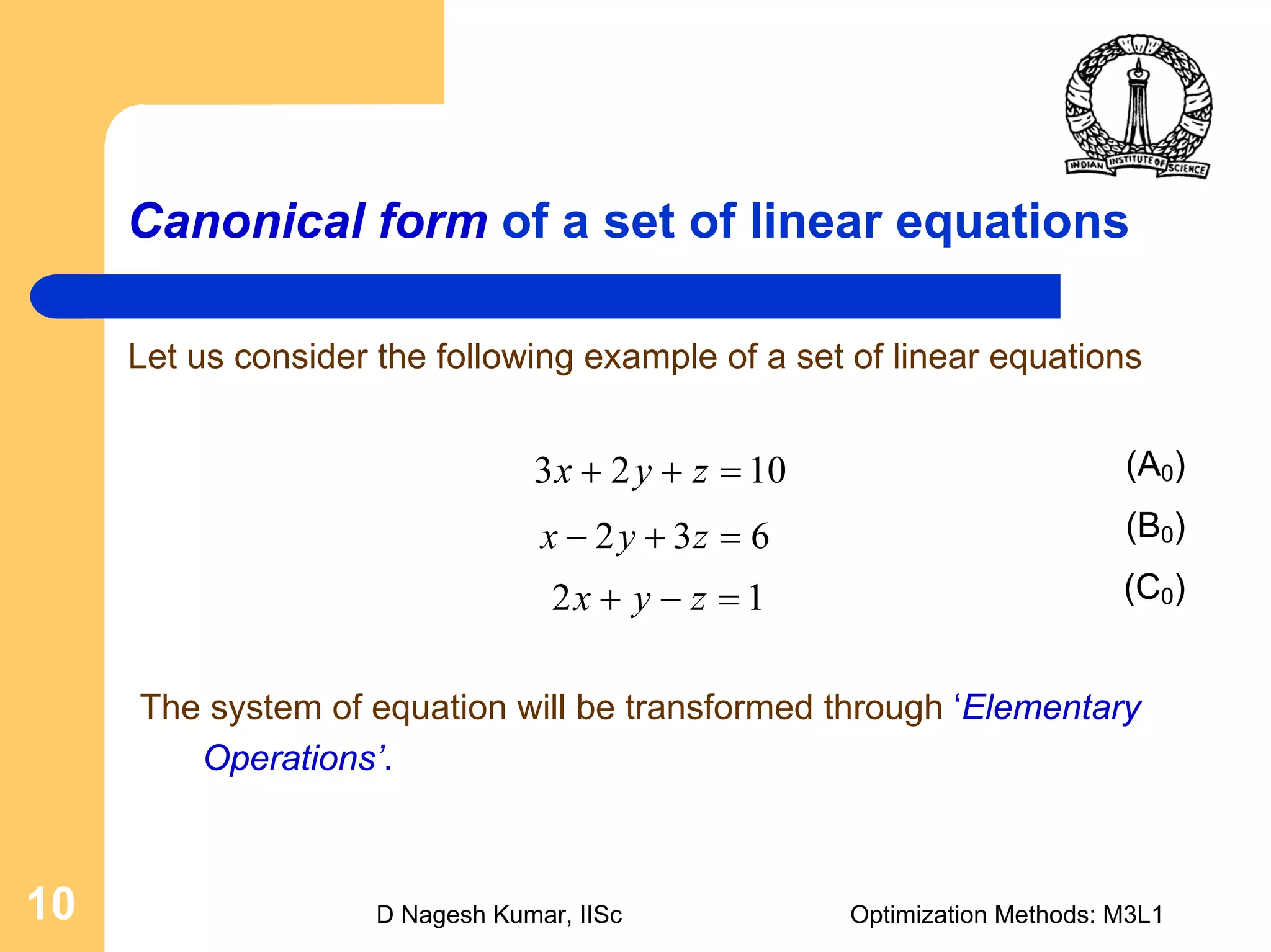
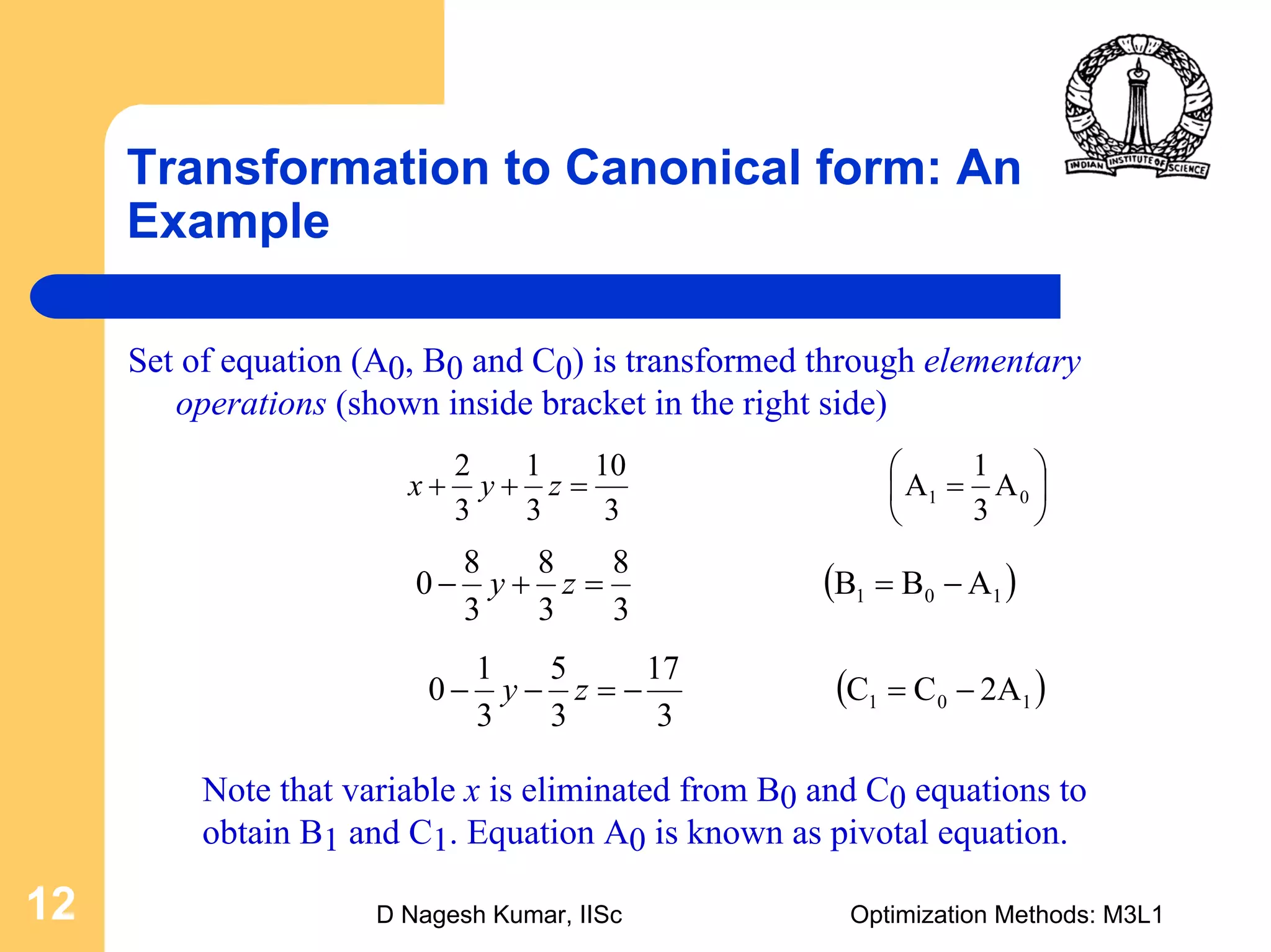
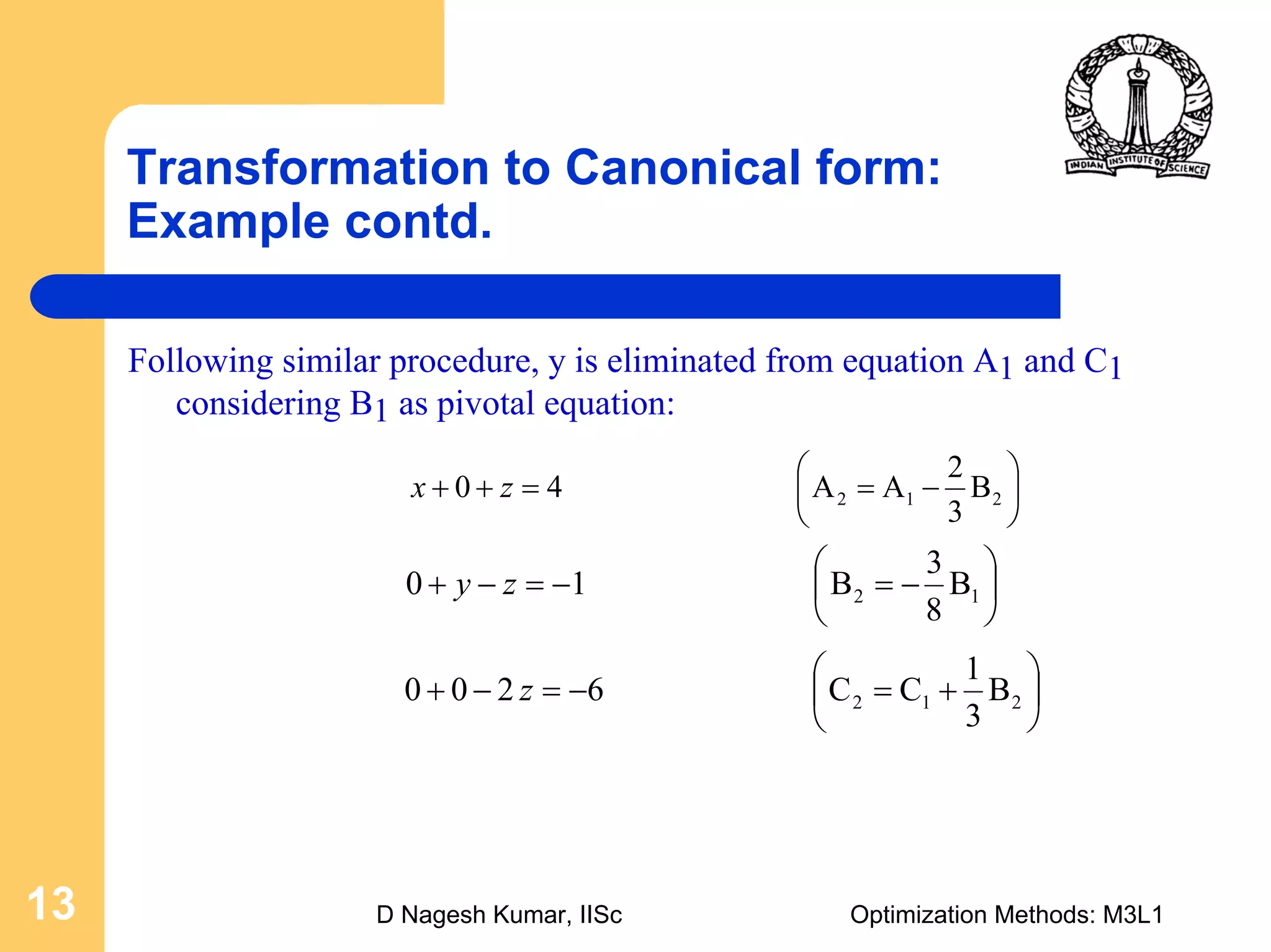
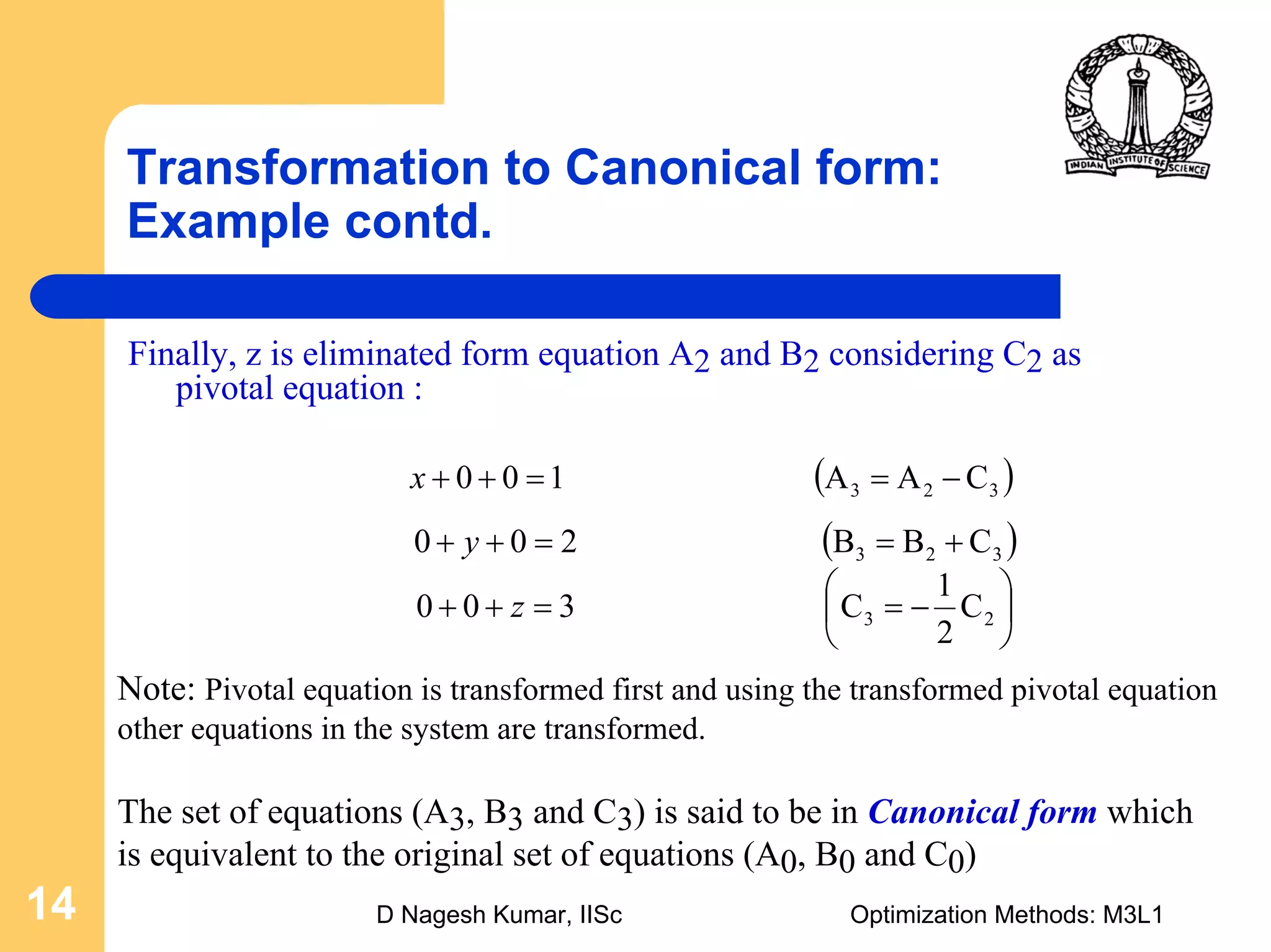
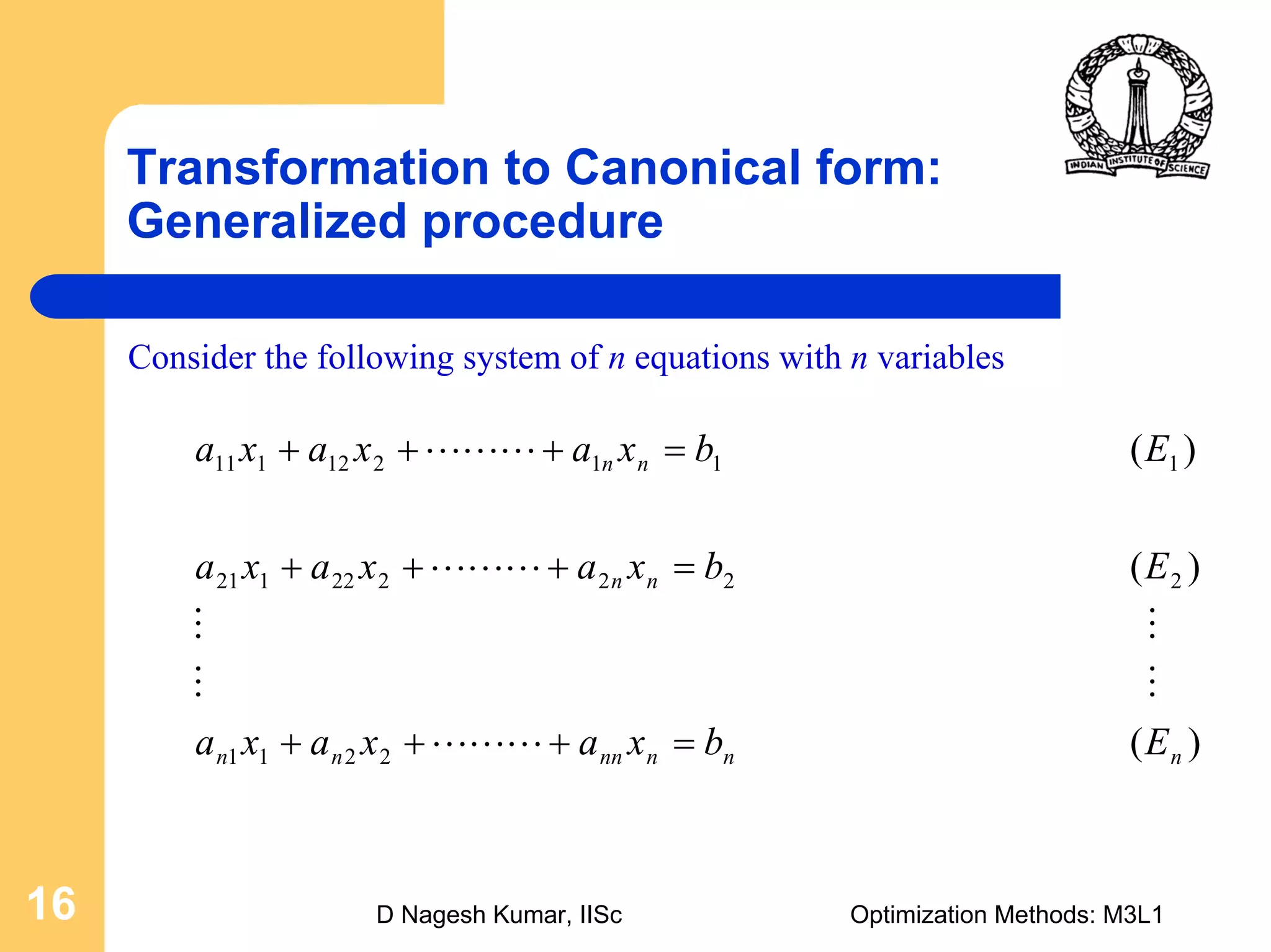
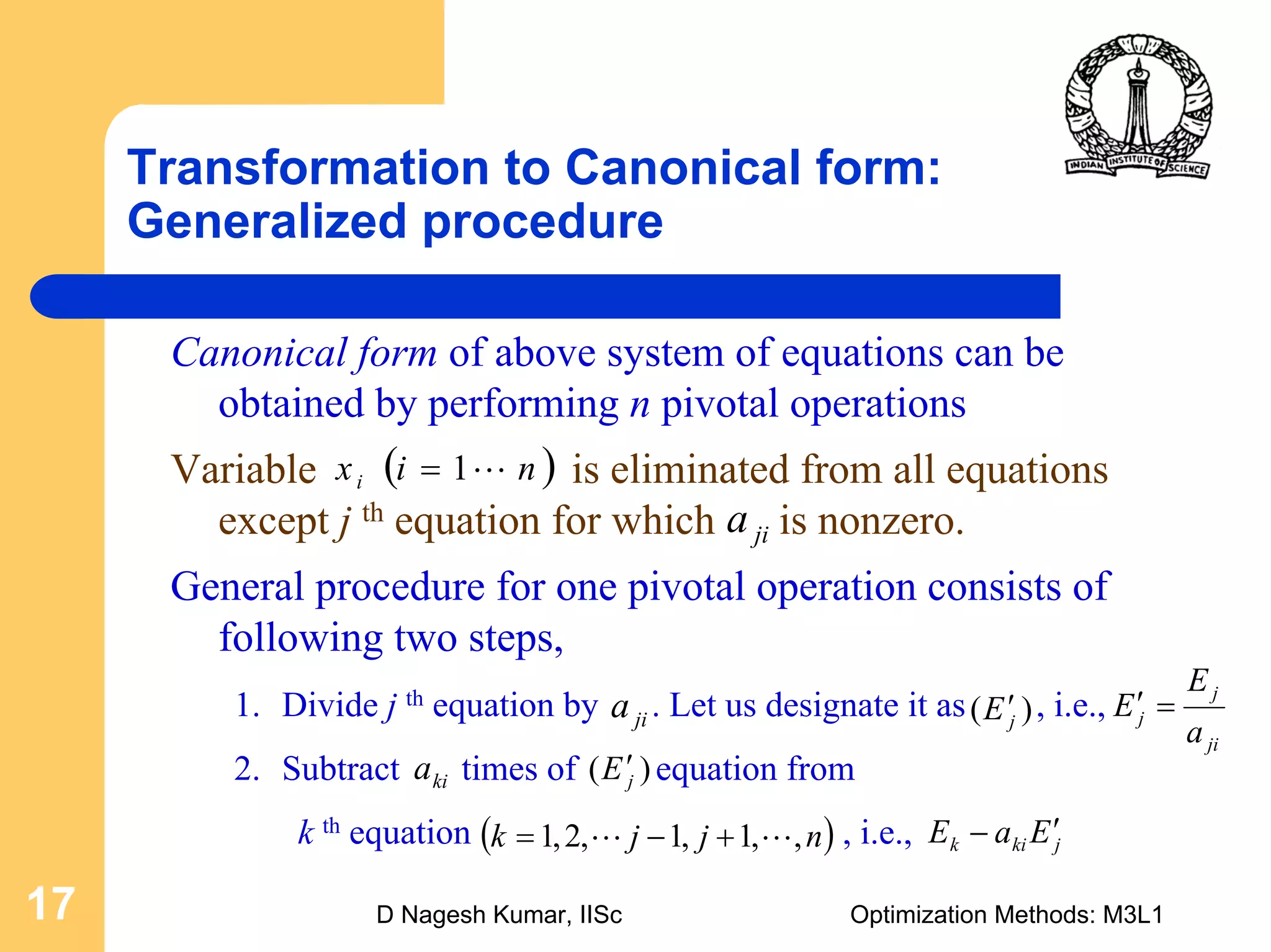
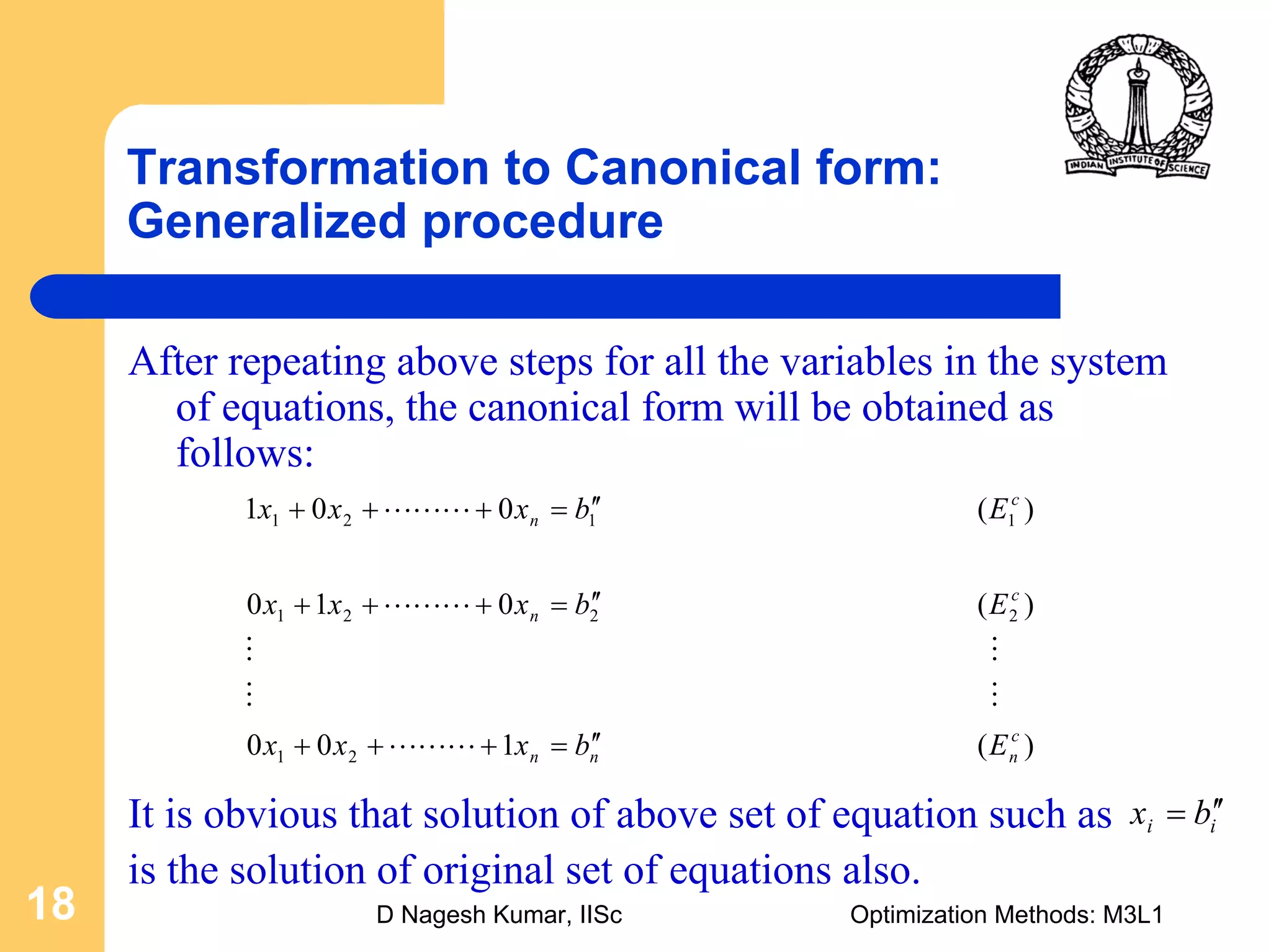
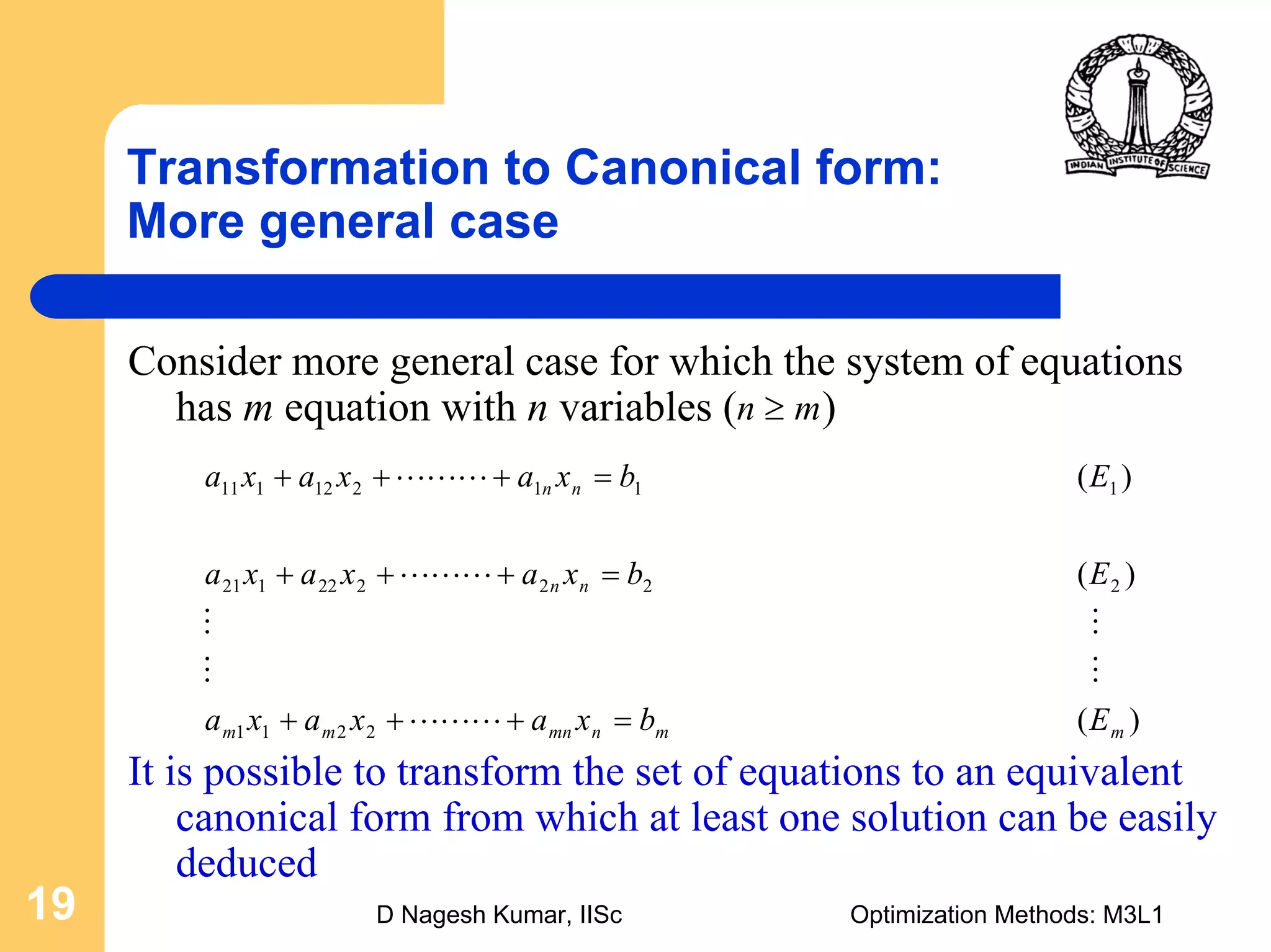
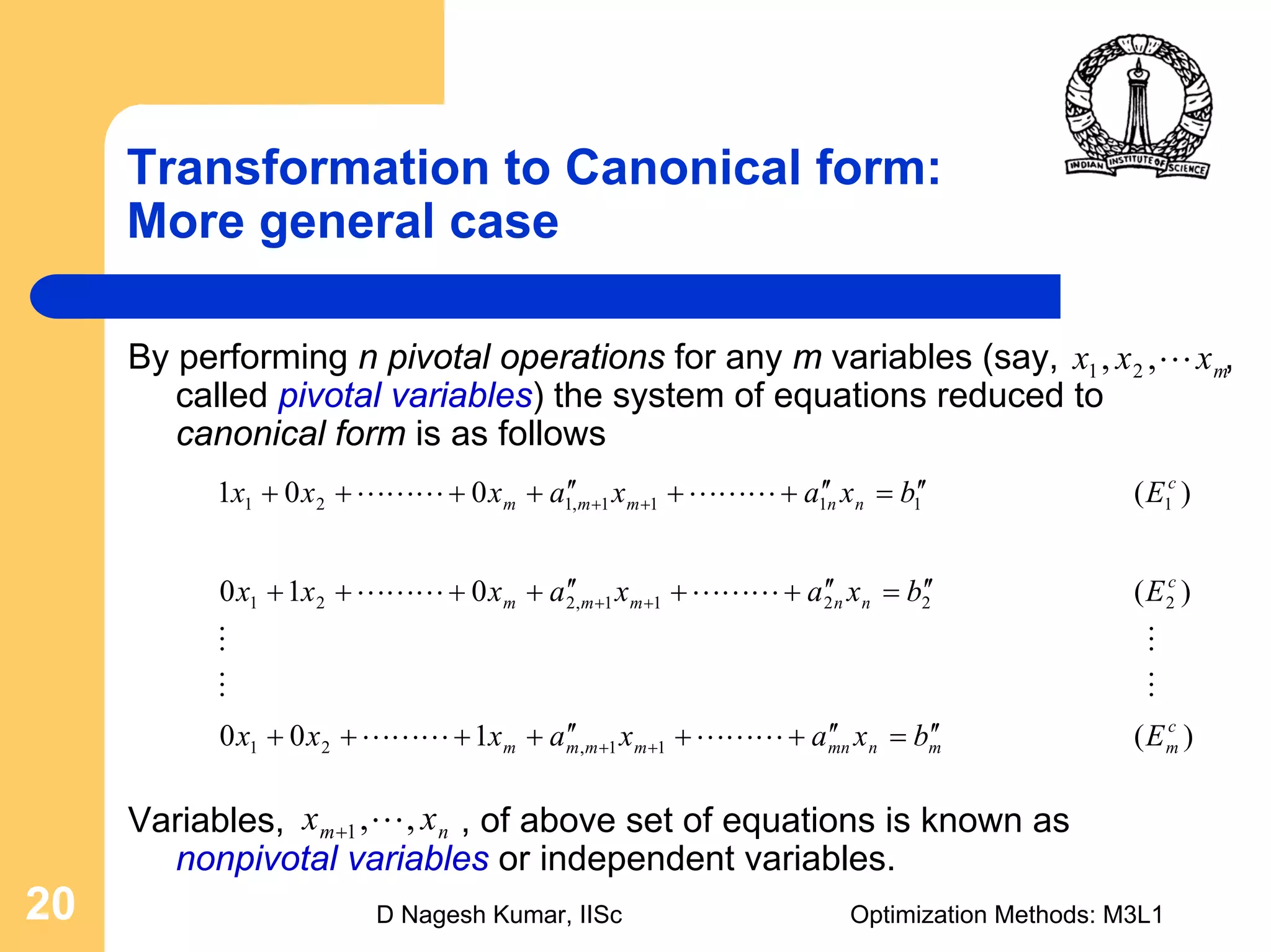
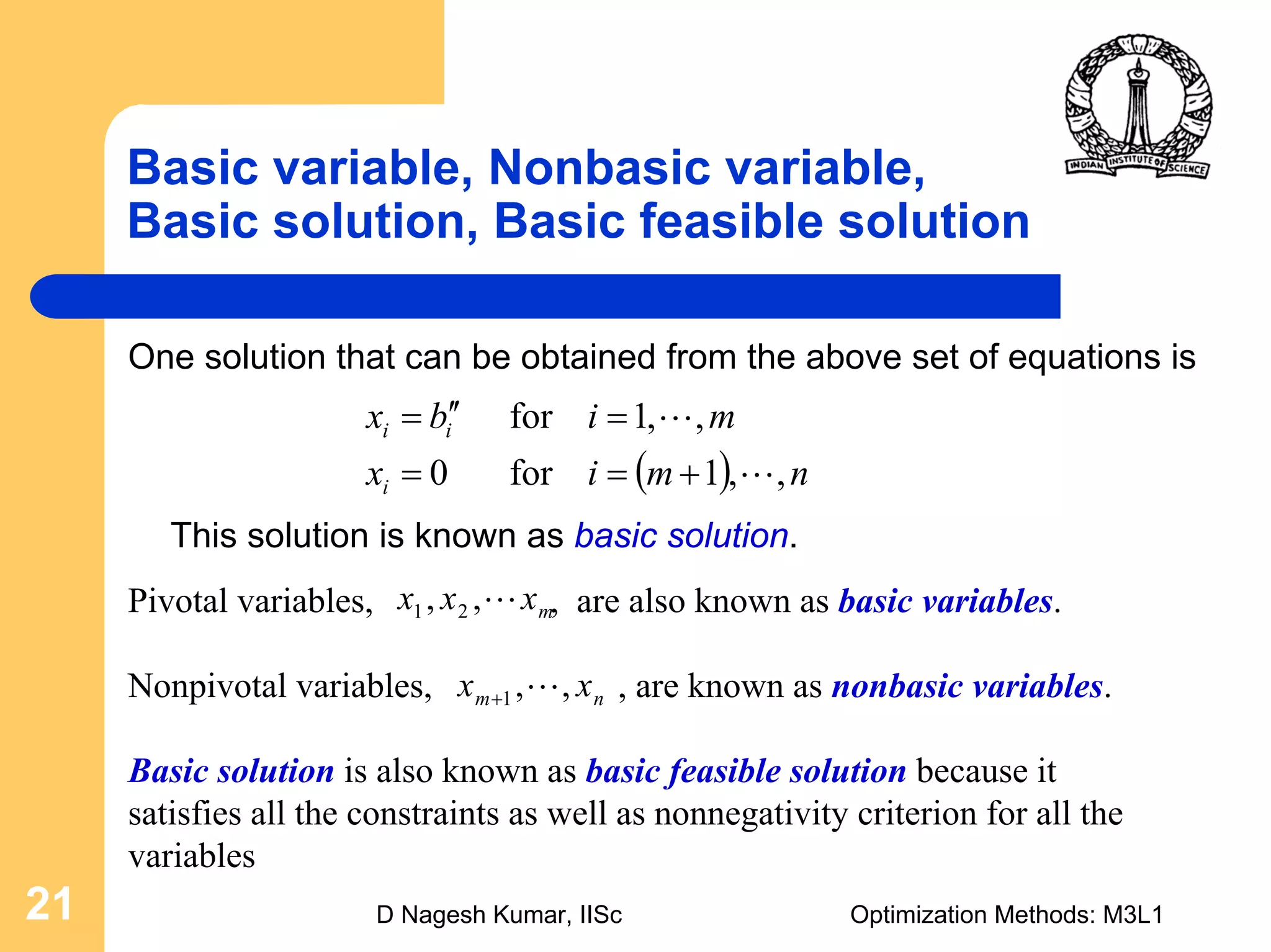
This document provides an overview of linear programming problems (LPP) and how to transform them into standard and canonical forms. It discusses that LPP have linear objective functions and constraints involving nonnegative decision variables. The standard form requires the objective to be maximized, constraints to be equalities, and variables to be nonnegative. General forms can be converted to standard form using slack, surplus and artificial variables. Canonical form is needed for the simplex method and involves eliminating variables through pivotal operations until the constraints are in upper triangular form with basic and nonbasic variables. Basic feasible solutions satisfy all constraints and nonnegativity.