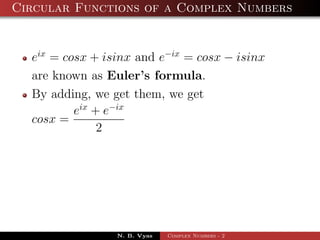
The document describes the expansion of sin nθ and cos nθ in powers of sinθ and cosθ using De Moivre's theorem and the binomial theorem. It shows that cos nθ can be expressed as the sum of terms involving nC0cosnθ, nC2cosn-2θsin2θ, etc. and sin nθ can be expressed as the sum of terms involving nC1cosn-1θsinθ, nC3cosn-3θsin3θ, etc. The expansions are obtained by equating the real and imaginary parts of (cosθ + i sinθ)n.















































































































![Hyperbolic Identities
Identities of Hyperbolic functions can be derived
from the identities of circular functions by
replacing x by ix
Now sin2 x + cos2 x = 1
sin2 (ix) + cos2 (ix) = 1 ⇒
[i sinh(x)]2 + [cosh(x)]2 = 1
N. B. Vyas Complex Numbers - 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexnumbers2-120305224718-phpapp01/85/Complex-numbers-2-113-320.jpg)
![Hyperbolic Identities
Identities of Hyperbolic functions can be derived
from the identities of circular functions by
replacing x by ix
Now sin2 x + cos2 x = 1
sin2 (ix) + cos2 (ix) = 1 ⇒
[i sinh(x)]2 + [cosh(x)]2 = 1
⇒ cosh2 (x) − sinh2 (x) = 1
N. B. Vyas Complex Numbers - 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexnumbers2-120305224718-phpapp01/85/Complex-numbers-2-114-320.jpg)
![Hyperbolic Identities
Identities of Hyperbolic functions can be derived
from the identities of circular functions by
replacing x by ix
Now sin2 x + cos2 x = 1
sin2 (ix) + cos2 (ix) = 1 ⇒
[i sinh(x)]2 + [cosh(x)]2 = 1
⇒ cosh2 (x) − sinh2 (x) = 1
Similarly we can obtain
N. B. Vyas Complex Numbers - 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexnumbers2-120305224718-phpapp01/85/Complex-numbers-2-115-320.jpg)
![Hyperbolic Identities
Identities of Hyperbolic functions can be derived
from the identities of circular functions by
replacing x by ix
Now sin2 x + cos2 x = 1
sin2 (ix) + cos2 (ix) = 1 ⇒
[i sinh(x)]2 + [cosh(x)]2 = 1
⇒ cosh2 (x) − sinh2 (x) = 1
Similarly we can obtain
sech2 (x) = 1 − tanh2 (x)
N. B. Vyas Complex Numbers - 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexnumbers2-120305224718-phpapp01/85/Complex-numbers-2-116-320.jpg)
![Hyperbolic Identities
Identities of Hyperbolic functions can be derived
from the identities of circular functions by
replacing x by ix
Now sin2 x + cos2 x = 1
sin2 (ix) + cos2 (ix) = 1 ⇒
[i sinh(x)]2 + [cosh(x)]2 = 1
⇒ cosh2 (x) − sinh2 (x) = 1
Similarly we can obtain
sech2 (x) = 1 − tanh2 (x)
cosech2 (x) = coth2 (x) − 1
N. B. Vyas Complex Numbers - 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexnumbers2-120305224718-phpapp01/85/Complex-numbers-2-117-320.jpg)


















