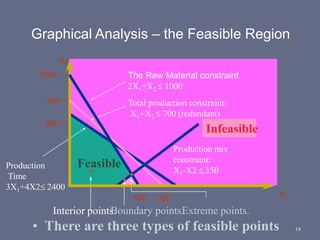
Linear programming is a mathematical modeling technique used to determine optimal resource allocation to achieve objectives. It involves converting a problem into a linear mathematical model with decision variables, constraints, and an objective function. The optimal solution is found by systematically increasing the objective function value until infeasibility is reached. For example, a linear programming model was used to determine the optimal production mix and levels of two drug combinations to maximize profit given resource constraints. The optimal solution was found to be 320 dozen of drug X1 and 360 dozen of drug X2, utilizing all available resources and achieving $4,360 in weekly profit.